Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: 3S105: Osteoarthritis & Joint Biology – Basic Science (886–891)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: The efferent vagus nerve can regulate inflammation via its principal neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh), a concept referred as the ‘cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway’. ACh interacts with members of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (Chrna) family, in particular with the alpha7 subunit (Chrna7), which is expressed not only by neurons but also by other cells involved in inflammation.
We aimed to decipher the roles of the non-neuronal and neuronal cholinergic systems in osteoarthritis (OA).
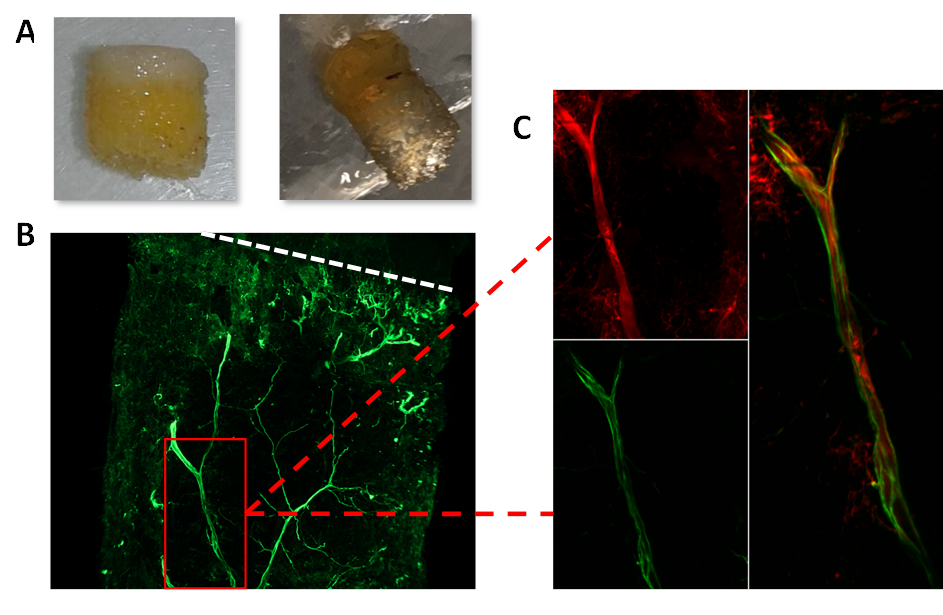
Methods: To explore the presence of neuronal cholinergic fibers in the joints, we used a whole joint immunolabeling protocol after 3Disco clearing. We evaluated the coexpression of peripherin (nerve marker) and choline acetyltransferase (cholinergic marker) in human bone-cartilage samples, from OA patients undergoing knee arthroplasty.
To explore the role of the non-neuronal cholinergic pathway, primary cultures of human OA chondrocytes and of WT and KO Chrna7-/- murine osteoblasts (OB) and chondrocytes were performed. The expressions of the molecular partners of Ach metabolism and of the cholinergic nicotinic receptors were assessed. In vitro, WT and Chrna7-/- chondrocytes and OB were treated with IL1b for 24h. In order to study the role of nicotinic receptors in cell activation, chondrocytes and OB were pretreated with nicotine at 1; 10 or 100 μM. We quantified the production of interleukin-6 (IL6) and metalloproteinase (MMP) along with RANK-ligand for OB by ELISA.
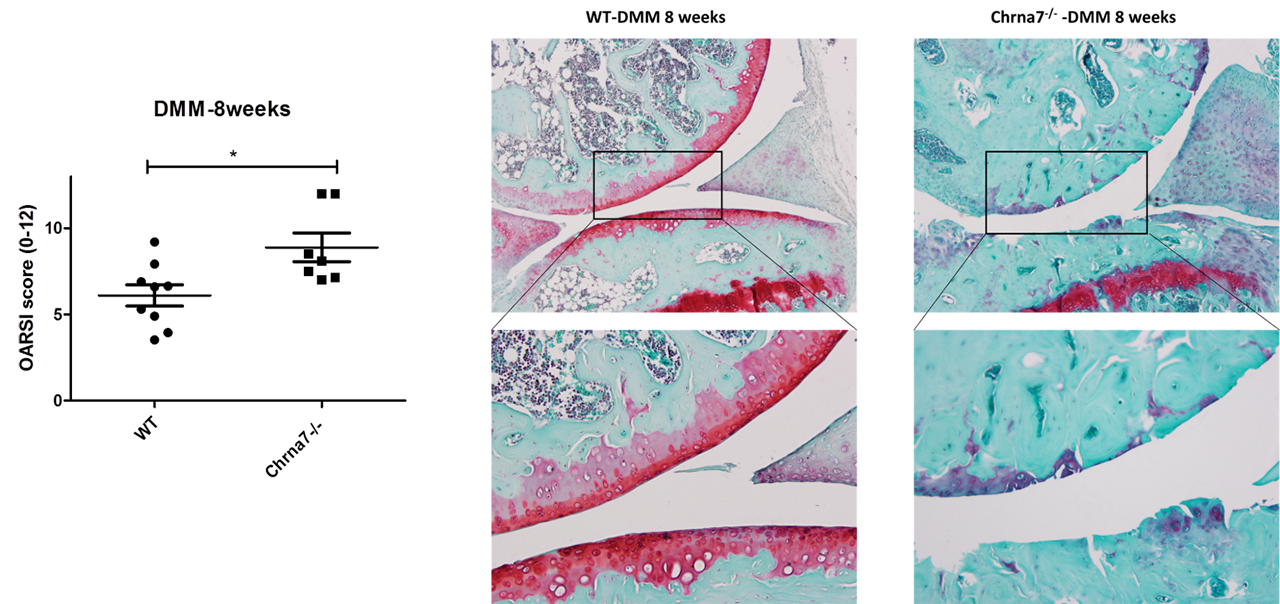
To induce OA, medial meniscus destabilization (DMM) of the knee was performed on 12-week-old WT and Chrna7 – / – mice and histological OARSI scoring was compared after 8 weeks between both genotypes.
Results: Cholinergic fibers were present in subchondral bone of all 3 OA joints explants analyzed coming from 3 different patients (Fig 1). Human OA and murine chondrocytes as well as murine OB express the whole machinery needed for the synthesis, transport and degradation of Ach. All these cells express nicotinic subunits a 4, 5, 6, 7 and β4. IL1β stimulation induced a significant increased production of IL6 and MMPs by WT and Chrna7-/- chondrocytes. Nicotine pretreatment counteracted this effect (decrease of 65% for IL6, 64% for MMP3 with nicotine 10µM, n=5; p< 0.05). Conversely to what happened in WT, nicotine had no effect on Chrna7-/- chondrocytes supporting a predominant role of this receptor in chondrocyte activation. In OB, stimulation of nicotinic receptors decreased the production of IL6, MMP3 and RANK-L induced by IL1β in the same manner in WT and Chrna7-/- OB, meaning that other subunits than a7 are involved in OB activation. After DMM, Chrna7 -/- mice displayed significantly more OA lesions than their WT counterparts with a mean±SD OARSI score of 8.9±0.82 for Chrna7 -/- and 6.1±0.6 for WT (Fig 2).
Conclusion: Neuronal and non-neuronal cholinergic systems are present in murine and human joints. The activation of nicotinic receptors displays anti-inflammatory, anti-catabolic and antiresorptive properties on bone and cartilage. In chondrocytes this protective effect is mediated by the Chrna7 suggesting that activating the cholinergic system could be a new therapeutic target in OA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Courties A, Do A, Leite S, Pigenet A, Belle M, Nourissat G, Sautet A, Chedotal A, Maskos U, Berenbaum F, Sellam J. Critical Role of the Cholinergic System Involvement in Osteoarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/critical-role-of-the-cholinergic-system-involvement-in-osteoarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/critical-role-of-the-cholinergic-system-involvement-in-osteoarthritis/