Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1221–1255) Pediatric Rheumatology – Clinical Poster II: Connective Tissue Disease
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Juvenile lupus (JSLE) and dermatomyositis (JDM) patients are at high risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD). The American Heart Association cardiovascular health (CVH) construct is the sum of protective factors against CVD. JSLE/JDM patients are at risk of premature loss of CVH that may increase lifetime risk for CVD. Emotional distress is often elevated in JSLE/JDM patients and may be a modifiable factor that adversely impacts CVH in this population. We hypothesize that emotional distress is associated with worse CVH in JSLE/JDM.
Methods: JSLE/JDM patients (5-22yo) were enrolled at Duke and UNC Children’s Hospitals. PROMIS® Pediatric (self-report) and/or Parent-Proxy measures of emotional distress were administered, including Psychological Stress Experiences, Depressive Symptoms, and Anxiety (PROMIS-Str/-Depr/-Anx). CVH indicators included CVH Behaviors (diet quality screener; PROMIS Physical Activity) and CVH Factors (body mass index, blood pressure, non-HDL cholesterol, HbA1c). CVH Summary (CVH-S, all 6 indicators), Behaviors (CVH-B) and Factors (CVH-F) scores were derived (range 0-100, higher scores indicate better CVH). Spearman’s correlations between PROMIS emotional distress measures and CVH scores were calculated for the overall cohort and for subgroups (race/ethnicity, age, diagnosis, gender, steroid use). Rank sum tests compared median CVH scores between patients with minimal vs moderate/severe emotional distress in the overall cohort. Rank sum tests also compared median CVH scores by subgroup among patients with moderate/severe emotional distress. Minimal vs moderate/severe emotional distress groups were based on published PROMIS T-score cutoffs. Variation of the association of PROMIS-Str/-Depr/-Anx with CVH by subgroups was assessed via interactions in regression models.
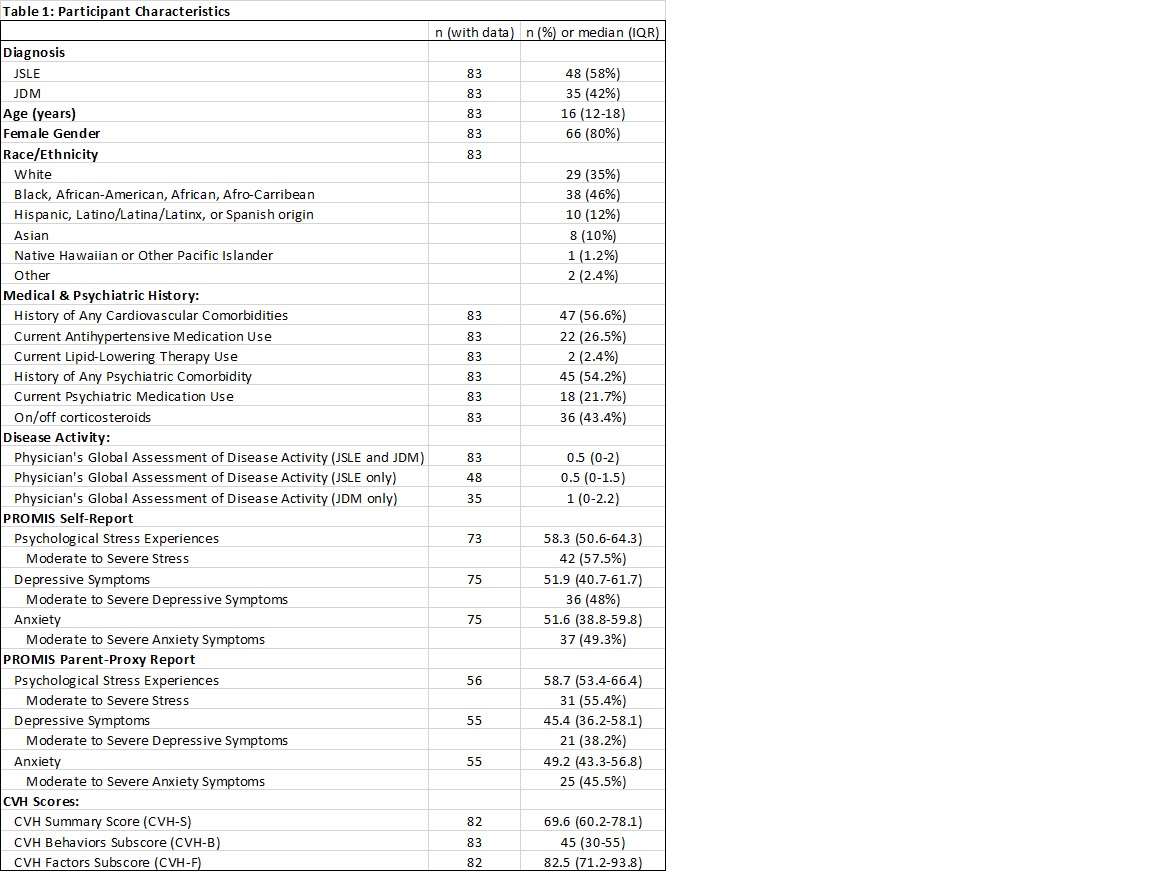
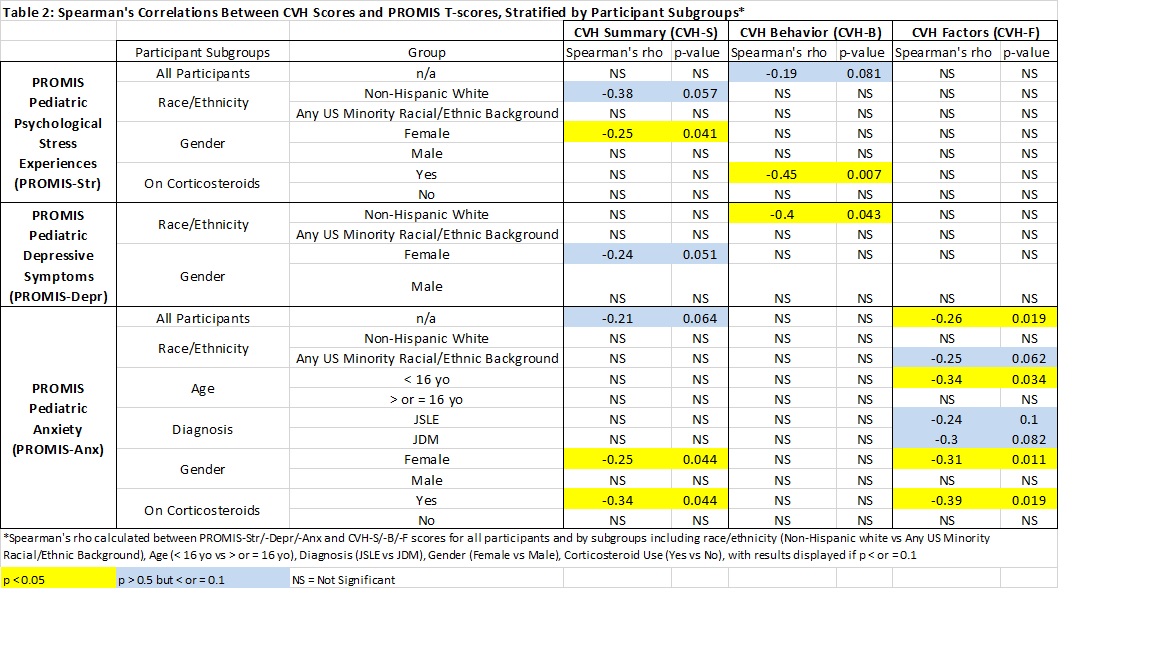
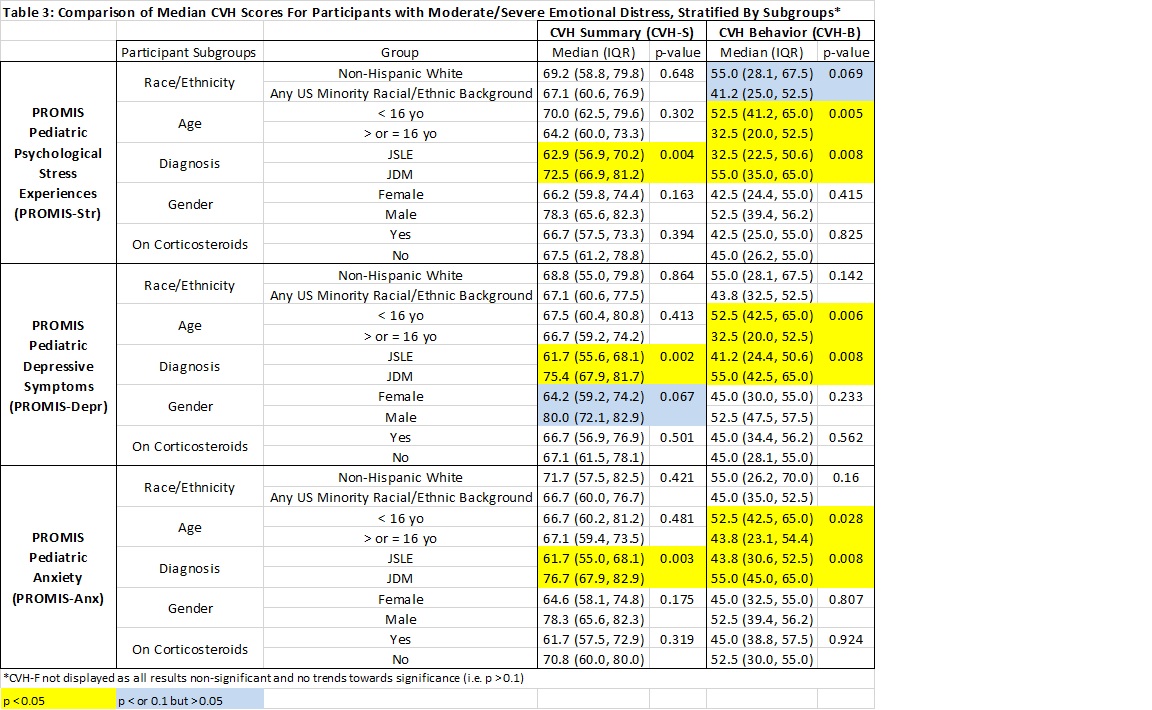
Results: Data were analyzed for 83 patients (Table 1). In the overall cohort, PROMIS-Anx modestly correlated with CVH-F (rho -0.26, p = 0.019) (Table 2) and patients with moderate/severe PROMIS-Anx scores had worse median CVH-F than those with minimal PROMIS-Anx (90 vs 77.5, p = 0.011). CVH-B scores were most strongly related to PROMIS-Str scores in patients on steroids relative to those who were not, and with PROMIS-Depr scores in non-Hispanic White relative to minority race/ethnicity patients (Table 2). Among patients with moderate/severe emotional distress, CVH-S/-B scores were lower in JSLE vs JDM patients and CVH-B scores were lower in older (≥16yo) vs younger (< 16yo) JSLE/JDM patients (Table 3). Interactions indicated JSLE diagnosis and non-Hispanic White race/ethnicity were associated with stronger inverse relationships between PROMIS-Depr scores and CVH-S (p = 0.043) and CVH-B (p = 0.017) respectively.
Conclusion: Moderate/severe emotional distress is associated with worse CVH, driven by lower CVH-B, in JSLE as well as ≥16yo JSLE/JDM patients. We also noted differences by race/ethnicity in the association of emotional distress with CVH-B. Future analyses will identify social determinants of health and clinical features that influence associations of emotional distress with CVH in JSLE/JDM patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ardalan K, Davalos A, Hong H, Reeve B, Hornik C, Moody M, Lloyd-Jones D, Wu E, Ward A, Sadun R, Dvergsten J, Reed A, Connelly M, Schanberg L. Cross-Sectional Associations of Emotional Distress and Cardiovascular Health in Juvenile Lupus and Dermatomyositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cross-sectional-associations-of-emotional-distress-and-cardiovascular-health-in-juvenile-lupus-and-dermatomyositis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cross-sectional-associations-of-emotional-distress-and-cardiovascular-health-in-juvenile-lupus-and-dermatomyositis/