Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The innate immune system not only participates in PsA pathogenesis but may also counteract with immunomodulatory elements. Proinflammatory and repairing roles according to monocyte subtype have been described in SpA and expansion of Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSCs) has been shown in psoriasis. However, their quantitative profile and potential clinical associations in PsA have not been previously assessed, which is the main aim of the present study.
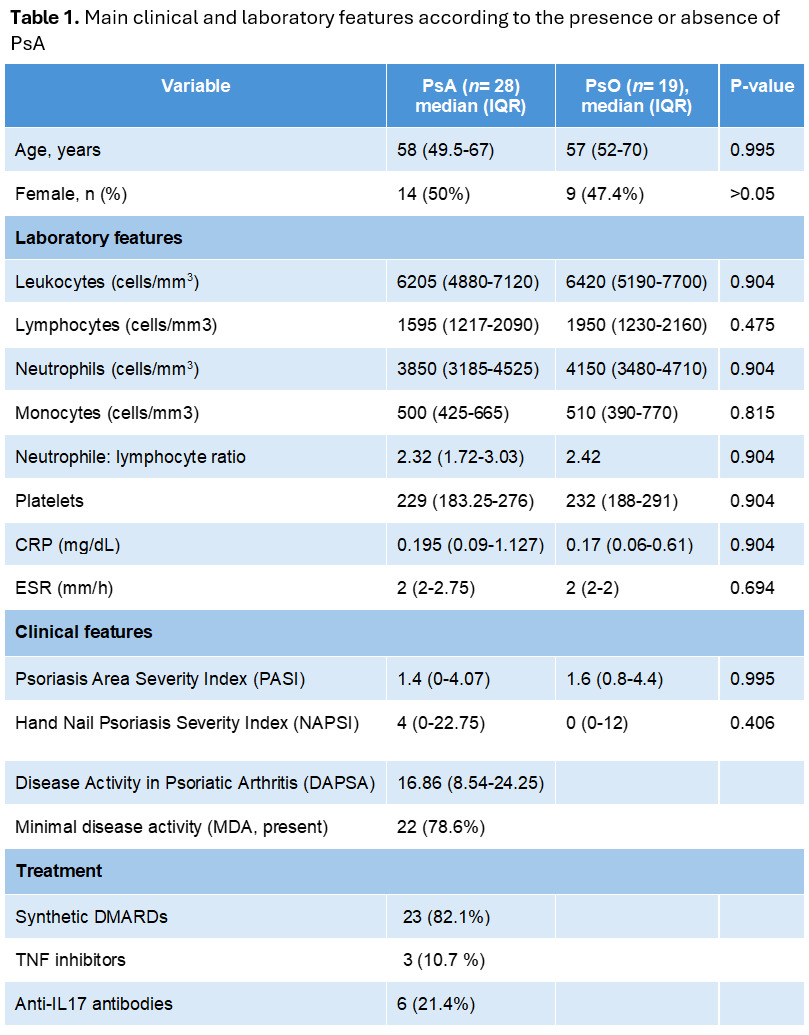
Methods: This cross-sectional study included 28 patients who fulfilled the Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis from a tertiary care centre in Mexico City. Granulocytic and monocytic MDSCs and monocyte subtypes (classical, non-classical and intermediate) from peripheral blood were analyzed by multiparametric flow cytometry and evaluated according to clinical manifestations and activity and damage scales (PASI, NAPSI, DAPSA, MDA, physician VAS). To evaluate potential differential cell compartments, particularly associated with PsA, samples from 19 psoriasis patients were compared. Quantitative variables according to clinical characteristics were compared with the Mann-Whitney U and Wilcoxon rank-sum tests. Correlations were assessed with Spearman’s ρ.
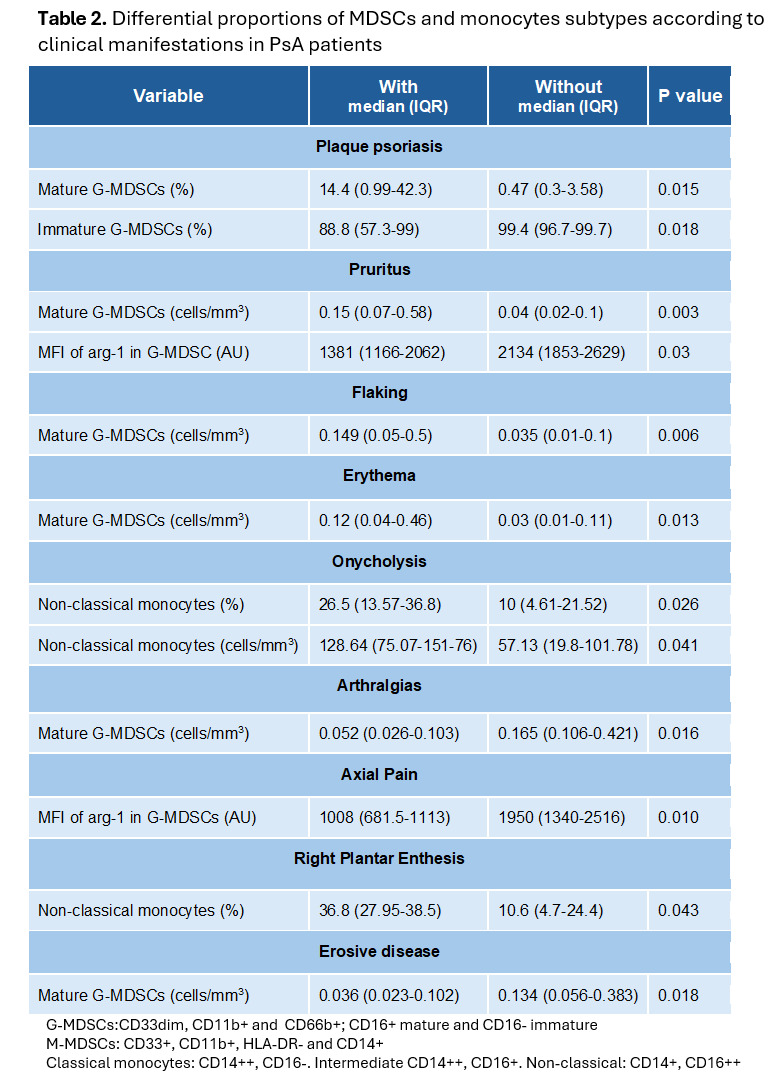
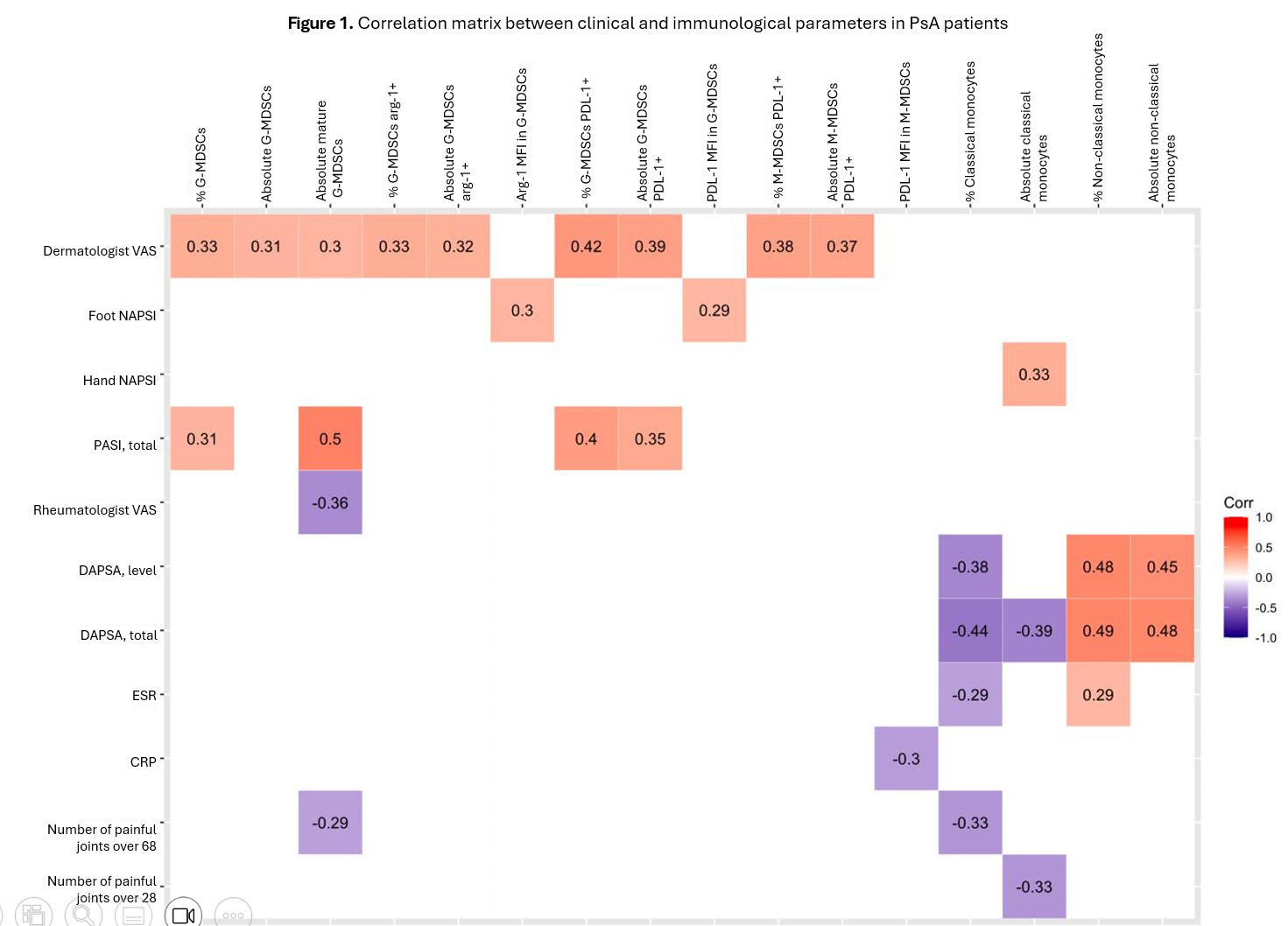
Results: Table 1 resumes demographic data of the study population. Significant differences of cell characteristics according to dermatological and musculoskeletal clinical features are shown in Table 2. Correlations between G-MDSCs, M-MDSCs, classical and non-classical monocytes and disease activity are depicted in Figure 1.
Regarding treatment, patients receiving leflunomide had stronger PDL-1 expression in G-MDSCs [2474 AU (2388-3843) vs 1928 (1621-2410) p= 0.014] as well as of arginase-1 (arg-1) in monocytic-MDSCs (M-MDSCs) [1919 AU (1234-1948) vs 1226 (1050-1886) p= 0.04]. In contrast, those under adalimumab showed a constant lowering effect on G-MDSCs, including percentage and absolute number [median 0.003% (0.002-0.004) vs 0.16% (0.04-0.25) p=0.021 and 0.075 cells/mm3 (0.054-0.096) vs 2.256 (0.61-5.18) p= 0.011], immature G-MDSCs [0.02 cells/mm3 (0.02-0.03) vs 1.34 (0.3-4.89) p= 0.016], arg-1 positive cells [ 0.0015% (0.0012 – 0.0017) vs 0.07 (0.009-0.23) p= 0.025] and PDL-1 positive G-MDSCs [9×10-4% (8×10-4-9.5×10-4) vs 0.03 (0.01-0.1) p= 0.034]. Additionally, ixekizumab was associated with a diminished amount of mature G-MDSCs [0.03 cells/mm3 (0.02-0.036) vs 0.1 (0.03-0.29) p= 0.04] and intermediate monocytes [4.1% (1.5-6) vs 9.5(5.4-17.7) p=0.02]. Psoriasis patients without musculoskeletal compromise showed increased G-MDSCs levels [0.15 cells/mm3 (0.08-0.41) VS 0.08 (0.02-0.1) p=0.04], but lower arg-1 levels in M-MDSCs [1164 AU (1008-1393) vs 1281(1110-1842) p= 0.02 ].
Conclusion: Our data shows that patients with PsA display a differential quantitative profile of MDSCs and monocytes, translating into particular clinical phenotypes and disease activity spectrum. Besides, DMARDs also play a role in modifying these subsets and might be useful as surrogate markers of biological efficacy. Longitudinal studies will be required to monitor the behaviour of these innate immune profile abnormalities in PsA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Balderas Miranda J, Torres Ruiz J, Guaracha Basañez G, Pascual Ramos V, Alcalá-Carmona B, Reyna-Juárez Y, Ostos-prado M, Mejía-Domínguez N, Juarez-Vega G, Gomez-martin D. Differential Quantitative Profile of Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells and Monocyte Subsets Relate to Clinical Phenotype and Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/differential-quantitative-profile-of-myeloid-derived-suppressor-cells-and-monocyte-subsets-relate-to-clinical-phenotype-and-disease-activity-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/differential-quantitative-profile-of-myeloid-derived-suppressor-cells-and-monocyte-subsets-relate-to-clinical-phenotype-and-disease-activity-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients/