Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Development of a
Dual Energy Computed Tomography Scoring System for Measurement of Urate Deposition in Gout
Background/Purpose:
Dual energy computed tomography (DECT) can visualize urate
crystal deposits in patients with gout and has a potential role as an outcome
measure in gout studies. Although automated software is available for urate volume assessment, this method is time-consuming, due
to the need to identify regions of interest and exclude areas of artefact. The
aim of this study was to develop a semi-quantitative DECT scoring system for
measurement of urate deposition in gout.
Methods: Following
a structured review of images, a semi-quantitative DECT urate
scoring method for foot/ankle scans was developed for testing. This method
included four regions, each scored from 0-3, with a maximum total DECT urate score of 12.
DECT scans from 224 patients (182 with gout, 42 without gout) were
scored by two independent readers. Automated urate
volumes were also measured. Paired scans
from eight patients receiving pegloticase were
analysed. A timing exercise was undertaken.
The properties of the DECT urate score were
analysed according to the Outcomes in Rheumatology Clinical Trials (OMERACT)
filter.
Results: The
inter-reader intraclass correlation coefficient
(95%CI) for the DECT urate score was 0.98
(0.97-0.98). All scored regions
contributed to the total DECT urate score. DECT urate scores
and urate volumes were highly correlated (r=0.91,
p<0.0001). Both DECT urate scores and urate volumes
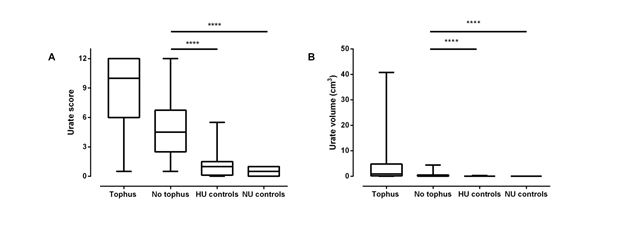
discriminated between gout and non-gout control participants, and between the tophaceous gout, non-tophaceous
gout and control groups (Figure). Compared with urate
volume, the DECT urate score had greater ability to
discriminate between responders and non-responders to pegloticase
therapy (p<0.001 for DECT urate score and >0.05
for urate volume).
The mean (SD) time required for the DECT urate
score was 121 (2) seconds and for urate volume was
240 (2) seconds (p=2×10-31).
Conclusion: We
have developed a novel semi-quantitative DECT scoring method for measurement of
urate deposition.
This method fulfils many aspects of the OMERACT filter.
Figure: Box and
whisker plot showing discrimination between groups.
A. DECT urate scores and
B. urate volumes for the following groups: tophaceous gout (tophus, n=89), non-tophaceous
gout (no tophus, n=93), hyperuricaemic (HU) controls
(n=28) and normouricaemic (NU) controls (n=14). Kruskall-Wallis
p<0.0001 for both methods, ****Dunn’s multiple comparisons test p<0.0001.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bayat S, Aati O, Rech J, Cavallaro A, Lell M, Araujo E, Petsch C, Stamp LK, Schett GA, Manger B, Dalbeth N. Development of a Dual Energy Computed Tomography Scoring System for Measurement of Urate Deposition in Gout [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-a-dual-energy-computed-tomography-scoring-system-for-measurement-of-urate-deposition-in-gout/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-a-dual-energy-computed-tomography-scoring-system-for-measurement-of-urate-deposition-in-gout/