Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 6:00PM-7:00PM
Background/Purpose: The COVID-19 pandemic created dramatic societal disruptions. Social distancing and measures to reduce disease spread rapidly reshaped healthcare delivery. Recognizing the burden of frequent monitoring and multiple medications in children with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), our study sought to describe the effect of pandemic-related disruptions on the health and wellbeing of these families.
Methods: The study consisted of a cross-sectional survey from a convenience sample of caregivers of pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients at Texas Childrens Hospital from April 2021 to March 2022. Surveys were administered through REDCap in English and Spanish. Participants were recruited during clinic visits and via email from a roster of158 active pediatric SLE patients maintained by the Rheumatology Division.
Results: 40 respondents completed the survey. Sample demographics are shown inTable 1.
Barriers to Care (Table 1)
Despite increased telehealth use, many families reported missed or delayed care for their child: 15 (37%) reported missed or delayed medical appointments, 10 (25%) reported problems seeing a doctor, 4 (10%) reported missed or delayed procedures or surgeries, 3 (7%) reported missed or delayed lab draws, 2 (5%) reported loss of health insurance coverage, and 1 (2%) missed or delayed immunizations.
Changes in Mental and Physical Health (Fig. 1)
Respondents reported declines in child mental and physical health. 57% reported a decline in their childs mental health, and 79% reported higher levels of stress in the home during the pandemic. Similarly, 46% reported a decline in their childs physical health, and 57% reported that their child exercised less often during the pandemic.
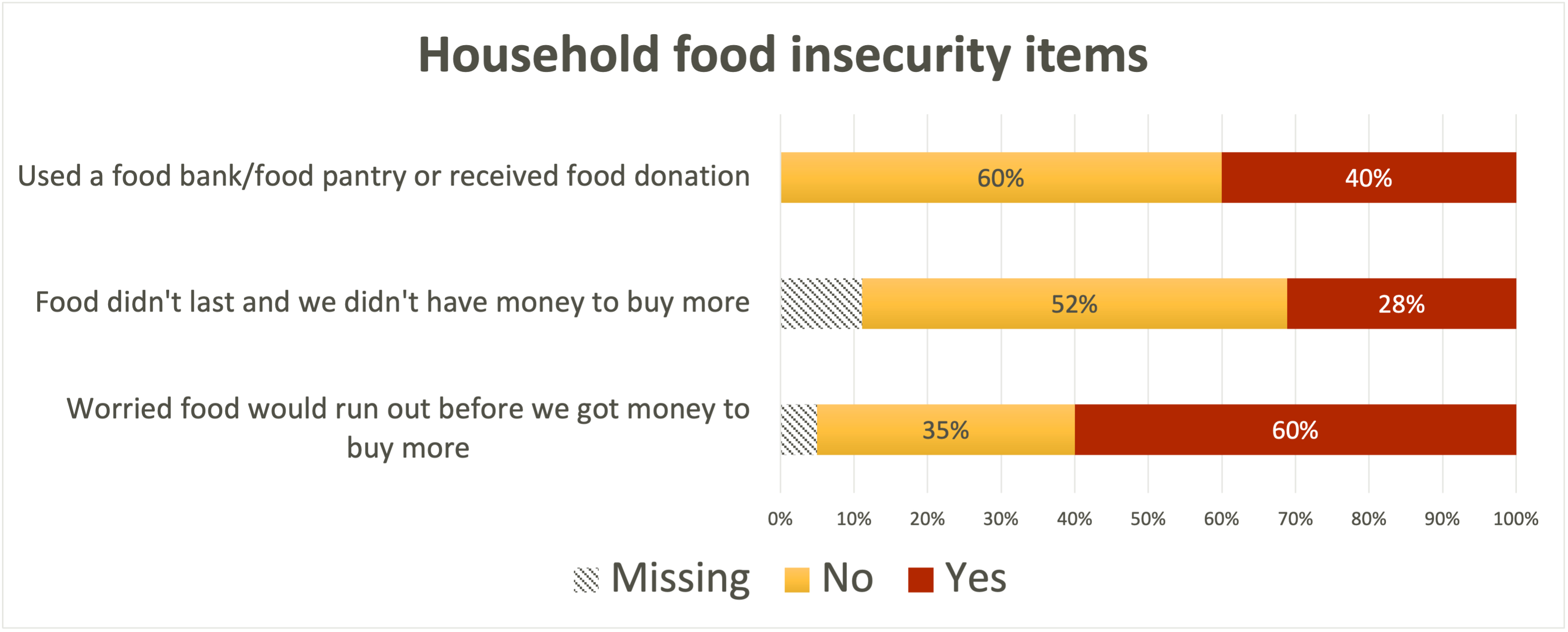
Food Insecurity (Fig. 2)
Our sample demonstrated a high prevalence of food insecurity: 64% endorsed concerns that food would run out before getting money to buy more, 32% endorsed that food had run out without money to purchase more, and 39% reported using a food pantry or receiving a food donation.
Conclusion: Our survey captured important experiences of families with pediatric SLE patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. Compared to national data, our sample may have demonstrated greater declines in child physical and mental health and higher rates of food insecurity.1,2 Our sample demonstrated a dramatic increase in the use of telehealth. Many delays in care were identified, most notably missed or delayed medical appointments in over one-third.
Given the cross-sectional design and convenience sampling, this data may not be representative of pediatric SLE patients nationally. Limited conclusions can be drawn from comparison to national data given differing data collection methods. However, in this vulnerable population, pandemic-related limitations in care are concerning and warrant further study.
Works Cited: Lebrun-Harris LA, Ghandour RM, Kogan MD, Warren MD. Five-Year Trends in US Childrens Health and Well-being, 2016-2020. JAMA Pediatr. 2022;176(7):e220056.
Coleman-Jensen A, Rabbitt MP, Gregory CA, Singh A. Statistical Supplement to Household Food Security in the United States in 2021. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service; 2022. AP-105.
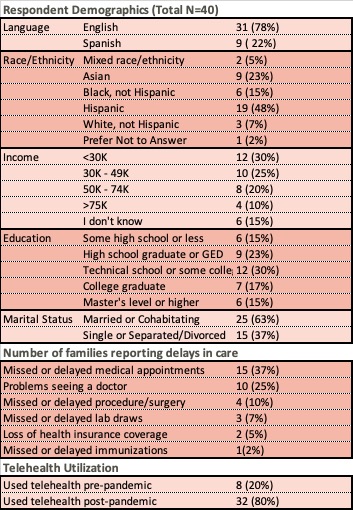 Respondent Demographics and Healthcare Utilization
Respondent Demographics and Healthcare Utilization
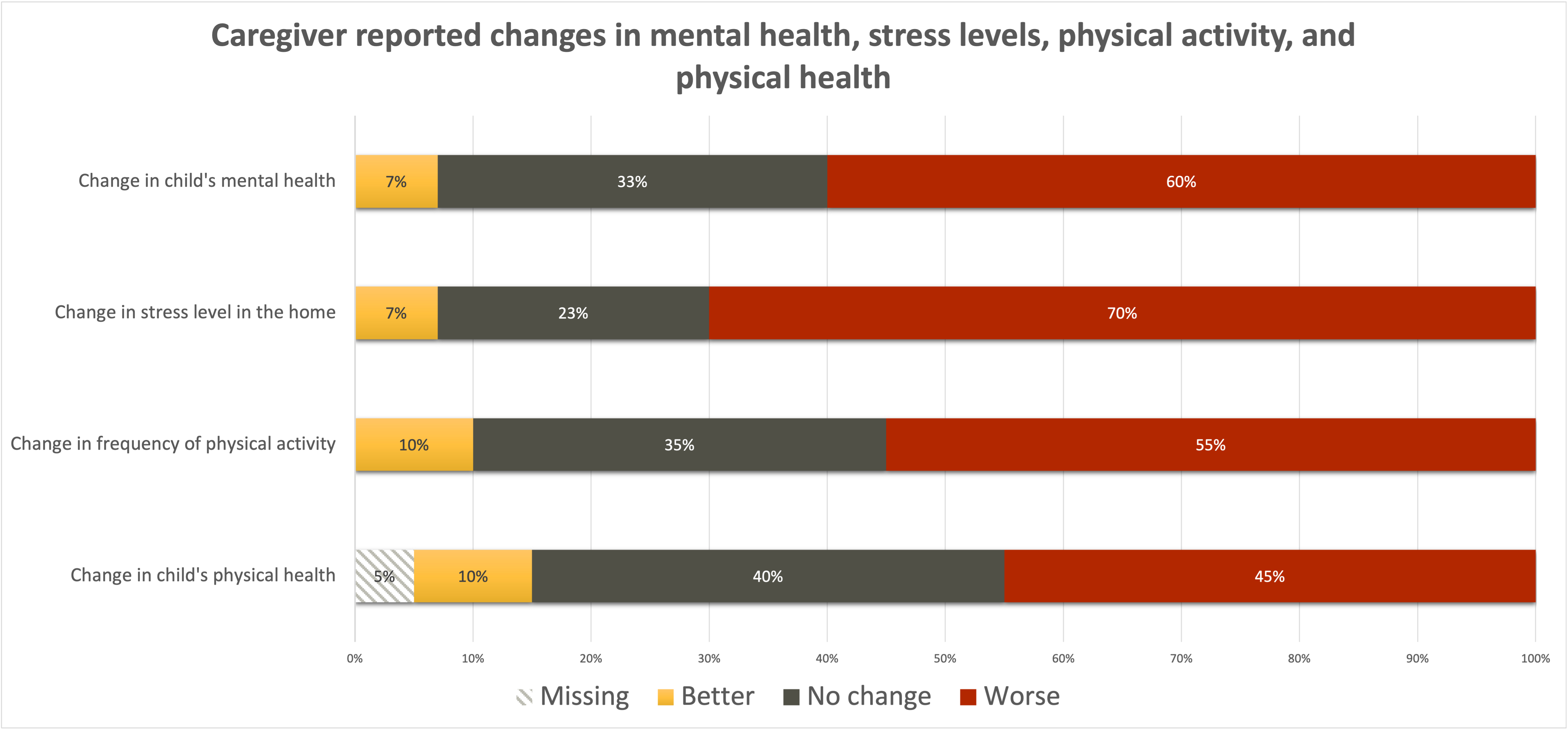 Changes in Physical and Mental Health
Changes in Physical and Mental Health
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hetrick R, Pereira M, De Guzman M. Delays in Care, Declines in Health, and Food Insecurity in Pediatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients During the COVID-19 Pandemic [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 4). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/delays-in-care-declines-in-health-and-food-insecurity-in-pediatric-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients-during-the-covid-19-pandemic/. Accessed .« Back to 2023 Pediatric Rheumatology Symposium
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/delays-in-care-declines-in-health-and-food-insecurity-in-pediatric-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients-during-the-covid-19-pandemic/