Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Matching most beneficial targeted therapy to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients with inadequate response or intolerance to current treatment is an important unmet clinical need. The aim of this study was to identify synovium-specific transcriptomic signals in blood that differentiate responders from non-responders and develop a test that predicts response to targeted therapies.
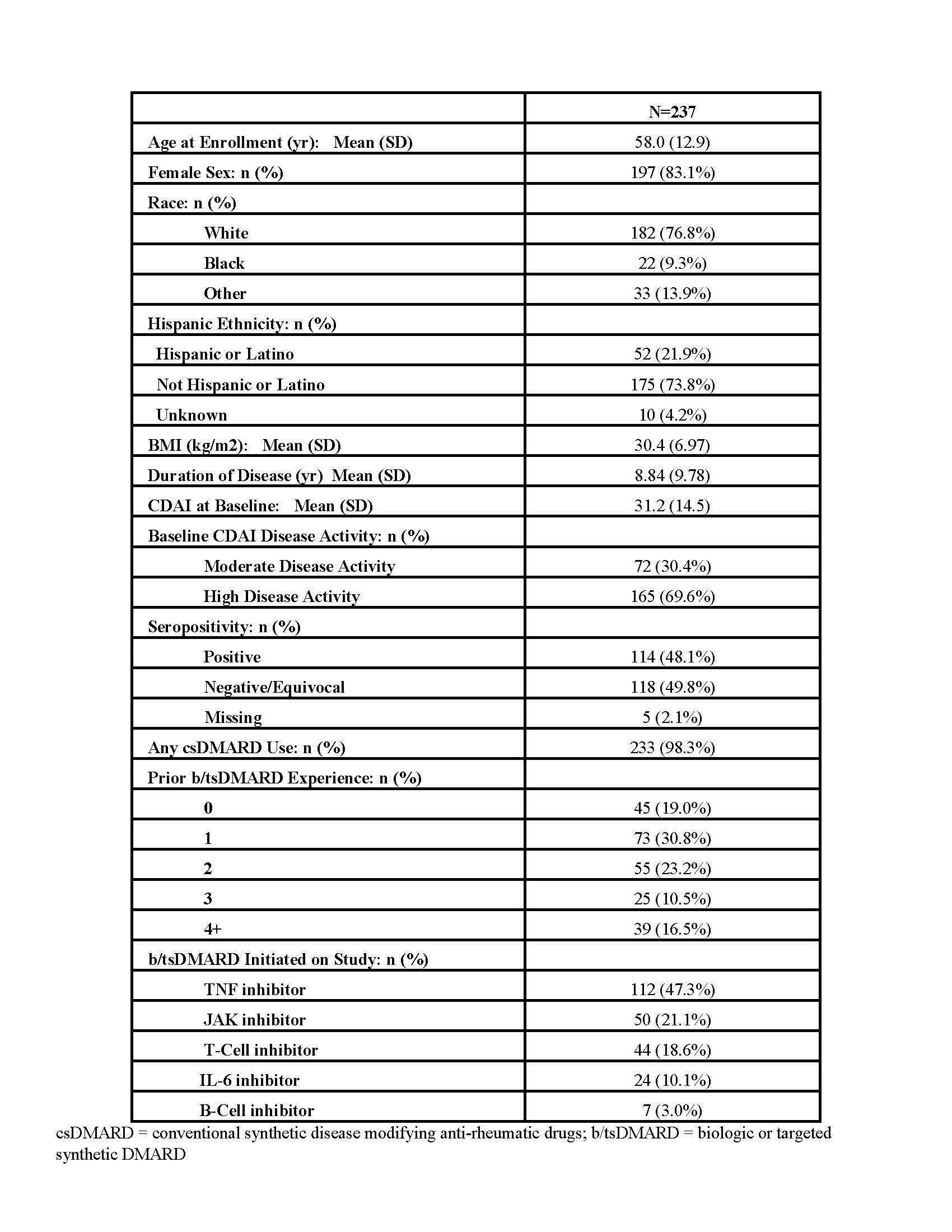
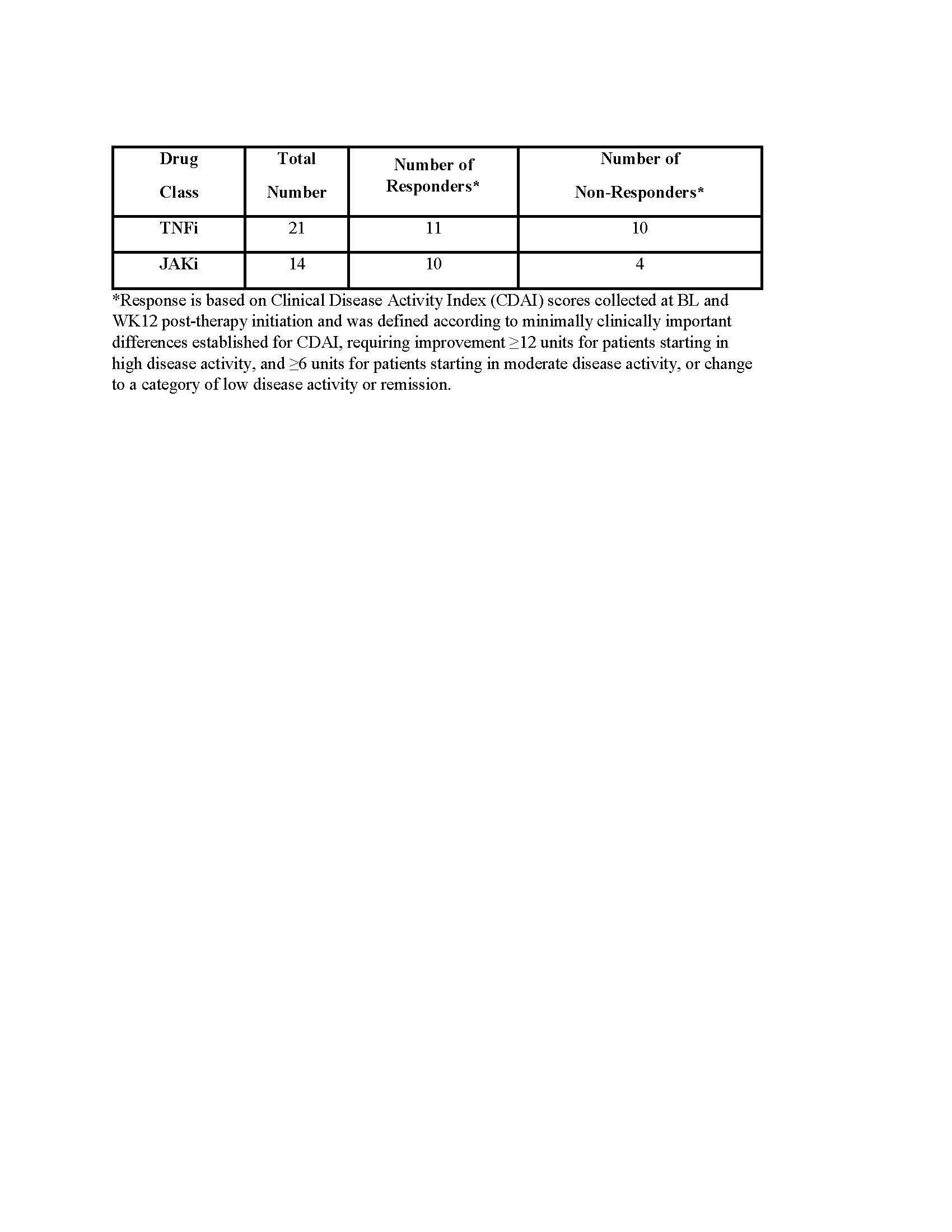
Methods: PRIMA-102 is a prospective, multi-center, observational study with blood collection and clinical outcome assessments at baseline (BL) and week 12 post-therapy initiation (NCT05936970). Target enrollment for PRIMA-102 is up to 830 subjects, with 237 currently enrolled (Table 1). An initial analysis was performed on 35 subjects initiating a TNFα inhibitor (TNFi) or Janus Kinase inhibitor (JAKi) who met study completion (Table 2). BL plasma samples were processed using a novel active chromatin cell-free DNA (cfDNAac) capture assay that yields a catalog of features linking circulating chromatin signals in blood to specific regulatory elements across the genome, including ~64K enhancers, ~37K promoters, and ~50K transcribed genes. This process allows for non-invasive access to tissue- and disease-specific molecular signatures. Key regulatory elements were identified using principal component analysis, based on the loadings from the principal component that significantly differentiated TNFi or JAKi responders and non-responders. Pathway and gene expression signature analyses were performed on active chromatin profiles to identify mechanisms that could discriminate responders and non-responders.
Results: Functional enrichment of the top ranked Differentially Regulated Active Chromatin Elements (DRACEs) associated with treatment response to TNFi and JAKi showed a striking diversity of synovial inflammatory signals with marked enrichment of myeloid, lymphoid, fibroblast, and endothelial cell subpopulations. Individual marker analysis showed the presence of transcriptional activity of pro-inflammatory mediators IL-32 and IL-33, chemokine involvement via promoter activation of CXCL9 and CXCL1 genes, vascular endothelial cell signals including promoter activation of ERG, and naive and central memory T cells as evidenced by promoter activation of SELL. These findings suggest that screening for DRACEs provides a non-invasive method for reconstructing lymphoid and myeloid sub-groups in RA. These sub-groups, previously identified only through synovial biopsy transcriptomics studies, were detected via cfDNAac, highlighting the platform’s ability to access tissue-specific signals linked to TNFi and JAKi response.
Conclusion: Synovium specific and cell-mediated inflammatory pathways were identified in RA subjects treated with either TNFi or JAKi therapy using a novel blood-based cfDNAac assay. These synovial related signatures overlap with pathways previously identified using synovial tissue biopsies. PRIMA-102 is an ongoing, prospective study that will support the development and validation of a non-invasive test with potential to predict therapeutic response to targeted therapy that could guide personalized treatment decisions in RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Taylor P, Lai K, Wu H, Carlson J, Abdueva D, Fransen S, Kivitz A, Lam G, Chernoff D. Development of a Blood-based Cell-free DNA Classifier Assay to Predict Biologic and Targeted Synthetic DMARDs Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients (PRIMA-102) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-a-blood-based-cell-free-dna-classifier-assay-to-predict-biologic-and-targeted-synthetic-dmards-response-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-prima-102/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-a-blood-based-cell-free-dna-classifier-assay-to-predict-biologic-and-targeted-synthetic-dmards-response-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-prima-102/