Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1155–1182) Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Dermatomyositis (DM) is an autoimmune disorder part of the group of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. It is characterized by proximal muscle weakness and skin involvement. Part of the diagnosis includes clinical features, muscle biopsy, electromyography, myositis specific antibodies and laboratory findings. We have seen an association of active DM disease (either new diagnosis or relapse of previously controlled disease) after COVID-19 infection and vaccination. The first cases reported in the literature were by Gokhale et al., who reported 5 cases in India. Other studies have seen a correlation between the vaccine and the positivity of anti-MDA5 antibodies.
Our study aimed to observe the characteristics of a DM cohort after COVID-19 infection and vaccination.
Methods: A retrospective chart review was performed on patients treated between March 1, 2020, and October 31, 2022, for DM. New DM diagnosis or relapse of preexisting DM symptoms following either SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19 vaccination was documented as active DM disease. Qualifying DM symptoms included characteristic rash, muscle weakness, and increased creatine kinase.
For the analysis of our primary aim, we estimated the proportion of patients who had active DM symptoms within 4 weeks after COVID-19 infection or vaccination; a two-sided 95% confidence interval for the single proportion was estimated using the score method. In an exploratory analysis we reported the number and percentage of patients who developed active DM symptoms within 4 weeks following COVID-19 infection or vaccination according to patient characteristics where continuous characteristics were categorized according to the sample median.
Results: 101 patients were treated for DM at our institution in the Division of Rheumatology. 15/101 patients (14.9%) had symptoms related to DM (relapse or new diagnosis) following SARS-COV-2 infection or vaccination. Three (3.0%) patients developed symptoms both with vaccination and infection, 10 (9.9%) patients developed symptoms post SARS-COV-2 infection and 8 (7.9%) developed symptoms post COVID-19 vaccination.
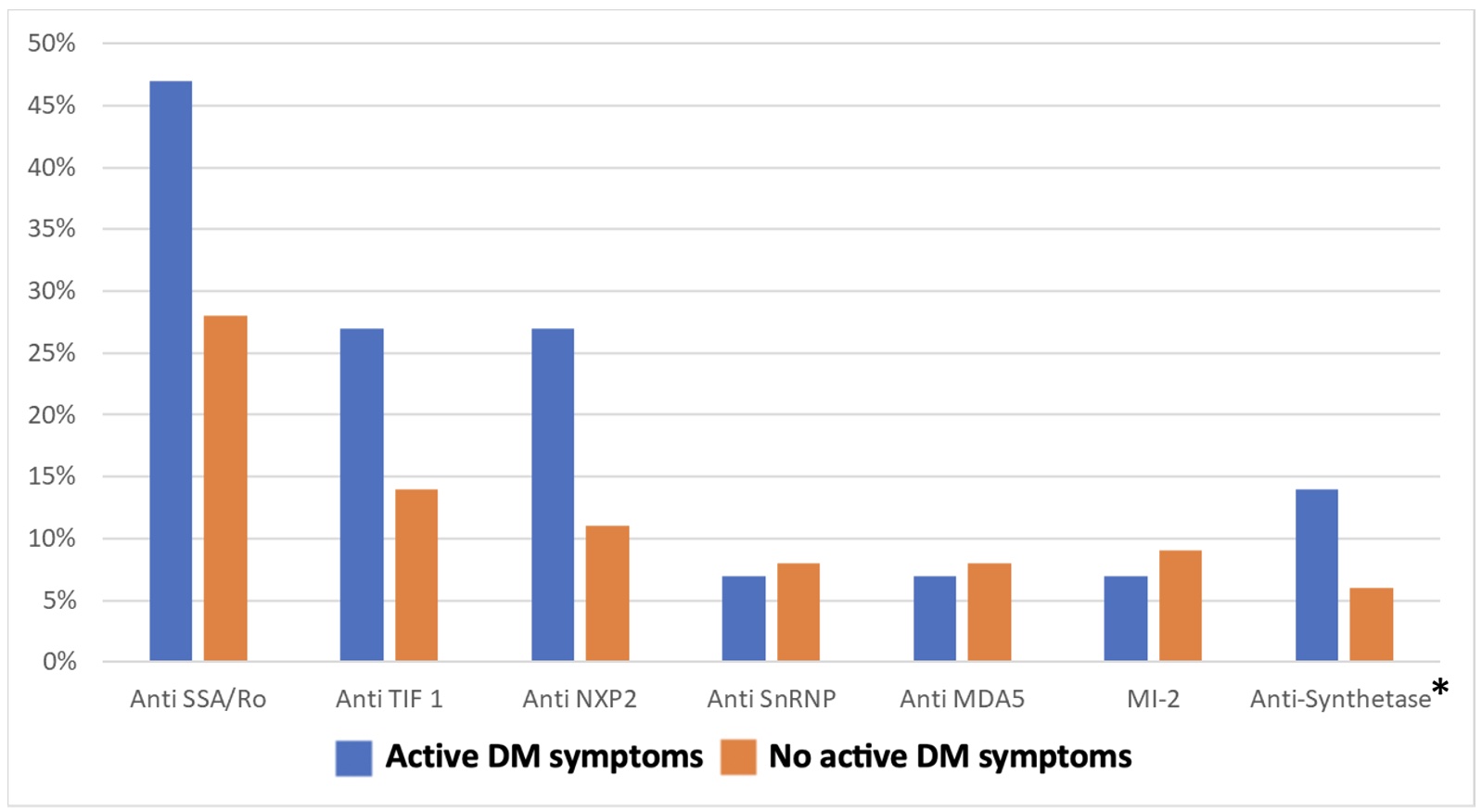
14/15 (93.3%) patients had a positive myositis antibody (see Figure 1). The ten patients who presented with symptoms post infection had a younger mean age of 50 compared to 62 in patients without a flare post infection (p=0.047) (see Table 1).
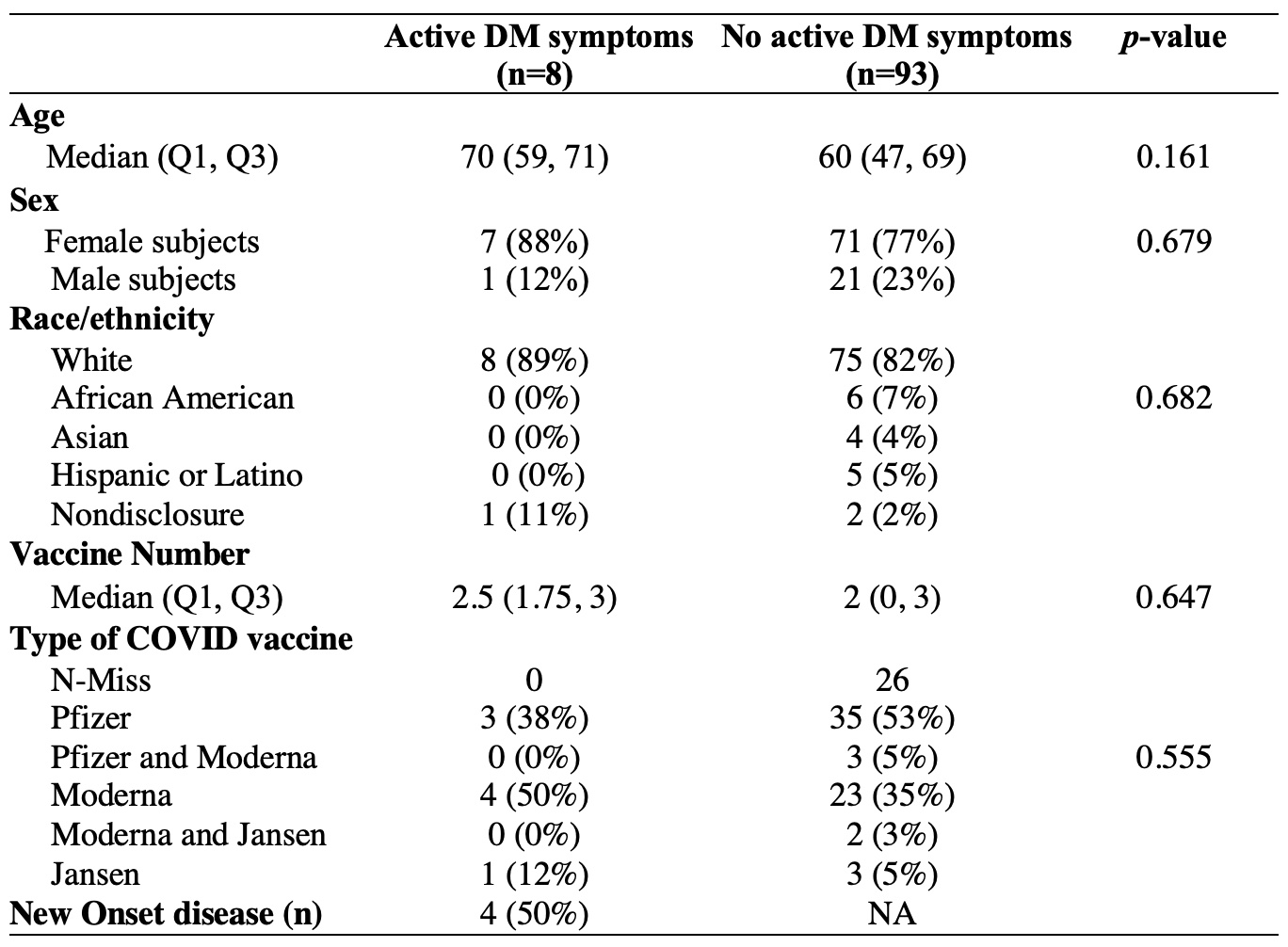
Of those who developed symptoms post-vaccination (3 patients had symptoms following both infection and vaccination), demographics and vaccine type are presented in Table 2.
The mean onset of symptoms following SARS-COV-2 infection was 2.6 days with a median of 1 (Q1: 0; Q3: 5) and following COVID-19 vaccination was 1.38 days, median of 1 (Q1: 0.5; Q3: 2).
Conclusion: This retrospective study revealed a strong temporal relationship between DM symptoms and Covid-19 infection or vaccination in 14.9% of all DM patients evaluated in our clinic during the pandemic. The higher prevalence of NXP2 in our cohort is unique from prior reports. Additional studies are required to understand the possible pathophysiology behind this association.
* Anti-Synthetase included anti-Jo_1, anti-PL-7, anti-PL_12, anti-OJ, anti-EJ, anti-KS, anti-SRP, anti-Zo, anti-HA, and anti-Ku
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Diaz Menindez M, Sullivan M, Wang B, Abril A, Majithia V, Butendieck R, Ball C, Berianu F. Dermatomyositis Flares After COVID-19 Vaccination and/or SARS-CoV-2 Infection [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dermatomyositis-flares-after-covid-19-vaccination-and-or-sars-cov-2-infection/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dermatomyositis-flares-after-covid-19-vaccination-and-or-sars-cov-2-infection/