Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The association of interstitial lung disease (ILD) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA) is increasingly recognized. The implications of ILD as it relates to clinical outcomes in patients with diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (DAH) due to MPA has not been well characterized. In this study, we sought to investigate the clinical features and prognosis of patients with MPA and DAH with ILD (MPA-ILD-DAH) and compare them to those with ILD without DAH (MPA-ILD) and to those with DAH but without ILD (MPA-DAH).
Methods: This was a retrospective observational cohort study and patients who were diagnosed with ANCA-associated vasculitis and DAH between 1997 to 2023 and had MPO-ANCA positivity were secreened. These patients fullfilled the 2022 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for MPA. Patients who had an ILD diagnosis based on high resolution CT pre-existing to the DAH event were included. In addition, each MPA-ILD-DAH patient was matched with one patient each with MPA-ILD and MPA-DAH based on age at diagnosis, gender and ANCA-type.
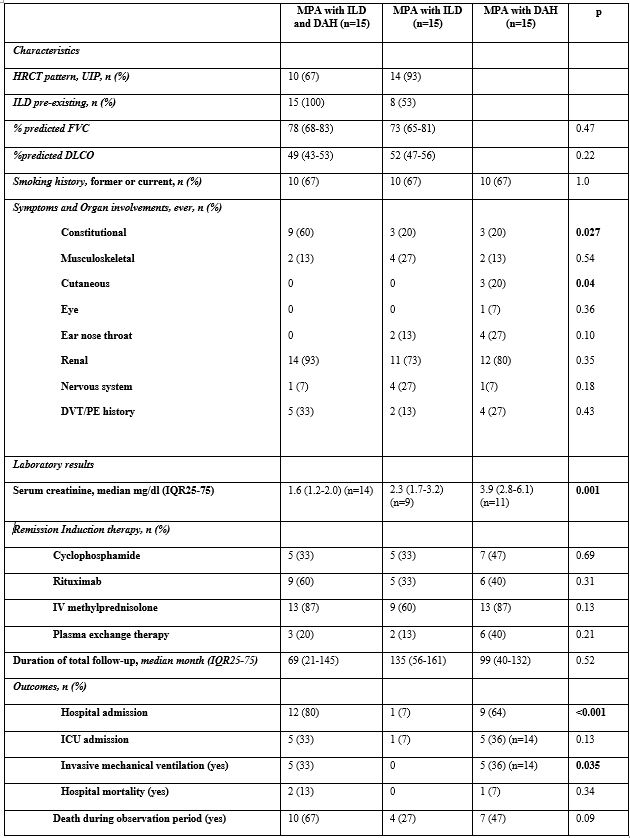
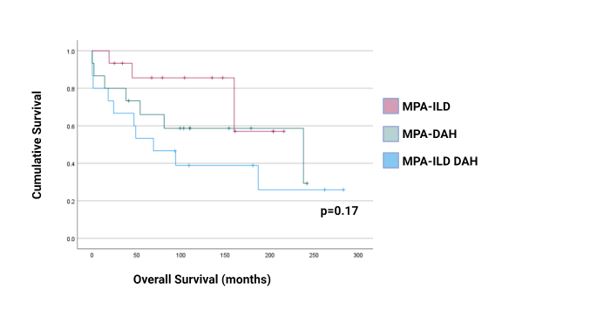
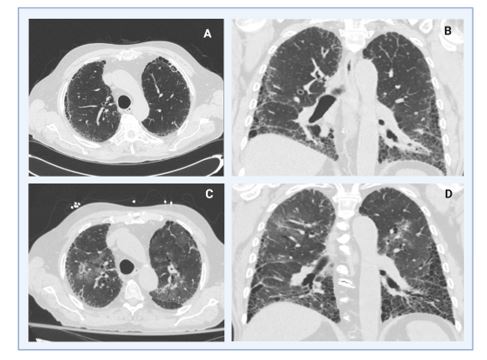
Results: Fifteen patients with DAH caused by MPA had pre-existing ILD with presenting characteristics and manifestations are shown in table 1. Median (IQR) time between ILD and DAH diagnosis was 9 (3-31) months. Ten patients (67%) had a UIP pattern on high-resolution CT scans of the chest, 5 had a non-UIP pattern. All patients had pulmonary function tests during their evaluation for ILD with evidence of a restrictive pattern. Chest imaging studies were performed in all patients, in addition, 12 patients had bronchoscopy to diagnose DAH. Overall survival was 80% at 1 year and 53% at 5 years in the MPA-ILD-DAH group. We compared the overall mortality between the 3 groups: although the patients in the MPA-ILD-DAH group had a higher mortality than matched patients in the MPA-ILD group, the difference of mortality of patients in the 3 groups was not statistically significant (p= 0.17, by the log-rank test) (Figure 1).
Conclusion: DAH may be a risk factor for hospital mortality and overall mortality in patients with MPA and ILD. In contrast, in patients with DAH, having a history of pre-existing ILD does not seem to affect mortality.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ediboglu E, Falde S, Baqir M, Cartin-Ceba R, Specks U. Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage in Patient with ANCA-associated Vasculitis AndInterstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/diffuse-alveolar-hemorrhage-in-patient-with-anca-associated-vasculitis-andinterstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/diffuse-alveolar-hemorrhage-in-patient-with-anca-associated-vasculitis-andinterstitial-lung-disease/