Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II: Diagnosis and Prognosis
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Near infrared (NIR) imaging studies of subdermal indocyanine green (ICG) in murine models of inflammatory arthritis established abnormal lymphatic vessel (LV) function during arthritic progression. Quantitatively, this LV dysfunction is primarily assessed by ICG clearance from the injection site via longitudinal (days) NIR imaging. As the role of LV function in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) pathogenesis is unknown, we tested the hypothesis that ICG clearance from the hands of RA patients experiencing flare is significantly decreased from that of normal healthy volunteers.
Methods: The web spaces of both hands of 8 healthy controls (Ctl) and 4 subjects in RA flare were injected with 0.1ml of 100μM ICG on 2-4 separate occasions and the NIR fluorescence of the dorsal aspect of the hands were imaged. To measure clearance of ICG from the web spaces, a subset of 3 Ctl and 3 RA subjects returned to the clinic 8-15 days after the first injections and any remaining NIR fluorescence in each hand was measured via region of interest analysis (n=6 per group, Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test). Controlling for the number of days between subjects, the change in intensity between the initial and second visit was divided by the number of days between visits. To assess the branching structure of the vessels, two independent graders quantified the total number of bifurcations of the LVs. Median values for each hand across all visits and graders were used to test for differences (n=13 Ctl, n=8 RA, Wilcoxon Rank-Sum Test).
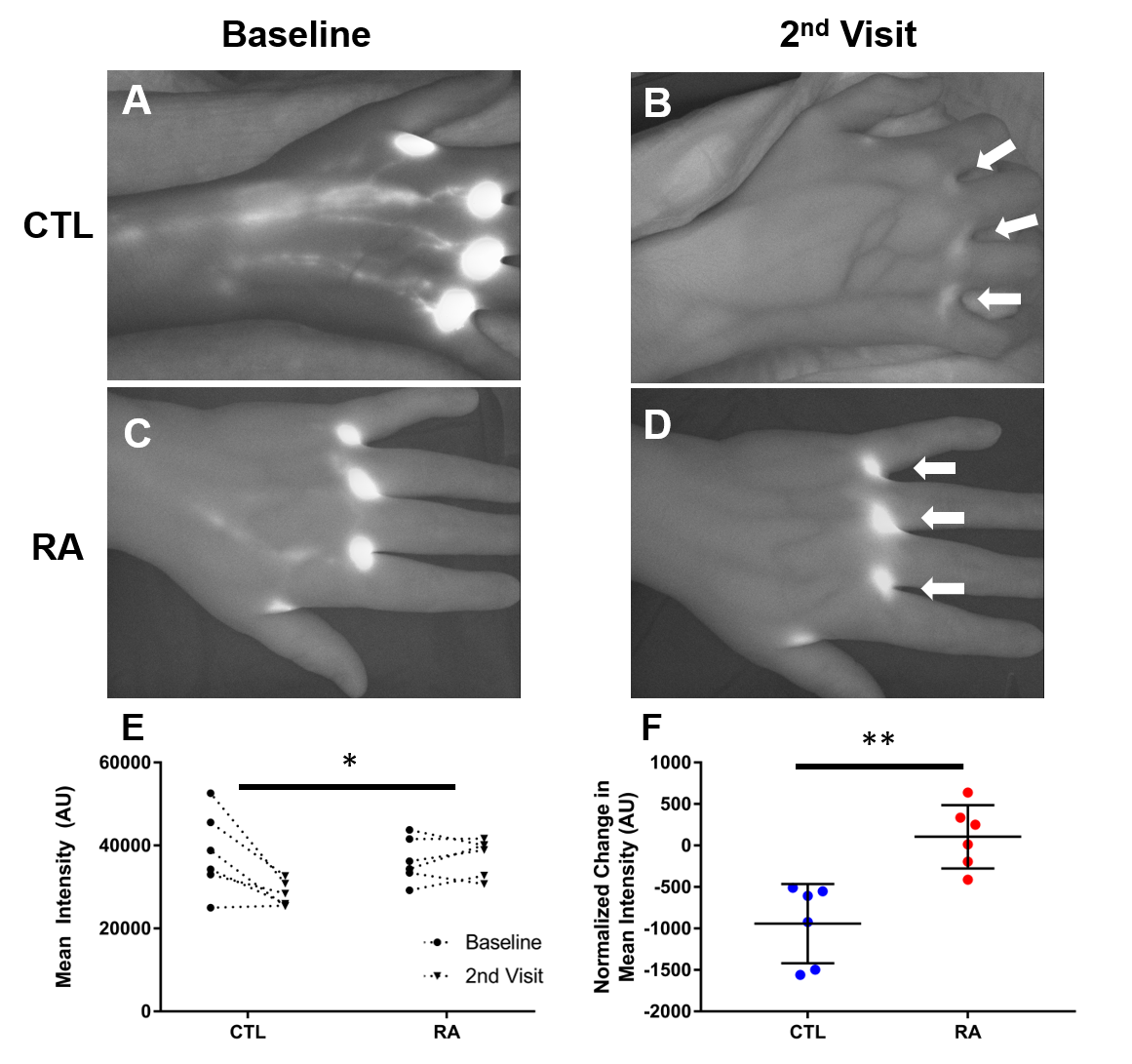
Results: Representative NIR images of Ctl and RA hands at baseline and at the second visit are presented in Fig 1A-D, demonstrating the dramatic retention of ICG at the injections sites (White Arrows) in RA subjects. Statistical analysis revealed a decrease in ICG clearance in the RA subjects compared to Ctls (Fig 1E, *p<0.05). When controlling for days between the initial visit and second visit the relationship holds (Fig 1F, **p<0.01). Interestingly, no differences were observed in bifurcation counts between RA and Ctl (p=0.11).
Conclusion: Imaging outcome measures of LV function in mice demonstrated diminished clearance of lymph from the inflamed joint during arthritic progression and we recently described functional and anatomic differences in the hands of RA subjects in joint flare compared to controls. Herein, we expand upon these findings by demonstrating a significant reduction in ICG clearance in RA patients during flare. Surprisingly, there was no difference in the bifurcations of LVs, however, this is likely due to relatively small sample size or differences in clinical characteristic in our cohort. The accumulation and retention of inflammatory cells and molecules in rheumatoid joints as a result of diminished lymphatic clearance likely triggers synovitis. This clinical pilot demonstrates the feasibility of quantifying LV function, and warrants formal investigation in clinical trials
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bell R, Rahimi H, Lieberman A, Wood R, Schwarz E, Ritchlin CT. Decreased Lymphatic Drainage in the Hands of Flaring RA Patients As Measured By Indocyanine Green Clearance Via Real Time Near Infrared Imaging [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/decreased-lymphatic-drainage-in-the-hands-of-flaring-ra-patients-as-measured-by-indocyanine-green-clearance-via-real-time-near-infrared-imaging/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/decreased-lymphatic-drainage-in-the-hands-of-flaring-ra-patients-as-measured-by-indocyanine-green-clearance-via-real-time-near-infrared-imaging/