Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0380–0422) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases on immunosuppressive medications are presumed to be at increased risk for hospital admissions and deaths related to COVID-19 infections. The aim of this study was to better characterize seroconversion response to the third dose of COVID-19 vaccine in patients with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis (RA) on various immunosuppressive therapy classes.
Methods: A prospective cohort study recruited patients with RA on immunosuppressive treatment (n=48) to evaluate immune response to the third COVID-19 vaccine compared to the general population (n=164). Patients with RA in the study group were further characterized into three categories based on their active treatment. These groups were patients on either synthetic DMARD alone, DMARD with biologic, or biologic only. Patients received their third dose of the COVID-19 vaccine of either BNT162b2 (Pfizer) or CX-04414 (Moderna). Serum IgG antibody titers to Anti-S1 spike protein were collected in three different time frames, 4-8 weeks post-immunization (phase 1), 12-16 weeks post-immunization (phase 2), and 24-28 weeks post-immunization (phase 3). Seroconversion was defined as antibody titers above 1500 U/ml. 5 patients were lost in follow-up in the treatment group along with 79 in the control group over course of the study. Sample matching analysis was used to better compare the control and study groups.
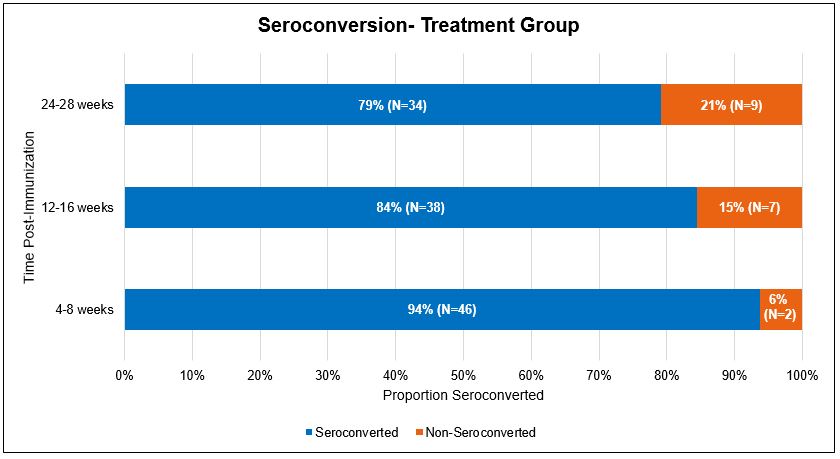
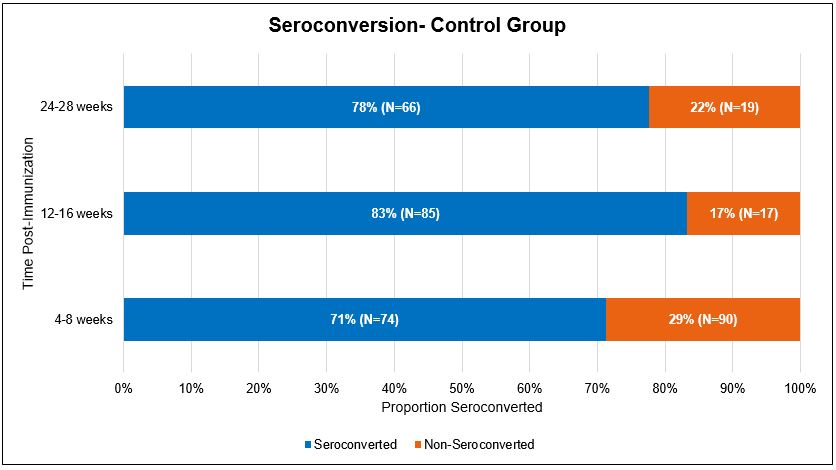
Results: In our treatment group, 94% (n=46) of patients seroconverted in phase 1, 84% (n=38) in phase 2, and 79% (n=34) in phase 3. In the control group, 71% (n=74) of patients seroconverted in phase 1, 83% (n=85) in phase 2, and 78% (n=66) in phase 3. After sample matching analysis, patients in the treatment group showed higher rates of seroconversion compared to the control group during phase 1 (p = 0.01). A decrease in seroconversion rates over time was observed in both groups. When evaluating patients on different classes of RA medications, patients on synthetic DMARDs with biologics showed lower rates of seroconversion than the other groups. All therapy classes showed decreased seroconversion rates over time.
Conclusion: Our study revealed that patients with RA demonstrated an adequate response to COVID vaccination despite being on immunosuppressive therapies. Immunogenicity decreases over time after the third COVID-19 vaccine in both immunocompromised and general populations as well as across therapy classes. Patients with RA on immunosuppressive therapies still show adequate levels of seroconversion in the early phase (phase 1) similar to the control group.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kovuru K, Waz S, Malik A. COVID Antibody Response to Third Dose Anti-SARS-COV2 mRNA Vaccine in Patients with Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis on Immunosuppressive Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/covid-antibody-response-to-third-dose-anti-sars-cov2-mrna-vaccine-in-patients-with-seropositive-rheumatoid-arthritis-on-immunosuppressive-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/covid-antibody-response-to-third-dose-anti-sars-cov2-mrna-vaccine-in-patients-with-seropositive-rheumatoid-arthritis-on-immunosuppressive-therapy/