Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-lasting inflammatory autoimmune disorder that ultimately leads to the destruction of joint architecture. The activity of this disease is measured by the assessment of clinical symptoms (generally using the DAS28). The aim of this study was to find and validate plasma biomarkers able to discriminate patients with different RA activities.
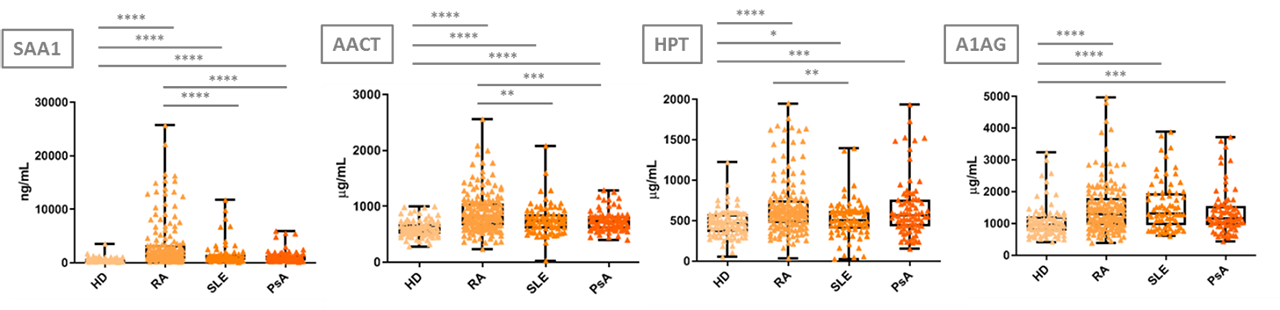
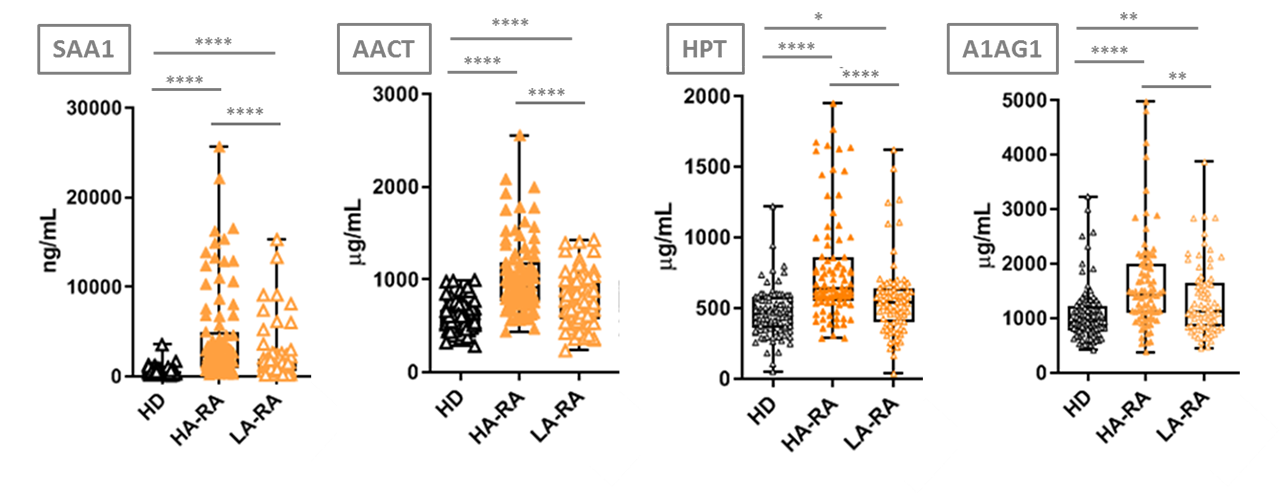
Methods: Plasma samples from patients with different IMIDs (Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases), used in this research belonged to the IMID Consortium. Plasma from RA patients were DAS28-classified as low activity (LA, DAS28: 2,6-3,2) and high activity (HA, DAS28 > 5,1). The study was conducted in three different stages. Firstly, an initial discovery phase was performed to identify an early panel of proteins with a RA activity differing role. Thus, 80 RA plasma samples (40 LA and 40 HA) were pooled in 8 groups (4 LA and 4 HA). These pools were albumin-depleted, digested, differentially labelled with iTraq 8-plex reagents, combined, desalted using StageTips-C18, HPLC-fractionated and analyzed by shotgun nanoLC-MS/MS. Secondly, the verification of the previously identified possible markers was carried out by a targeted Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM) strategy on a QTRAP 5500. Particularly, the same 80 RA plasma samples (40 LA and 40 HA) were individually measured, employing stable isotope-labeled standards (SIS) peptides for absolute protein quantitation. Lastly, the verified proteins were validated by ELISA on additional 420 plasma samples from patients with RA (170), psoriatic arthritis (PsA, 80), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE, 80) and healthy donors (HD, 90). PsA and SLE patients were used as disease controls.
Results: In the discovery stage, 186 proteins were identified, whereas 11 of these proteins significantly differed between RA patients with LA and HA (p< 0.05). A targeted MRM method using SIS peptides was developed for the verification and absolute quantitation of this 11-protein panel on 80 RA plasma samples. A significant increase in the HA condition for Haptoglobin (HPT), Serum Amyloid A1 (SAA1), Alpha-1-antichymotrypsin (AACT) and Alpha-1-acid Glycoprotein 1 (A1AG1) was shown, in accordance with the discovery phase tendency. Equally, the validation results show a significant increase of the 4 verified proteins in HA RA patients from LA RA patients and HD, as well as in LA RA patients from HD, therefore confirming their RA activity monitoring capacity. Furthermore, SAA1 and AACT significantly discriminate among RA, SLE, PsA patients and HD, as well as between RA patients and the related disease controls. Moreover, these proteins are related with the RA process and its effects (inflammation and immune disorder in joints), giving significance to the results obtained.
Conclusion: A three-step proteomic approach (including discovery, verification and validation phases) has been followed for the identification of protein biomarkers for assessing RA disease activity in plasma. A panel of four proteins has been validated as increased in plasma from HA RA patients, and could be useful for the molecular monitoring of the disease, even when they are measured among plasma samples from other IMID patients and/or HD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
González-Rodríguez L, Calamia V, Paz-González R, Fernández-Puente P, Ruiz-Romero C, Julià A, Fernández-Nebro A, Tornero J, Marsal S, Blanco F. Discovery, Verification and Validation of Rheumatoid Arthritis Activity Monitoring Biomarkers [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/discovery-verification-and-validation-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-activity-monitoring-biomarkers/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/discovery-verification-and-validation-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-activity-monitoring-biomarkers/