Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Synovial fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) actively participate in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). FUN14 domain-containing protein 1 (FUNDC1), a novel mitophagy receptor, plays critical roles in receptor-mediated mitophagy and participates in pathogenesis of a variety of diseases. However, the roles of FUNDC1 and FUNDC1-mediated mitophagy in RA remain unknown. Here we aimed to explore the role of FUNDC1-mediated mitophagy in RA-FLS deterioration phenotype and its clinical significance.
Methods: We observed the expression of FUNDC1 at both lining and sublining layers in RA and Orth.A synovium by immunohistochemistry. According to the median value of sublining FUNDC1 expression level, RA patients was further divided into high expression group and low expression group. Primary RA-FLS were cultured in vitro and pretreated with siNC and siFUNDC1. We measured the level of mitophagy through transmission electron microscope. Their effects on migration and invasion were detected by wound healing and transwell assays. The proteome Profiler Human Protease Array kit was used to determine the treated supernatant level.
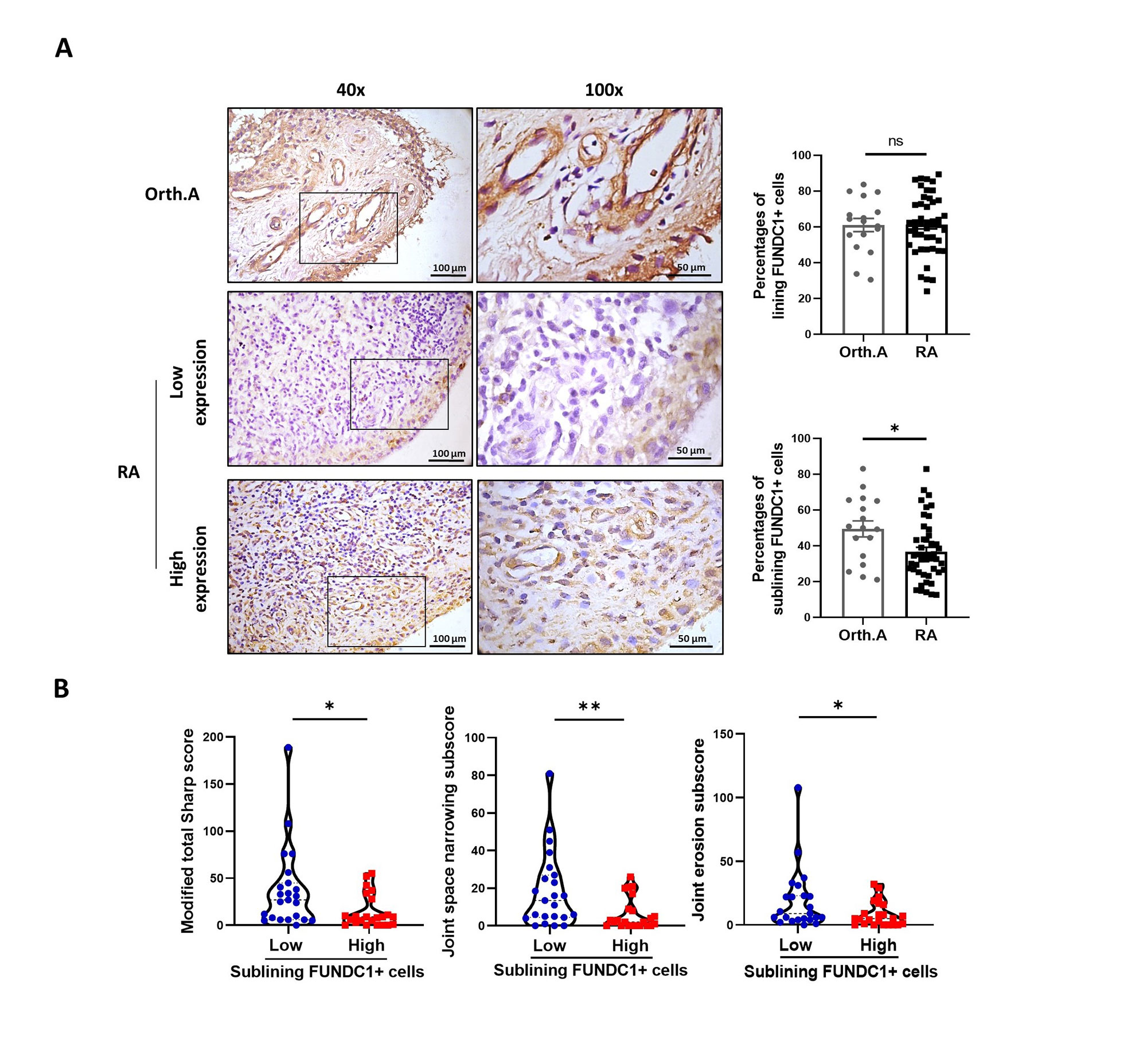
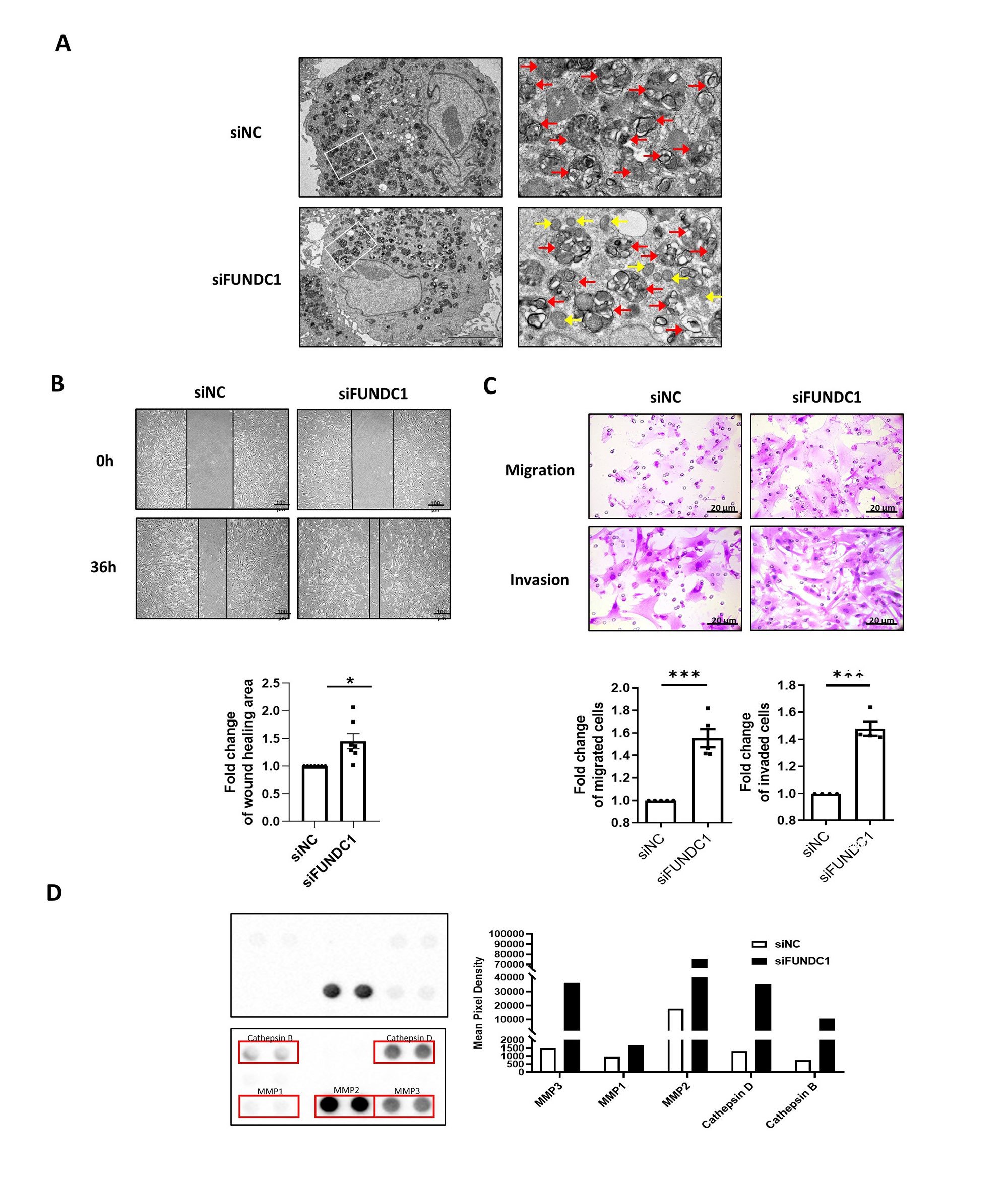
Results: FUNDC1 expression in the sublining area of RA synovium was significantly lower than that of Orth.A (Figure 1A). RA patients with low sublining FUNDC1 expression showed significantly higher modified total Sharp score (mTSS), joint space narrowing (JSN) subscore and joint erosion (JE) subscore (Figure 1B). After FUNDC1 siRNA transfection, mitophagy decreased (Figure 2A). Besides, RA-FLSs obtained more intensive abilities of migration and invasion (Figure 2B-C). Furthermore, screening results showed that the supernatant levels of MMP1, MMP2, MMP3, cathepsin B, and cathepsin D were all significantly increased after FUNDC1 knockdown (Figure 2D).
Conclusion: Decreased expression of FUNDC1 in RA synovium was associated with radiographic joint destruction. In RA-FLSs, when FUNDC1 was knockdown, mitophagy decreased, aggravating the movability and the secretion of multiple proteases.
(A) Representative immunohistochemical images of synovial FUNDC1 expression. (scale bar = 100 μm – 50 μm). (B) Comparisons of joint destruction indicators between sublining FUNDC1 high/low expression groups.
(A) Representative transmission electron microscopy images showing mitophagy level in RA-FLSs after transfection of siNC or siFUNDC1 (yellow arrows: mitochondria, red arrows: autolysosomes , scale bar = 5 μm – 500 nm). (B) Wound healing assay was used for evaluation of cell motility (scale bar = 100 μm). (C) Cell migration was performed using transwell assay, 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) was placed in the lower chamber used as chemoattractant. For invasion assay, transwell chambers were precoated with Matrigel, and FBS (15%) was placed in the lower chamber as chemoattractant (scale bar = 20 μm). (D) Cell culture supernatants were analyzed using the Proteome Profiler Human Protease Array kit after transfection of siNC or siFUNDC1.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhang Q, Wu T, Ma J, Zou Y, Zhang X, Zheng H, Jing J, Zou Y, Chen L, Dai L. Deficiency of FUN14 Domain-Containing Protein 1-Mediated Mitophagy in Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes Causes Aggressive Behaviors Leading to Joint Destruction in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/deficiency-of-fun14-domain-containing-protein-1-mediated-mitophagy-in-fibroblast-like-synoviocytes-causes-aggressive-behaviors-leading-to-joint-destruction-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/deficiency-of-fun14-domain-containing-protein-1-mediated-mitophagy-in-fibroblast-like-synoviocytes-causes-aggressive-behaviors-leading-to-joint-destruction-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/