Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Comorbidities
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: WHO survey showed that the prevalence of anxiety and depression in Chinese population and Chinese patients with chronic diseases were between 3.1% – 4.2% and 3.1% – 7.3%, respectively. SLEDAI-2K and Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) are commonly used to evaluate SLE patients’ disease activity and mental health. All the Assessments were mainly performed by health professionals (HCPs) with paper questionnaire previously. SSDM is a novel smart disease management tool that allows patients to do self-assessments on SLEDAI-2K and HADS by mobile App.The purpose of this study is to investigate the prevalence of anxiety and depression in Chinese patients with SLE and to analyze the potential association between disease activity of SLE and mental health.
Methods: Under the guidance and training by HCPs, SLE patients downloaded SSDM and performed self-assessments bundle of SLEDAI-2K and HADS with SSDM. SLEDAI-2K < =4, 5-9, 10-14 and >=15 are defined SLE inactive, low (LDA), moderate (MDA) and high (HDA) disease activity, respectively. SLEDAI-2K score < = 4 is set as the main criteria for Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS) and achievement of T2T. HADS score >=8 can be diagnosed with anxiety or depression.
Results: From June 2016 to Jan 2020, 3,332 SLE patients (199 male, 3,133 female) with a mean age of 36.34 ± 12.80 (10-91) years and the median disease duration of 3.43 years from 216 hospitals performed bundle self-assessments for 4,967 times in total. According to the HADS and SLEDAI-2K Assessment results, the prevalence of anxiety and depression in all patients was 36.7% and 39.3% respectively, which was significantly higher than that in the WHO survey in Chinese population and chronic disease patients. The proportion of patients achieved and failed on LLDAS was 53% and 47%, respectively. The prevalence of anxiety (A) and depression (D) was 19% and 27% among LLDAS achievers; 41% and 47% among LLDAS failures, respectively (pA< 0.01, pD< 0.01).
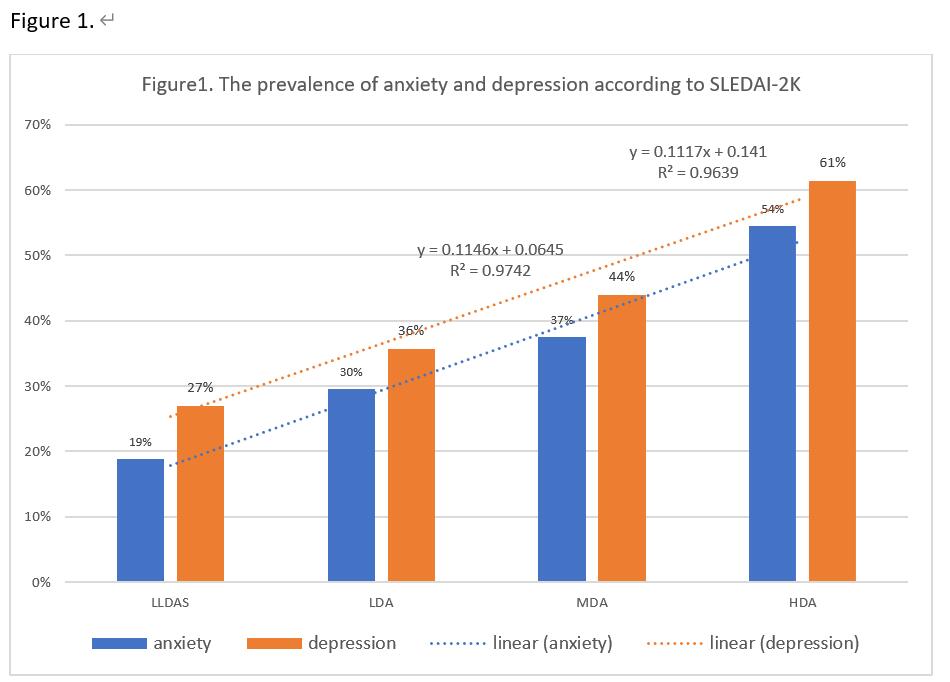
According to SLEDAI-2K, in LLDAS, LDA, MDA and HDA subgroups, the prevalence of anxiety and depression was 19%, 30%, 37%, 54% and 27%, 36%, 44%, 61%, respectively. The correlation coefficients of anxiety (A) and depression (D) with SLEDAI-2K were rA=0.9957 and rD=0.9819. It suggested that with the increase of disease activity, the proportion of SLE patients with anxiety and depression increased significantly. (Figure 1)
Conclusion: Conclusion: Higher prevalence of anxiety and depression were Associated with higher levels of disease activity in SLE patients. SSDM is an effective mobile interface to monitor and study entanglement of disease activity and mental health in SLE patients, which build a foundation for proactive interventions physically and mentally in future.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wang Y, Wei H, Wu R, Wu J, Zhang S, Li Q, Li Y, Sun Y, Zhao Y, Shu Q, Kang L, Wu B, Qin L, Jiang F, Yang H, Zhang J, Xiao H, Wu B, Jia Y, Xiao F, Sun L. Disease Activity and Mental Health in SLE Patients: A Cross-section Study with Self-Assessments Based on Smart System of Disease Management (SSDM) Mobile Tools [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-activity-and-mental-health-in-sle-patients-a-cross-section-study-with-self-assessments-based-on-smart-system-of-disease-management-ssdm-mobile-tools/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-activity-and-mental-health-in-sle-patients-a-cross-section-study-with-self-assessments-based-on-smart-system-of-disease-management-ssdm-mobile-tools/