Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Spondylarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis - Pathogenesis, Etiology Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA), an inflammatory musculoskeletal disease, develops in
approximately 30% of patients with psoriasis. We previously identified C-X-C
motif chemokine 10 (CXCL10) as a predictive biomarker of PsA in patients with psoriasis.
This study explores the expression of CXCL10 in the joint of PsA patients.
Methods: Synovial
fluid (SF) was obtained from patients with PsA, osteoarthritis (OA) and gout
undergoing routine joint aspirations. PsA patients with paired SF and serum
samples were identified from the cohort of patients followed prospectively. The
expression of CXCL10, TNFα, IL-17A and IFNγ were measured using the
Milliplex MAP human chemokine/cytokine magnetic bead panel (EMD Millipore),
according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Data was acquired using the
Luminex 200 system and analyzed with the Bio-Plex Manager software (Bio-Rad
Laboratories). Statistical differences in protein levels between groups were identified
by Wilcoxon signed rank test for paired samples and by Wilcoxon rank sum test
for comparison between PsA patients and controls (p<0.05 was accepted as significant).
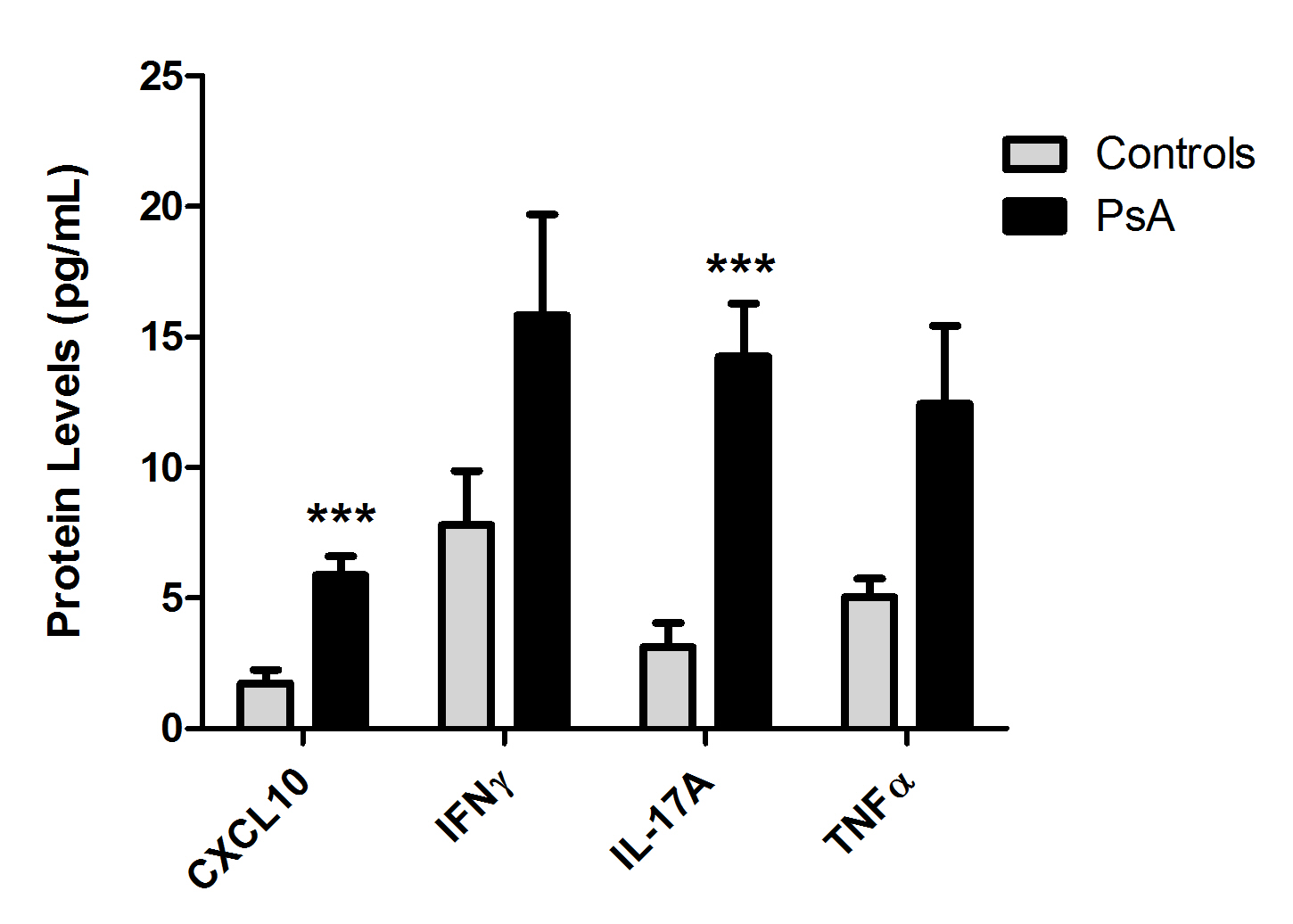
Results: Cytokine
and chemokine expression was measured in SF from 40 patients with PsA and 17
controls (OA and gout). CXCL10 (5.87 ± 4.53 vs. 1.73 ± 2.08 ng/ml, p=4.6×10-5)
and IL-17A (14.3 ± 11.6 vs. 3.13 ± 3.1 pg/ml, p=0.0001) were significantly elevated
in PsA patients compared to controls (Figure 1). In paired samples from 11 PsA
patients (mean age 43 years, 91% males, psoriasis duration 17 years, PsA
duration 11 years, PASI 7.7, tender joint count 2, swollen joint count 2),
CXCL10 was significantly (p=0.001) increased in SF (6.3 ± 4.3 ng/ml) compared
to serum (0.4 ± 0.3 ng/ml) while both TNFα (53.7 ± 68.0 vs. 9.0 ± 6.5
pg/ml, p=0.001) and IFNγ (154.3 ± 318.6 vs. 16.3 ± 24.3 pg/ml, p=0.01)
were significantly reduced. Additionally, we
measured the change in CXCL10, TNFα, IL-17A and IFNγ in SF from 15
PsA patients after follow-up, however no significant differences were found.
Conclusion: This
study confirms previous reports of elevated synovial CXCL10 and IL-17A in
PsA patients. The differences in SF and serum levels of CXCL10, TNFα and IFNγ
that were observed may be important in the pathogenesis of PsA.
Figure 1:
Histogram of CXCL10, IFNγ, IL-17A and TNFα expression in SF from 40
PsA patients and 17 controls (OA and gout). ***indicates a significant
difference compared to controls. CXCL10 concentration was converted to ng/ml.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Muntyanu A, Abji F, Liang K, Chandran V, Gladman D. CXCL10 Expression Is Elevated in Synovial Fluid of Psoriatic Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cxcl10-expression-is-elevated-in-synovial-fluid-of-psoriatic-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cxcl10-expression-is-elevated-in-synovial-fluid-of-psoriatic-arthritis-patients/