Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Phenotypic changes of chondrocytes toward hypertrophy might be fundamental in the pathogenesis of OA, of which type X collagen is a well-known marker. The purpose was to develop a specific immunoassay for quantification of a newly identified neo-epitope of type X collagen to assess its diagnostic value for radiographic knee osteoarthritis (OA).
Methods:
A neo-epitope of type X collagen was identified in human urine from OA patients by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). A monoclonal antibody against the neo-epitope was produced. To identify the enzyme responsible for the cleavage of Col10, articular cartilage isolated from patients who underwent total knee replacement (TKR) was cleaved by numerous proteases in vitro and immunodetected. Immunohistochemical detection of this neo-epitope was performed on human OA cartilage from femoral condyle. A specific enzyme-linked immunoassay was developed by employing the neo-epitope antibody and quantified in plasma samples of two clinical studies: the C4Pain-003 and the NYU OA progression study. ROC curve analysis was carried out to evaluate the discriminative power of Col10neo between OA and RA.
Results:
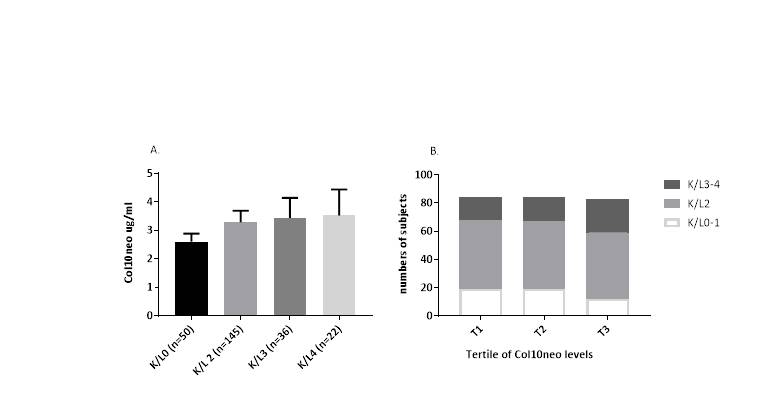
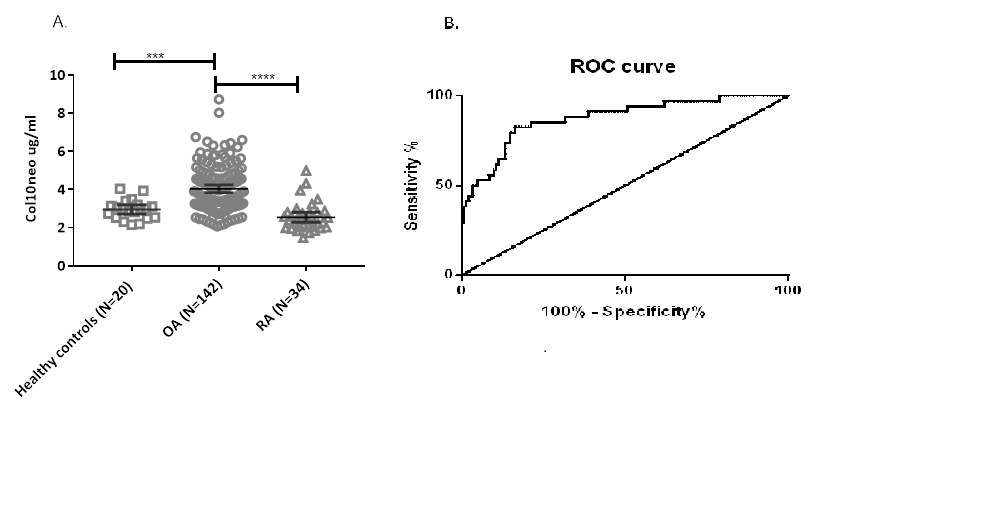
A mAb 2F4 targeting Cathepsin K- generated 479GIATKG neo-epitope was produced. In knee cartilage sections with mild or moderate cartilage degradation stained with Safranin O/Fast green, GIATKG neo-epitope was localized to the pericellular matrix of chondrocytes, while specimen with advanced cartilage degradation, its presence was extended to the territorial matrix of chondrocyte clusters and more prominent in superficial fibrillation. In the C4Pain study, there was a trend toward a higher level of Col10neo in subjects with greater KL. The greatest percent of subjects with KL3-4 was in the group of the highest tertile of Col10neo. In the NYU study, Col10neo was statistically higher in OA than control or RA. No significant difference was seen between control and RA (Figure 1). When adjusted for age, gender, and BMI, Col10neo remains significantly higher in OA compared to control and RA (Figure 2A). ROC curve analysis revealed area under the curve (AUC) was 0.88 (95% CI 0.81-0.94) (Figure 2B).
Fig. 1
Fig.2
Conclusion:
Our findings indicate that Col10neo could be used as a diagnostic biochemical marker for knee OA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
He Y, Manon-Jensen T, Arendt-Nielsen L, Petersen K, Gantzel T, Samuels J, Abramson SB, Karsdal MA, Attur M, Bay-Jensen AC. Development of a Neo-Epitope Specific Assay for Serological Assessment of Type X Collagen Degradation and Its Potential Diagnostic Value for Knee Osteoarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-a-neo-epitope-specific-assay-for-serological-assessment-of-type-x-collagen-degradation-and-its-potential-diagnostic-value-for-knee-osteoarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-a-neo-epitope-specific-assay-for-serological-assessment-of-type-x-collagen-degradation-and-its-potential-diagnostic-value-for-knee-osteoarthritis/