Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Abstracts: B Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease I
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: CD19-targeting chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has proved potential for achieving long-term drug-free remission in patients with autoimmune diseases (AIDs). Its effectiveness likely stems from deep B cells depletion in tissues, although this effect has not been confirmed in humans in vivo.
Methods: We performed consecutive ultrasound-guided inguinal lymph node (LN) biopsies in 5 patients with AIDs (3 SLE and 2 SSc) before and after CD19-CAR T-cell therapy and compared them with inguinal LN biopsies from 5 patients (2 SSc and 3 granulomatosis with polyangiitis; GPA) collected after rituximab (RTX) treatment. All patients had no circulating B-cells at the time of the biopsy. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining was performed to quantify the number of B cells (CD19 and CD20), plasma cells (CD138), follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) (CD23), follicular T helper cells (TFH) (PD-1), proliferation fraction of germinal centre B cells (Ki67), T cells (CD3) and macrophages (CD68).
Results: The follow up biopsy in the CD19-CAR-T therapy group was performed 60.8 days ± 5.81 (mean ± SD) after infusion, whereas the mean biopsy time after RTX initiation was 98 days ± 45.63.
Patients receiving CD19-CAR T-cell therapy displayed younger age (34 years ± 10.2) and similar disease duration (43.2 months ± 23.43) as compared to the RTX-treated group (56.8 years ± 7.56), (44.4 months ± 50.31), respectively.
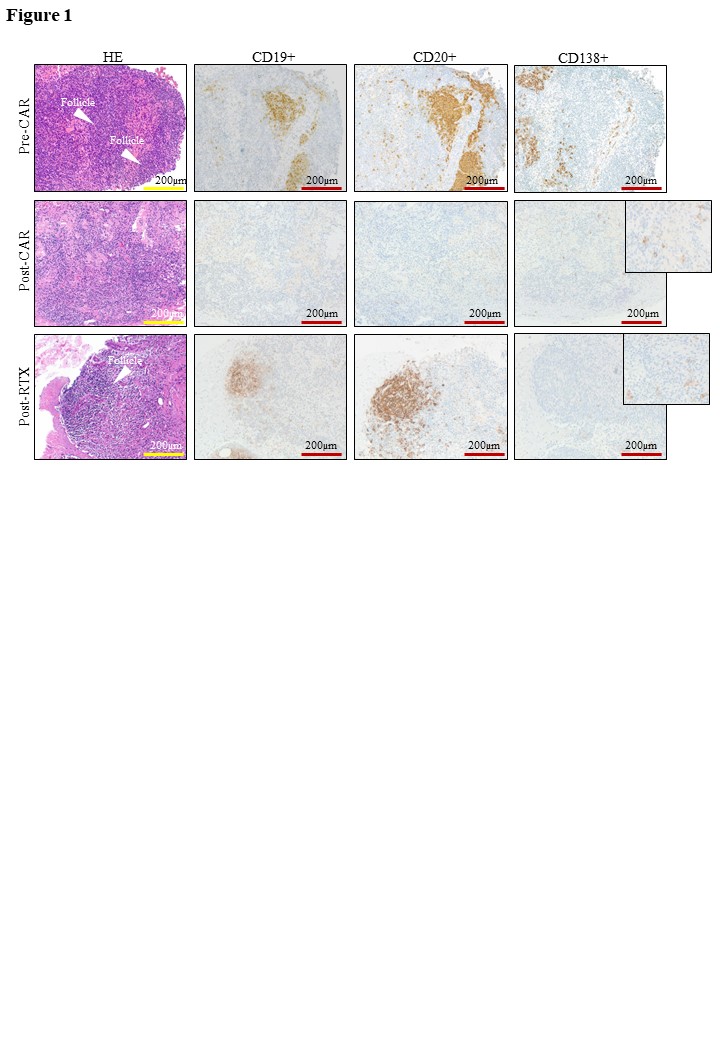
A complete depletion of CD19+ and CD20+ B cells occurred in the LNs of CD19-CAR T-cells treated patients (median [IQR] pre-treatment: CD19+ B cells: 656 cells/mm2 [361 – 922.5]; CD20+ B-cells: 1159 cells/mm2 [549 – 3771]; post-treatment: both CD19+ and CD20+ cells = 0 cells/mm2 [0-0]) (Figure 1). No such depletion was achieved in the inguinal LNs of patients after RTX treatment, showing persistence of both CD19+ and CD20+ B cells (196 cells/mm2 [59.5 – 1032]; 1443 [201.5 – 2659], respectively). CD138+ plasma cells were not affected after CD19-CAR T-cell therapy (P =0.625) or after RTX (P = 0.206).
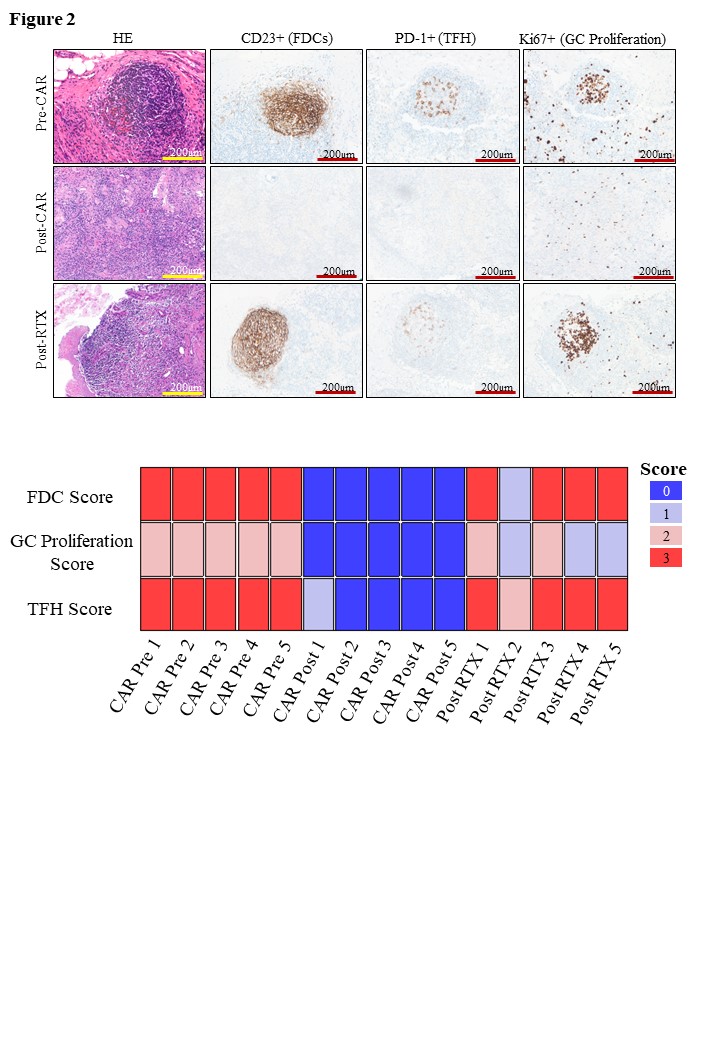
Changes in the B follicular structure were assessed through FDCs, TFH cells and follicle proliferation rate quantification and a comprehensive B-cell compartment architecture score was developed (Figure 2). In RTX-treated patients, the FDC network and the presence of TFH cells were mostly unaltered, accompanied by regular ( > 90%) or slightly reduced germinal centre proliferation rates. In contrast, while regularly configured in pre-CAR T-cell state (B-cell compartment score 14 [14 – 14]), the B-cell maturation compartment was completely abolished after CD19-CAR T-cell treatment including disappearance of FDC networks and TFH cells as well as decrease (< 90%) of proliferation rate (B-cell compartment score 0 [0 - 0.5]).
Distribution of T cells and macrophages in the extra-follicle areas remained stable after CD19-CAR T-cell therapy and no difference in macrophages was found between CD19-CAR T-cell therapy and RTX-treated patients (P > 0.999).
Conclusion: This study demonstrates for the first time that the CD19-CAR T-cell therapy induces a complete B-cell depletion in secondary lymphoid tissues of AID patients and highlights the importance of tissue analysis after B-cell depleting therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tur C, Eckstein M, Joachim V, Bergmann C, Auth J, Bucci L, Corte G, Hagen M, Wirsching A, Grieshaber-Bouyer R, Reis P, Kittan N, Wacker J, Rauber S, Rigau A, Ramming A, D'Agostino M, Hartmann A, Müller F, MAckensen A, Bozec A, Schett G, Raimondo M. Deep B Cell Tissue Depletion Following Anti-CD19 CART Cells Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/deep-b-cell-tissue-depletion-following-anti-cd19-cart-cells-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/deep-b-cell-tissue-depletion-following-anti-cd19-cart-cells-therapy/