Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: A delay in initiating disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) has been linked to poor outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Several studies have implicated the association between disease duration of RA and treatment responses of DMARDs. However, few studies have elucidated the association between disease duration and clinical efficacy of biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) and Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi). In this study, we compared the changes of disease activity scores about bDMARDs and JAKi depending on different disease duration in b/ts-DMARDs naïve patients in the real-world setting.
Methods: This was a retrospective cohort study using the Kansai Consortium for Well-being of Rheumatic Disease Patients (ANSWER) cohort, a multicenter observational registry of patients with RA in Japan. bDMARDs or JAKi-naïve patients with RA who were started bDMARDs or JAKi were recruited. Patients were stratified based on disease duration (Early, ≤ 1 year; Late, >1 year). Mean change ratios of clinical disease activity index (CDAI) and Health Assessment Questionnaire Disease Index (HAQ-DI) from Day 0 to Day 365 (Day 365/Day 0) after the initiation of bDMARDs or JAKi calculated by the generalized estimating equations were compared between the Early and the Late group.
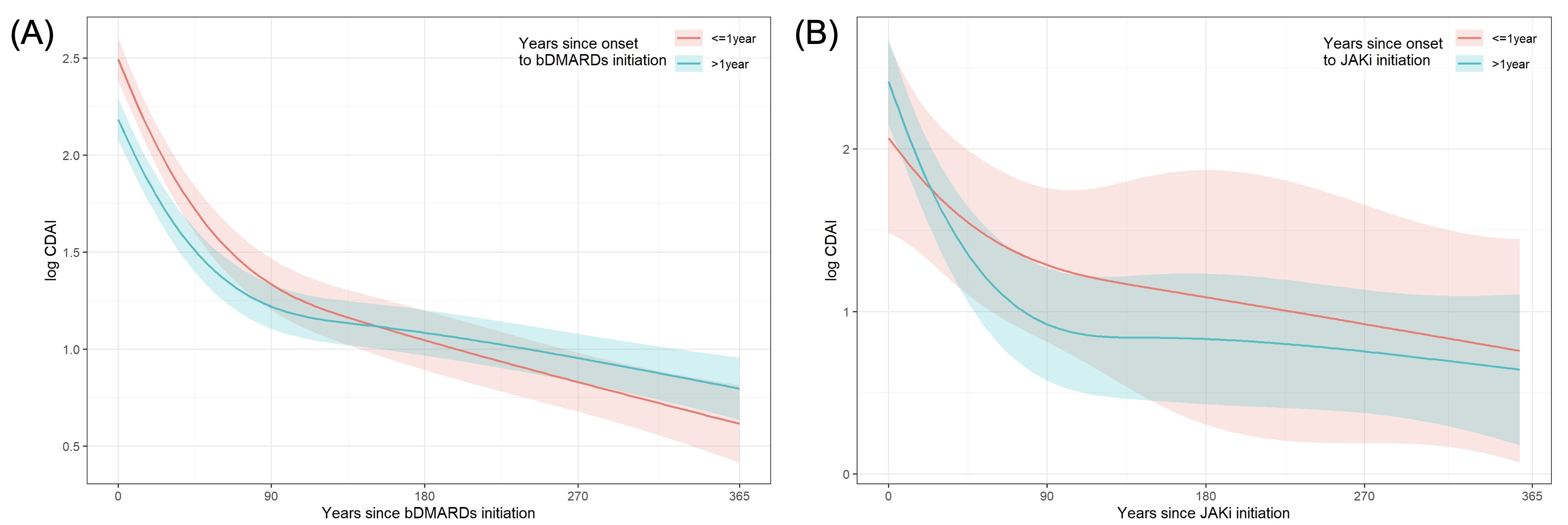
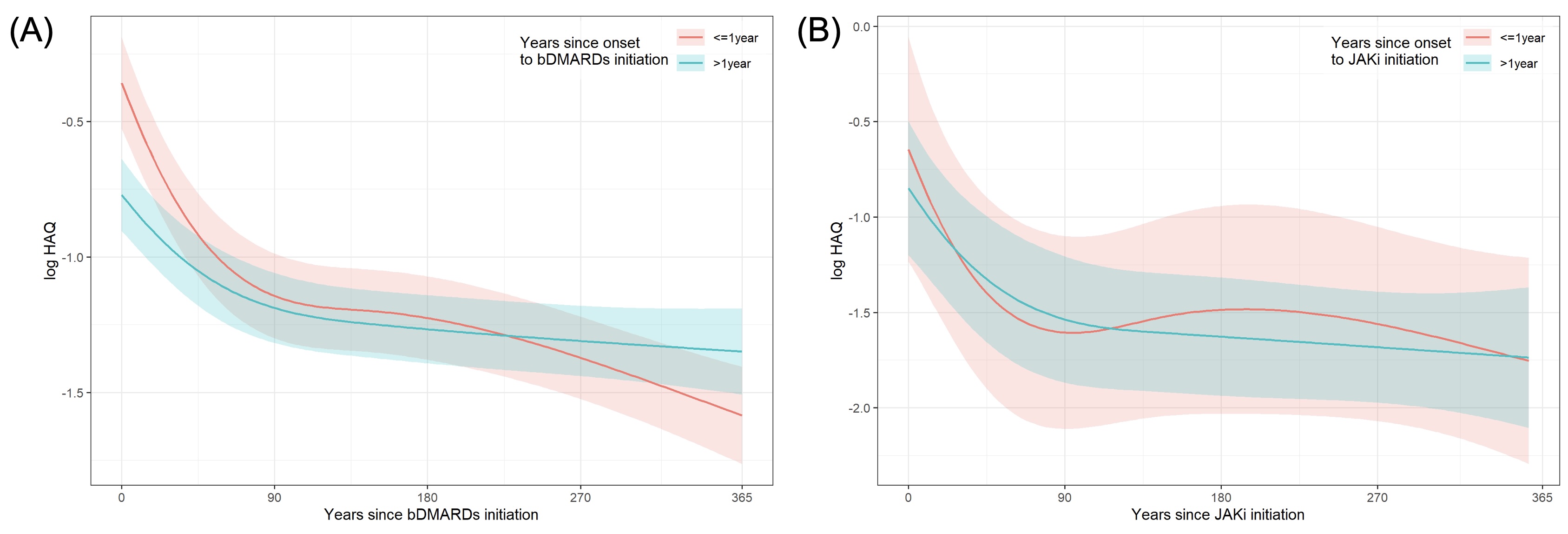
Results: A total of 2,344 patients with RA were enrolled. The median disease duration at the initiation of bDMARDs of the Early group was 0.5 years and the Late group was 3.6 years. The median disease duration at the initiation of JAKi of the Early group was 0.5 years and the Late group was 5.7 years. In bDMARDs-treated group, mean change ratios (Day 365/Day 0) of CDAI were 0.15 (95%CI 0.13-0.19) in the Early group and 0.25 (95%CI 0.21-0.29) in the Late group (p< 0.001) (Figure 1A). In contrast, in JAKi-treated group, mean change ratios (Day 365/Day 0) of CDAI were 0.27 (95%CI 0.12-0.58) in the Early group and 0.17 (95%CI 0.10-0.28) in the Late group (p=0.09) (Figure 1B). In bDMARDs, mean change ratios (Day 365/Day 0) of HAQ-DI were 0.29 (95%CI 0.24-0.36) in the Early group and 0.56 (95%CI 0.48-0.65) in the Late group (p< 0.001) (Figure 2A). In JAKi, mean change ratios (Day 365/Day 0) of CDAI were 0.32 (95%CI 0.18-0.59) in the Early group and 0.41 (95%CI 0.27-0.60) in the Late group (p=0.71) (Figure 2B).
Conclusion: bDMARDs were more effective in patients with shorter disease duration, while JAKi were effective irrespective of disease duration. The initiation of bDMARDs should be performed as early as possible in patients with shorter disease duration, and in patients with longer disease duration, JAKi can be a good treatment option.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nakayama Y, Kabata D, Yamamoto W, Makino H, Nagai K, Yoshida N, Son Y, Katayama M, Yamada H, Nishimura K, Hara R, Watanabe R, Etani Y, Ebina K, Onizawa H, Fujii T, Onishi A, Murakami K, Murata K, Tanaka M, Matsuda S, Morinobu A, Shintani A, Hashimoto M. Disease Duration Differentially Affects the Clinical Efficacy of Biologics and JAK Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The ANSWER Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-duration-differentially-affects-the-clinical-efficacy-of-biologics-and-jak-inhibitors-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-the-answer-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-duration-differentially-affects-the-clinical-efficacy-of-biologics-and-jak-inhibitors-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-the-answer-cohort-study/