Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: PROs, Biomarkers, Systemic Inflammation & Radiographs
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Assessment of disease activity in RA with validated measures, such as the Disease Activity Score with 28 joint count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR) and the Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI), is useful in evaluating therapeutic efficacy and guiding treatment. The multi-biomarker disease activity (MBDA) score was developed to provide an objective laboratory assessment of disease activity. We assessed DAS28-ESR, CDAI, and MBDA scores in a multicenter, placebo-controlled, randomized, phase 4 withdrawal study of repository corticotropin injection (RCI, Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals), a naturally sourced complex mixture of adrenocorticotropic hormone analogs and other pituitary peptides, in patients with persistently active RA despite treatment with stable low-dose glucocorticoids and 1 or 2 nonbiologic and/or biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (ClinicalTrials.gov ID: NCT02919761).
Methods: Patients received 80 U of RCI subcutaneously (SC) twice weekly during a 12-week open-label period; those who achieved low disease activity (LDA; DAS28-ESR < 3.2) were randomly assigned to receive 80 U of RCI or placebo SC twice weekly during a 12-week double-blind period. Disease activity was assessed using the DAS28-ESR, CDAI, and MBDA at baseline (BL), week (W) 12, and W24; changes were evaluated via t tests. Correlations for the total MBDA score and its individual components with both DAS28-ESR and CDAI scores at BL, W12, and W24 were assessed via Pearson correlation coefficients for subgroups with/without LDA at W12 or W24. Analyses used the modified intent-to-treat population, defined as patients who received ≥1 dose of study drug and contributed any efficacy data.
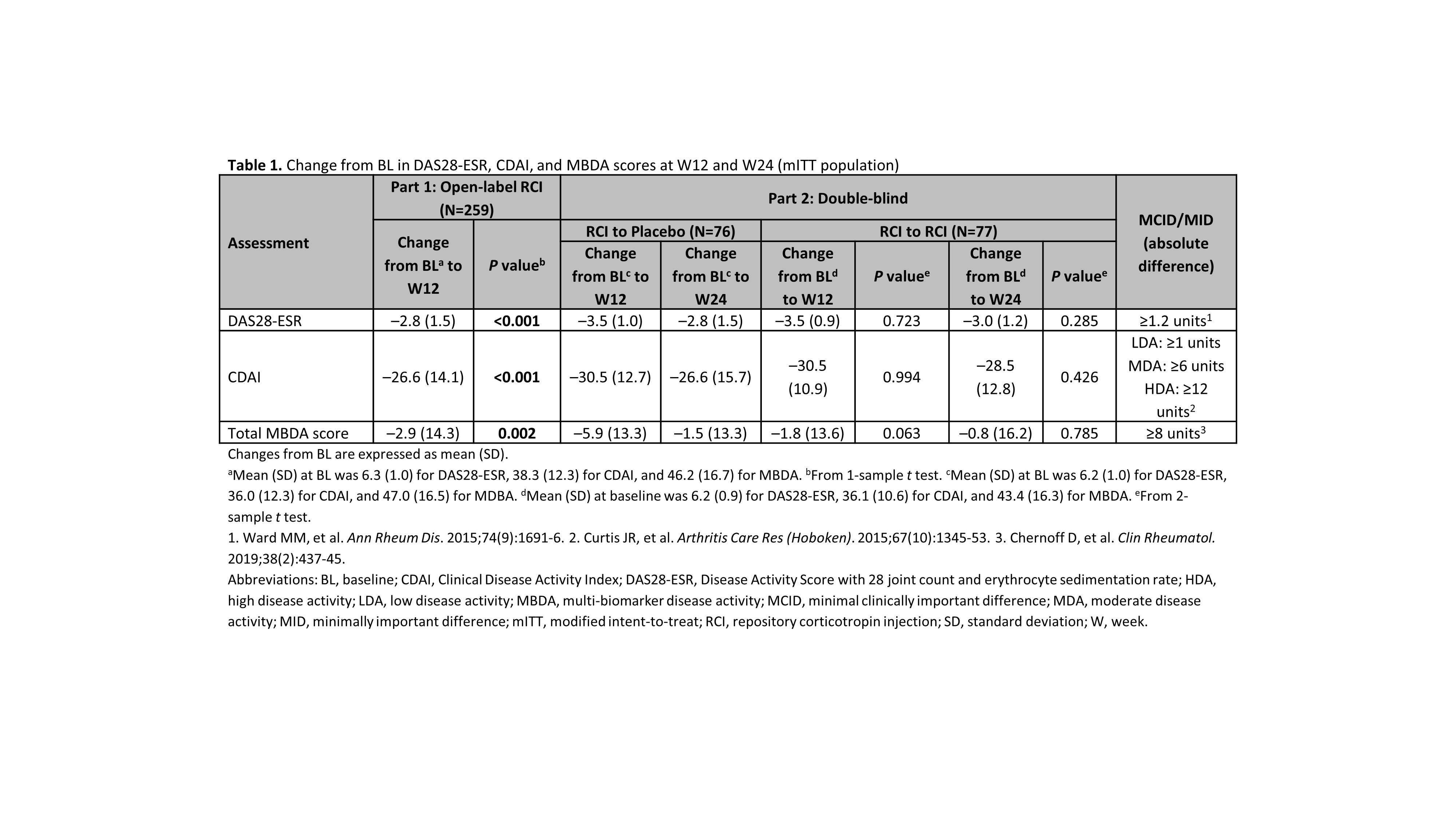
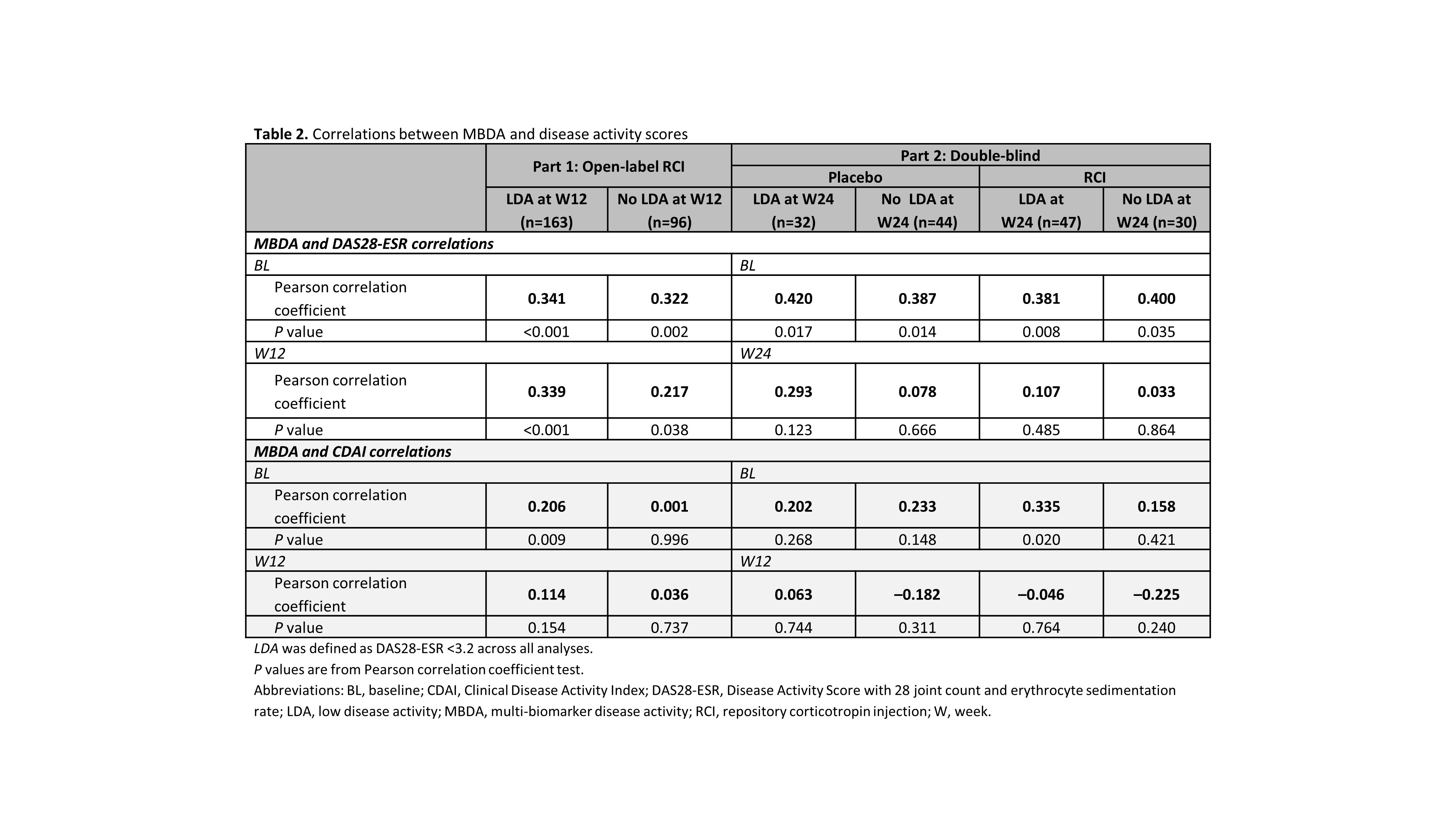
Results: RCI therapy was associated with clinically meaningful improvements in disease activity; mean decreases exceeded the minimal clinically important difference thresholds for the DAS28-ESR and CDAI, but not the minimally important difference for the MBDA (Table 1). Statistically significant correlations between MBDA and DAS28-ESR scores were seen at BL and W12 in patients with and without LDA at W12, but low correlation coefficients suggested weak relationships (Table 2). Low correlation coefficients (most nonsignificant) also suggested weak relationships between MBDA and CDAI scores (Table 2). Among individual MBDA components, some significant correlations were noted with both the DAS28-ESR and CDAI scores at BL, W12, and W24; low correlation coefficients suggested weak relationships (data not shown).
Conclusion: In this study of RCI therapy in patients with persistently active RA, clinical disease activity scores were weakly correlated with MBDA total and individual component scores. Similar results have been seen with 3 other agents with different mechanisms of action.1,2 These findings support the 2019 ACR recommendations against use of MBDA as a preferred measure for disease activity in RA.3
References
- Reiss WG, et al. Rheumatol Int. 2016;36(2):295-300.
- Fleischmann R, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(9):2083-9.
- England BR, et al. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2019;71(12):1540-55.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fleischmann R, Liu J, Zhu J, Segurado O, Furst* D. Discrepancy Between the Multi-biomarker Disease Activity Score and Clinical Disease Activity Scores in a 2‑Part, Multicenter Study of Repository Corticotropin Injection (Acthar® Gel) for Patients with Persistently Active Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/discrepancy-between-the-multi-biomarker-disease-activity-score-and-clinical-disease-activity-scores-in-a-2%e2%80%91part-multicenter-study-of-repository-corticotropin-injection-acthar-gel-for/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/discrepancy-between-the-multi-biomarker-disease-activity-score-and-clinical-disease-activity-scores-in-a-2%e2%80%91part-multicenter-study-of-repository-corticotropin-injection-acthar-gel-for/