Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-3:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease with currently no effective prevention strategies. Single-cell technologies have been used to investigate established RA heterogeneity (1), but it is unknown if the immune populations identified from RA tissues play important roles in blood during the preclinical phase of disease. Thus, identifying pathogenic immune phenotypes in individuals who are at risk for future RA, designated “At-Risk RA”, is crucial to establishing prevention strategies.
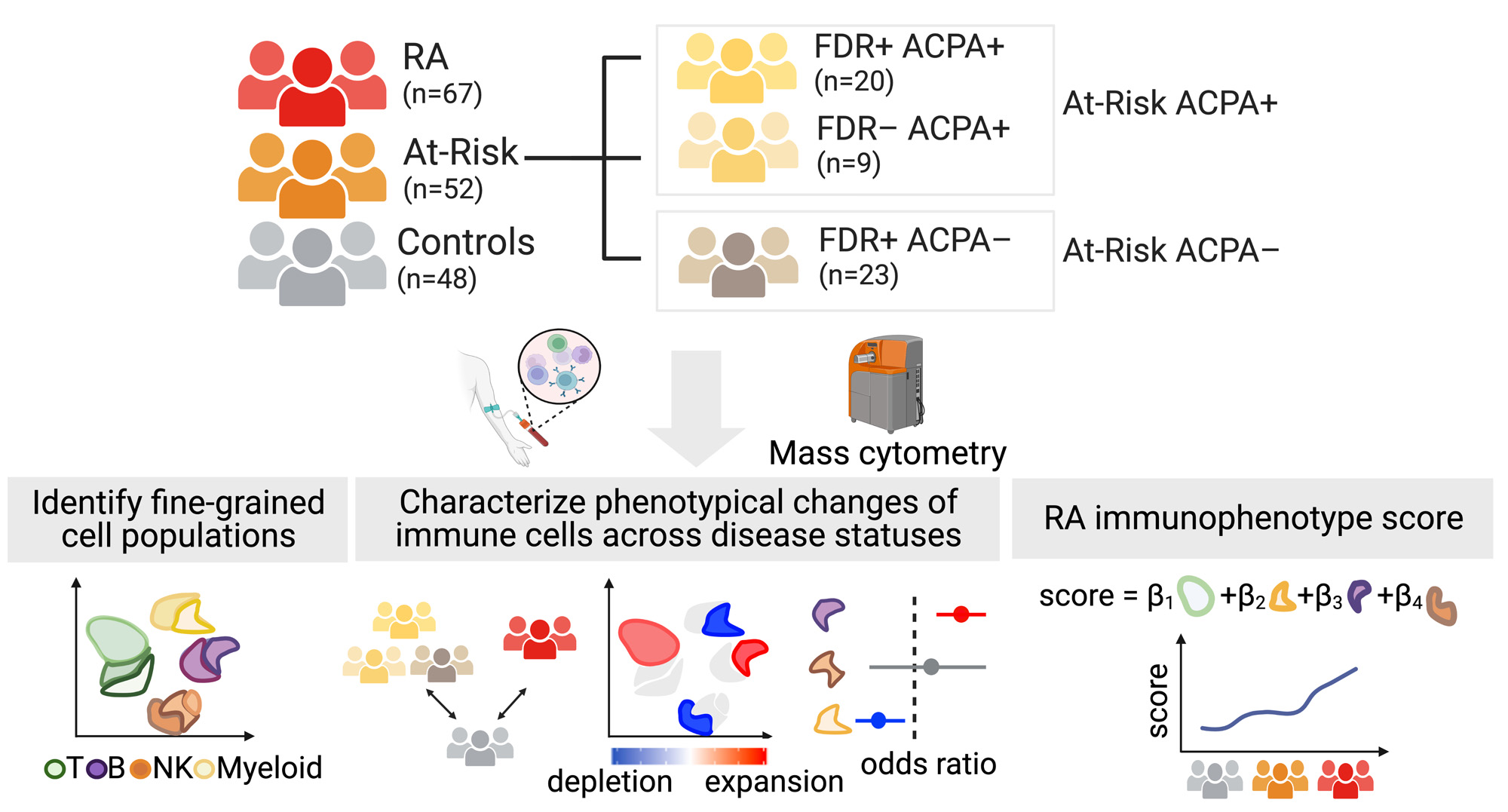
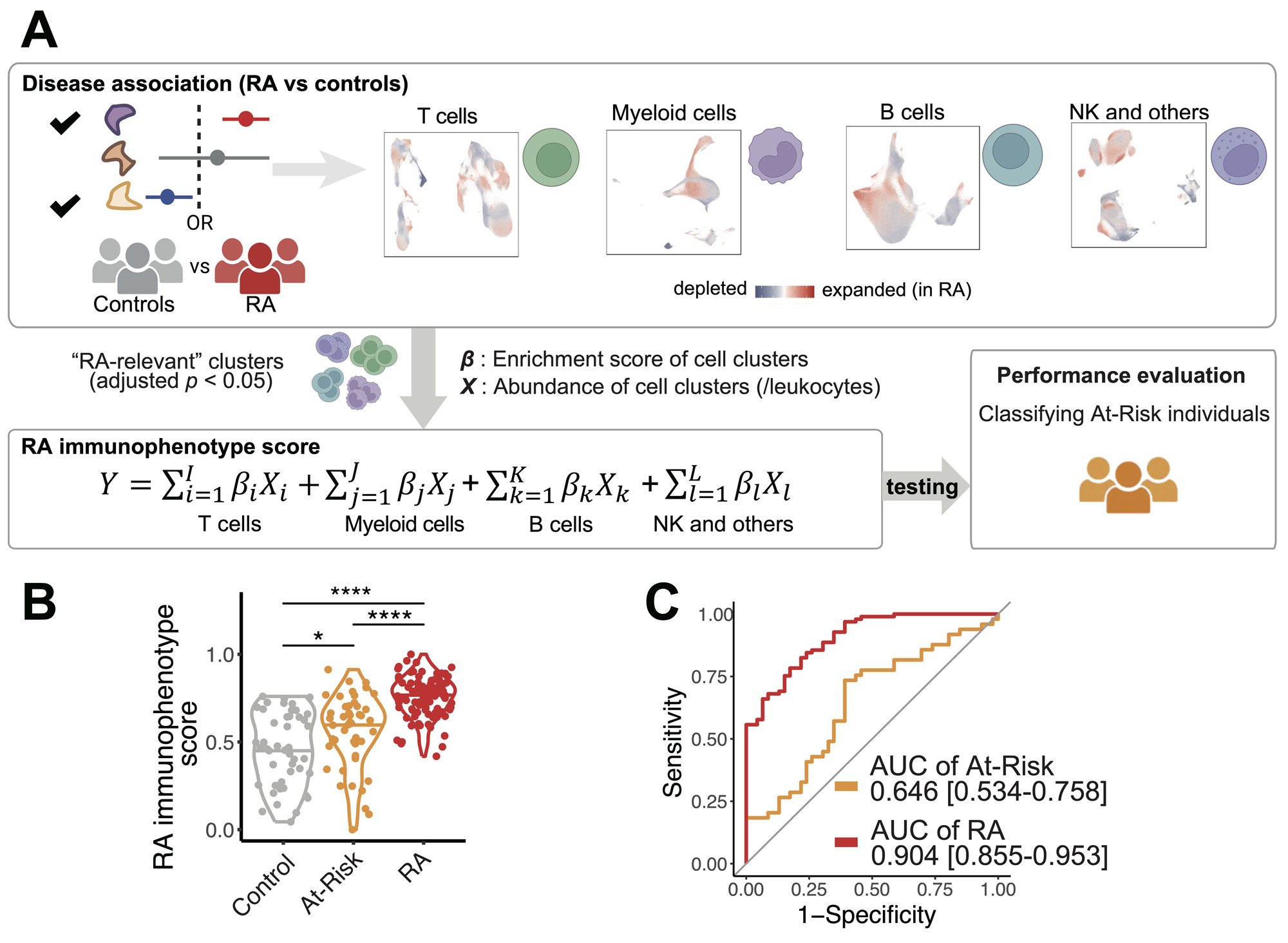
Methods: We applied mass cytometry to deeply characterize immunophenotypes in PBMCs (peripheral blood mononuclear cells) from At-Risk individuals based on the presence of antibodies to citrullinated protein antigens (ACPA) and/or first-degree relative (FDR) status (n=52), established RA (n=67), and healthy controls (n=48) (Figure 1). We performed co-varying neighborhood analysis to characterize immunophenotypes in At-Risk individuals and identify phenotypical changes between At-Risk subpopulations accounting for batch effect, age, sex, and inter-individual variation. We further developed an “RA immunophenotype score” for cross-phenotype classification using mixed-effect modeling and logistic regression.
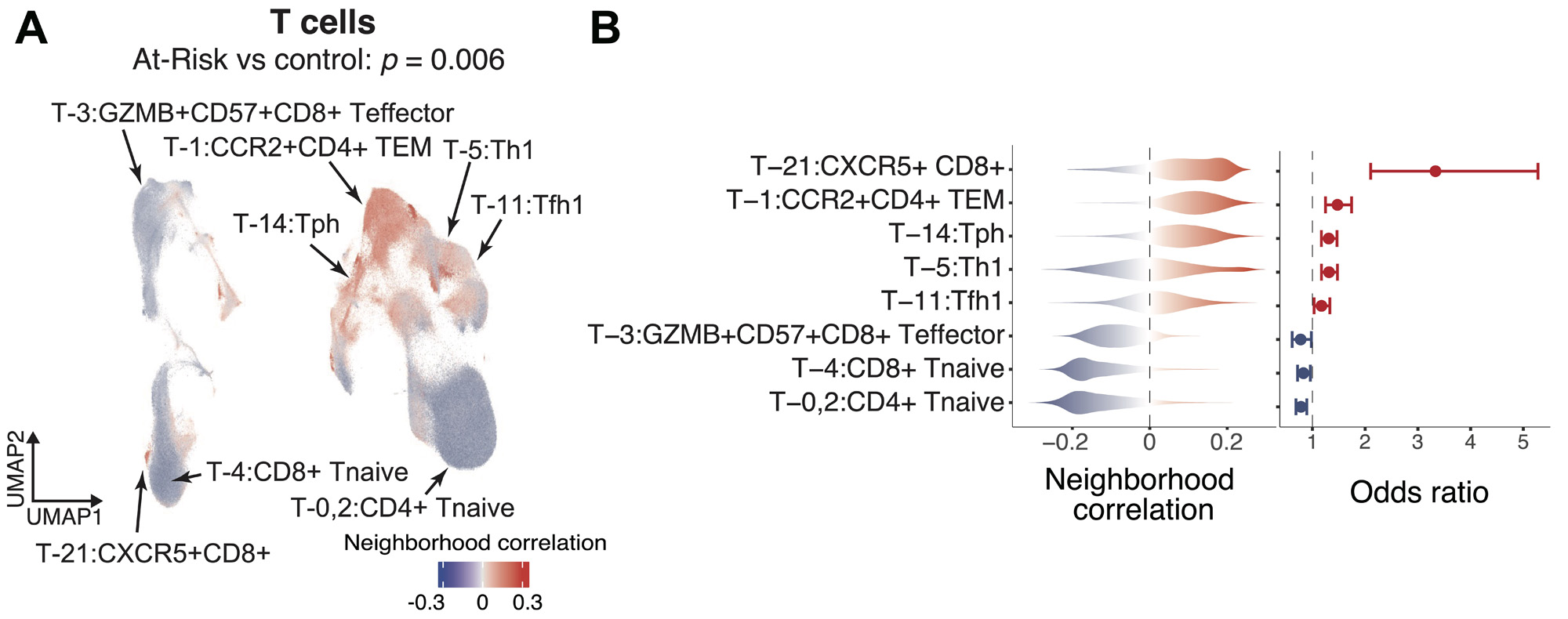
Results: We quantified the immune populations and uncovered significant cell expansions in At-Risk individuals compared with controls (p = 6e-3), including CCR2+CD4+ effector memory T cells (TEM) (OR = 1.47), T peripheral helper cells (Tph) (OR = 1.30), type 1 T helper cells (OR = 1.31), and CXCR5+CD8+ T cells (OR = 3.33) (Figure 2A-B). We further confirmed the expansions of these T cell phenotypes in the At-Risk individuals using our validation cohort with 57 At-Risk and 23 healthy individuals. In addition, we found that CD15+ classical monocytes were especially expanded in ACPA-negative At-Risk individuals who had FDR (p = 1e-3, OR = 1.30), and an activated PAX5low naïve B cell population expanded in ACPA-positive individuals who also had an FDR with RA (p = 9e-3, OR = 1.35). Further, we demonstrated that our “RA immunophenotype score” classification method built based on the degree of enrichment and the abundance of cell states relative to established RA (adjusted p < 0.05) (Figure 3A) is able to significantly distinguish At-Risk individuals from the control (p = 0.039, AUC >0.6) (Figure 3B-C).
Conclusion: We systematically characterized altered circulating immune phenotypes in At-Risk individuals, along with immunophenotypical differences among ACPA+ and FDR At-Risk subpopulations. Our classification model may provide a promising approach for understanding the pathogenesis of preclinical RA with the goal to develop preventive strategies and novel therapeutic targets.
References:
1. Zhang, F. et al. Cellular deconstruction of inflamed synovium defines diverse inflammatory phenotypes in rheumatoid arthritis. bioRxiv (2022) doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.25.481990
Disclosures: J. Inamo: None; J. Keegan: None; A. Griffith: None; T. Ghosh: None; A. Horisberger: None; K. Howard: None; J. Pulford: None; E. Murzin: None; B. Hancock: None; J. Seifert: None; M. Feser: None; J. Norri: None; A. Jonsson: None; Y. Cao: None; W. Apruzzese: Pfizer, 3; S. Bridges: None; V. Bykerk: AbbVie, 2, Bristol Myers Squibb, 1, 2, 5, Pfizer, 1, 2; S. Goodman: NIH, 5, Novartis, 5; L. Donlin: Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 2, Stryker, 2; G. Firestein: Eli Lilly, 5; H. Perlman: None; J. Bathon: None; L. Hughes: None; D. Tabechian: amgen, 12, share holder; A. Filer: Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 5, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 5, Janssen, 5, Nascient, 5, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, 2; C. Pitzalis: None; J. Anolik: None; L. Moreland: Boehringer-Ingelheim, 12, member of independent Data Safety Monitoring Board, Celltrion, 12, member of independent Data Safety Monitoring Board; J. Guthridge: None; J. James: Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 5, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 2, Novartis, 2, Progentec Biosciences, 5; M. Brenner: 4FO Ventures, 2, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 2, Mestag Therapeutics, 2, 8, Third Rock Ventures, 2; S. Raychaudhuri: AbbVie, 6, Janssen, 1, Mestag, Inc, 2, 8, Pfizer, 1, Sanofi, 1, Sonoma, 1, 8; J. Sparks: AbbVie, 2, Amgen, 2, Boehringer Ingelheim, 2, Bristol-Myers Squibb, 2, 5, Gilead, 2, Inova Diagnostics, 2, Janssen, 2, Optum, 2, Pfizer, 2, ReCor, 2; T. RA/SLE Network: None; M. Holer: None; K. Deane: Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 1, Gilead, 5, Janssen, 5, Werfen, 1, 12, Biomarker kits; J. Lederer: None; D. Rao: AstraZeneca, 2, Bristol-Myers Squibb, 2, 5, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 2, Hifibio, 2, Janssen, 5, Merck, 5, Scipher Medicine, 2; F. Zhang: None.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Inamo J, Keegan J, Griffith A, Ghosh T, Horisberger A, Howard K, Pulford J, Murzin E, Hancock B, Seifert J, Feser M, Norri J, Jonsson A, Cao Y, Apruzzese W, Bridges S, Bykerk V, Goodman S, Donlin L, Firestein G, Perlman H, Bathon J, Hughes L, Tabechian D, Filer A, Pitzalis C, Anolik J, Moreland L, Guthridge J, James J, Brenner M, Raychaudhuri S, Sparks J, RA/SLE Network T, Holer M, Deane K, Lederer J, Rao D, Zhang F. Deep Immunophenotyping Reveals Circulating Activated Lymphocytes in Individuals at Risk for Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/deep-immunophenotyping-reveals-circulating-activated-lymphocytes-in-individuals-at-risk-for-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/deep-immunophenotyping-reveals-circulating-activated-lymphocytes-in-individuals-at-risk-for-rheumatoid-arthritis/