Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The 2020 ACR Guideline for the Management of Gout conditionally recommends testing for the HLA-B*5801 risk allele prior to starting allopurinol for patients of Southeast Asian descent (Han Chinese, Korean, Thai) and African American patients. Patients with this allele have a substantially increased risk of developing severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs) with drug initiation; testing in high-risk populations is cost-effective. Despite this, less than 5% of eligible high-risk patients had been screened by primary care providers prior to initiating urate-lowering therapy (ULT) at our facility. Working with an interprofessional team of pharmacists and physicians, we aimed to improve appropriate HLA-B*5801 screening rates in patients starting ULT in the primary care setting.
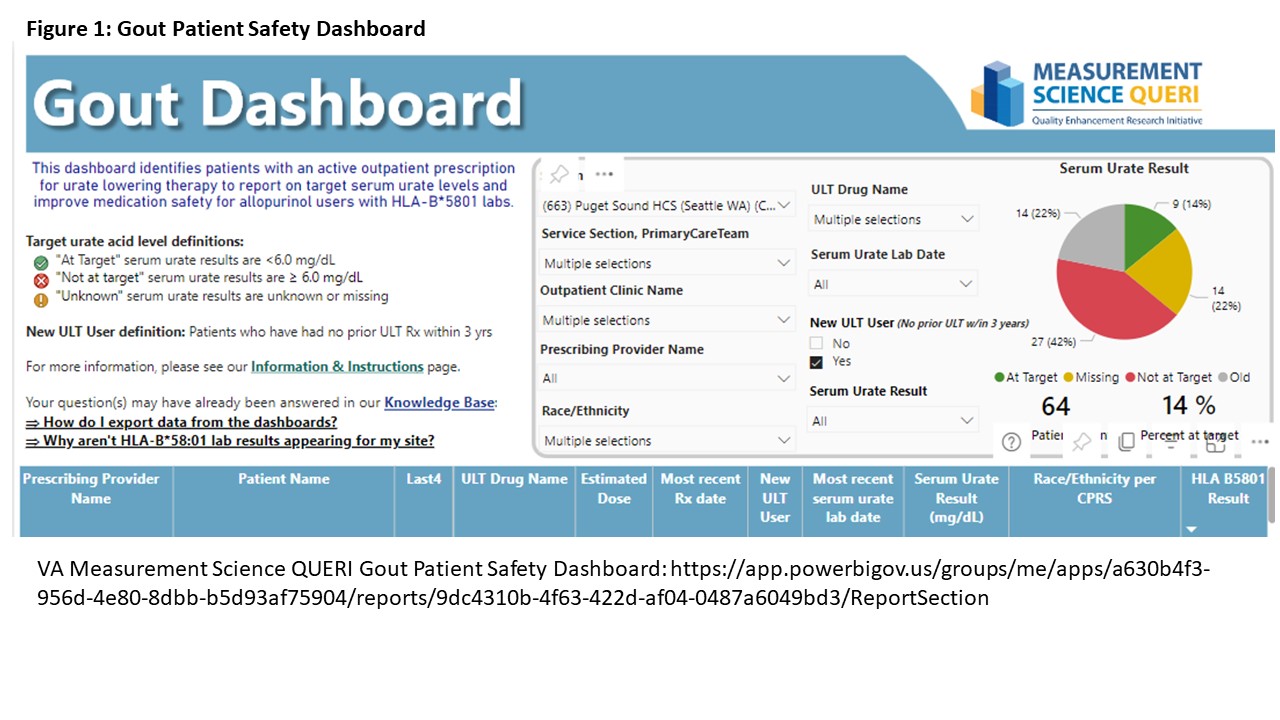
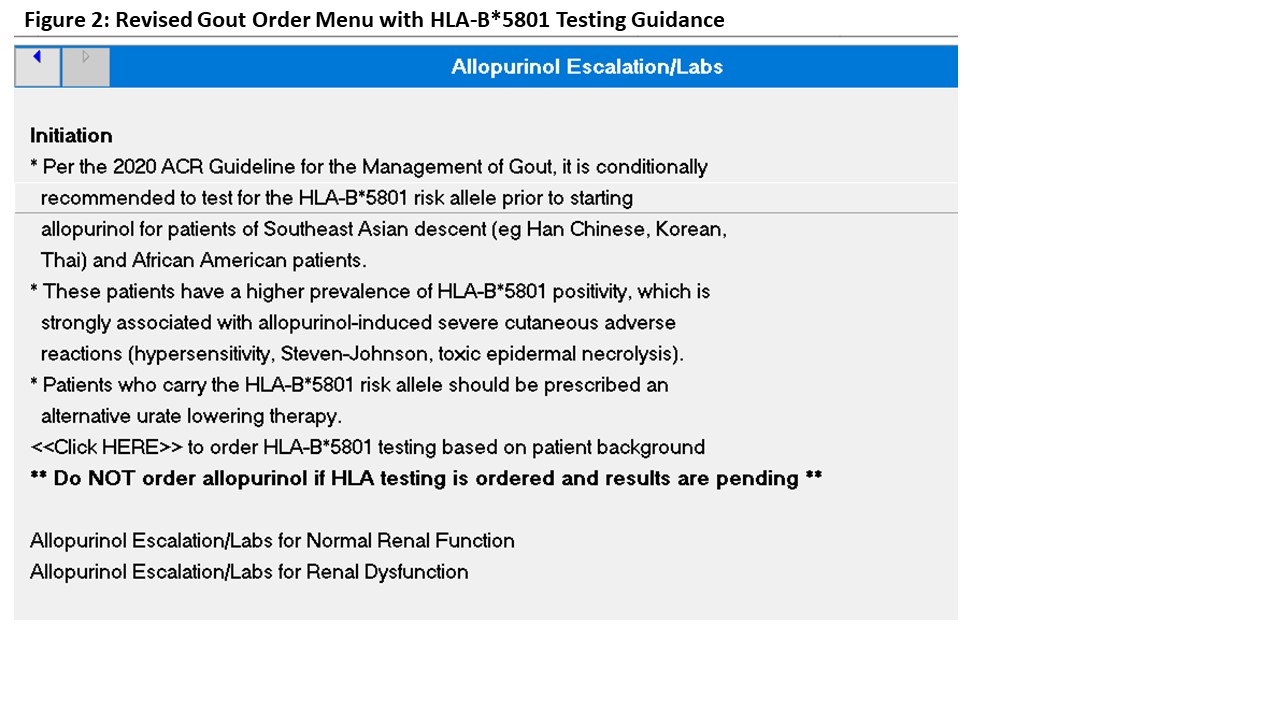
Methods: The Veterans Affairs (VA) Measurement Science Quality Enhancement Research Initiative (QUERI) Gout Medication Safety Dashboard identifies patients on ULT at each VA. This site identifies patients with HLA-B*5801 testing and allows stratification by self-reported race/ethnicity and provider location (figure 1). The dashboard was used to identify Asian/African American patients screened for the HLA-B*5801 risk allele prior to ULT initiation by primary care between 9/2020 and 9/2023. High risk patients starting alternative ULT (febuxostat or probenecid) were reviewed for documented allopurinol SCARs. HLA-B*5801 carriers were assessed for whether they received appropriate alternative ULT. Multidisciplinary meetings between Primary Care, Pharmacy, and Rheumatology were held between October 2023 and January 2024 to develop a revised gout order menu, which was released in February 2024 (figure 2). Order set changes and rationale were communicated at a Primary Care Monthly provider meeting that month, followed by a formal pharmacy communication summarizing the change. Post-intervention data on HLA-B*5801 screening was collected in April 2024. As a balancing measure, Rheumatology providers monitored consultation requests for questions about the menu revision.
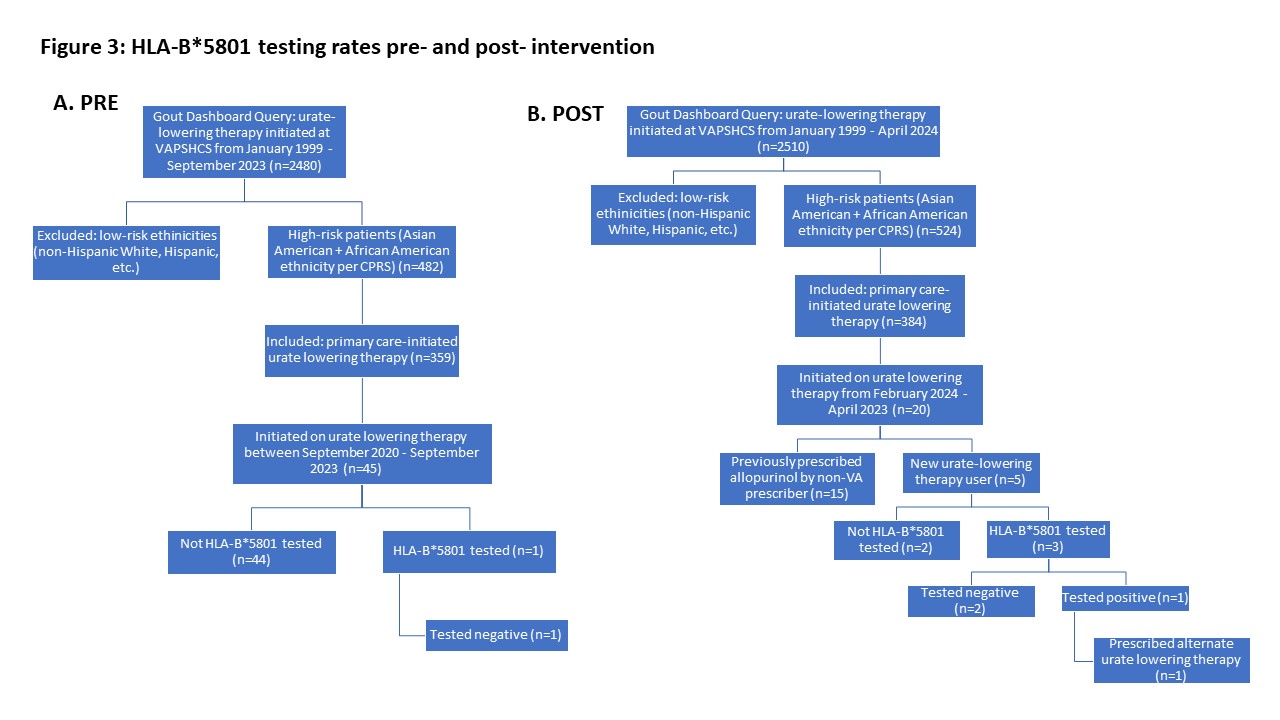
Results: Between September 2020 – September 2023, 45 high-risk patients were initiated on urate lowering therapy; one patient (2.2%) had HLA-B*5801 testing. Two out of 15 (13.3%) patients on alternative ULT reported past SCARs; all HLA-B*5801 carriers identified during this time appropriately received alternative ULT. After the order set revision, 5 Asian/African American patients were identified as new urate lowering therapy users, and 3 out of 5 (60%) eligible patients had HLA-B*5801 screening. Of the patients tested, only 1 patient was found to be an HLA-B*5801 carrier and was prescribed an alternative urate-lowering therapy (figure 3). Rheumatology did not report any questions about the menu revision.
Conclusion: Utilization of a widely available medication safety dashboard facilitated identification of gout patients at high risk of SCAR. A collaborative process revision of ULT order sets coupled with provider education led to a substantial increase in HLA-B*5801 screening and treatment in high-risk gout patients in primary care. Continued monitoring of this population will be essential to ensure these gains are sustained.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vo C, Nguyen C, Hagan S, Aalami S, Wahl E. Dashboard Utilization and Order Menu Revision Improve HLA-B*5801 Testing Prior to Allopurinol Initiation in High-Risk Patients in a Veteran-based Primary Care Setting [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dashboard-utilization-and-order-menu-revision-improve-hla-b5801-testing-prior-to-allopurinol-initiation-in-high-risk-patients-in-a-veteran-based-primary-care-setting/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dashboard-utilization-and-order-menu-revision-improve-hla-b5801-testing-prior-to-allopurinol-initiation-in-high-risk-patients-in-a-veteran-based-primary-care-setting/