Session Information
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
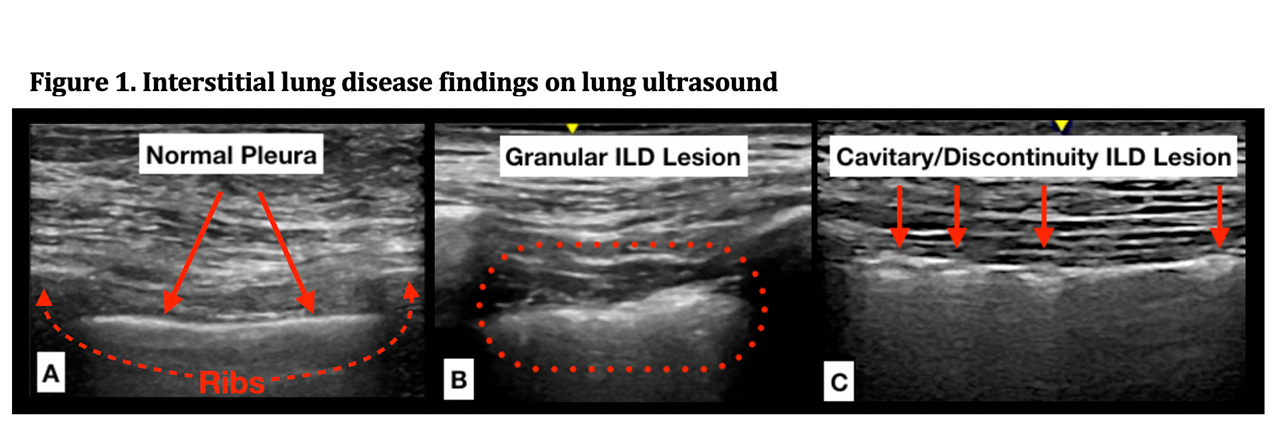
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a frequent complication of systemic sclerosis (SSc), and screening, characterization, and monitoring of disease activity are important for therapeutic decision-making and prognostication. High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is the gold standard for ILD diagnosis. More recently, lung ultrasonography (LUS) has been proposed as a potential alternative imaging modality for ILD detection. In this study, we develop and test a novel LUS interpretation criteria for detecting SSc-ILD.
Methods: Patients with prevalent SSc and prior or planned HRCT within 3 months were prospectively enrolled and assessed by LUS. We included 14 lung positions and used a novel acquisition technique, collecting several seconds of real-time images rather than still images with the probe oriented in a sagittal rather than transverse orientation. This technique affords better visualization and tracking of pleural lesions with respiration. Prior studies identified B-line quantification, pleural irregularity, and pleural thickness as features sensitive for SSc-ILD. Although B-line quantification has been extensively studied, it is a less specific and artifactually based finding and highly dependent on ultrasound technique and machine settings. Given the high resolution of current US machines, granular appearing pleural thickening and pleural irregularity (defects in the pleural surface) were easy to visualize and highly reproducible (Figure 1). Using a combination of these features, we developed LUS interpretation criteria for SSc-ILD detection (Figure 2). These interpretation criteria were used to evaluate LUS examinations of our SSc cohort and were read by two independent readers (1 ultrasonographer and 1 non‑ultrasonographer) who were blinded to HRCT results and ILD diagnosis. The sensitivity and specificity for SSc-ILD detection was assessed and agreement was measured with Cohen’s Kappa statistic.
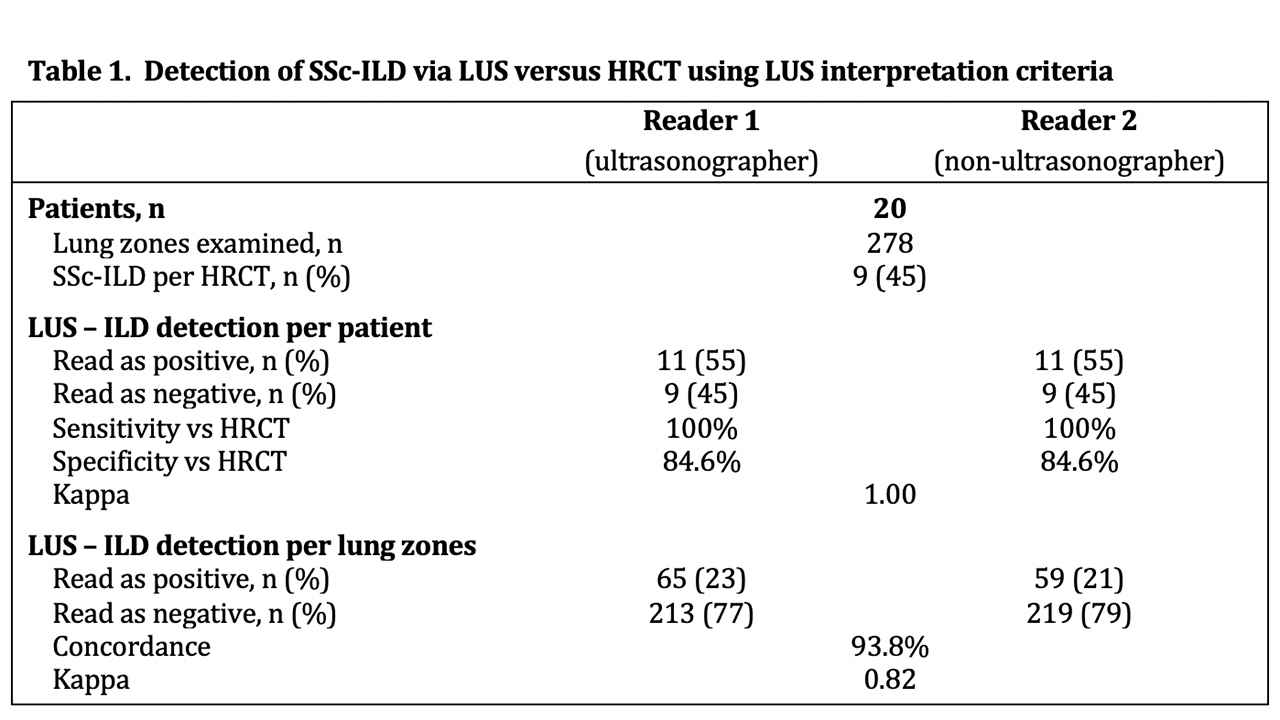
Results: We evaluated 20 SSc patients by LUS examination (278 lung zones) and HRCT. HRCT confirmed ILD in 9 patients (45%). LUS was read as positive for SSc-ILD in 11 patients (55%) with a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 84.6% versus HRCT with perfect agreement between the two readers (κ= 1). Analysis by individual lung zones found excellent agreement between readers with 93.8% concordance and κ = 0.82 (Table 1).
Conclusion: We developed a novel ultrasound technique and interpretation criteria that are highly sensitive and specific for ILD detection in an SSc cohort. Our interpretation criteria are feasible and reliable, affording perfect agreement between ultrasonographer and non‑ultrasonographer readers for SSc-ILD detection. Moving forward we hope to validate these criteria in a larger cohort of patients with SSc, dermatomyositis and polymyositis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fairchild R, Yang D, Chung M, Sharpless L, Li S, Chung L. Development and Preliminary Validation of a Novel Lung Ultrasound Interpretation Criteria for the Detection of Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-and-preliminary-validation-of-a-novel-lung-ultrasound-interpretation-criteria-for-the-detection-of-interstitial-lung-disease-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-and-preliminary-validation-of-a-novel-lung-ultrasound-interpretation-criteria-for-the-detection-of-interstitial-lung-disease-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/