Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: COVID-19 vaccines are safe and effective, though patients with rare rheumatic diseases like idiopathic inflammatory myositis (IIMs), and those with multiple comorbidities continue to be hesitant in taking the vaccine. Adverse events (AEs) after vaccination are not extensively studied in those with multiple coexisting autoimmune diseases. Patients with IIM often have multiple autoimmune rheumatic and autoimmune non-rheumatic comorbidities (IIM-AIDs), with potentially increased risk of AEs. The COVAD study aimed to assess COVID-19 vaccination-related adverse events (AEs) till seven days post-vaccination in IIM-AIDs compared to IIMs and healthy controls (HCs) group.
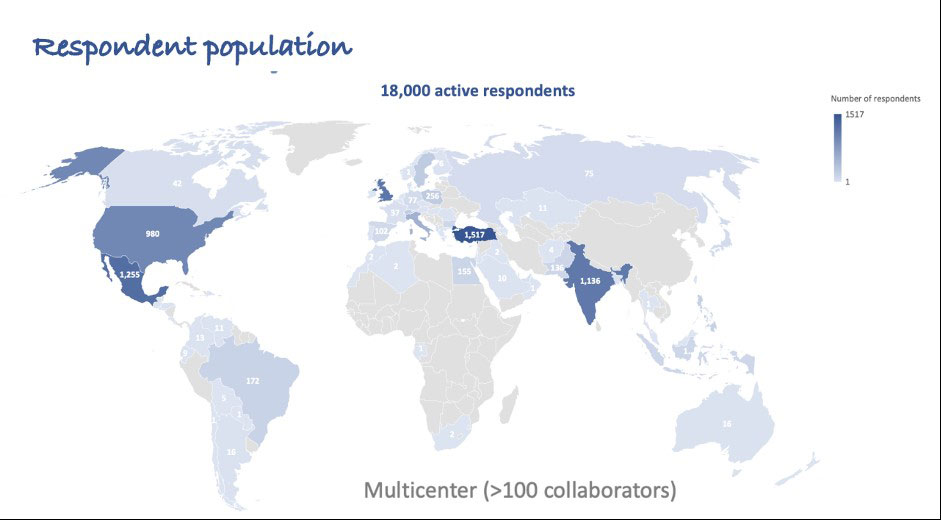
Methods: The COVAD study group comprised >110 collaborators across 94 countries. The study was conducted from March-December 2021. A survey monkey platform-based self-reported online survey captured data related to COVID-19 vaccination-related AEs in IIMs, AIDs, and HCs. IIM-AIDs patients comprised rheumatic AIDs like overlap syndromes, vasculitis, etc and non-rheumatic AIDs like inflammatory bowel disease, multiple sclerosis, hypothyroidism etc. We compared COVID-19 vaccination-related AEs among IIM-AID patients and IIM alone and HCs, adjusting for age, gender, ethnicity, COVID-19 vaccine type, immunosuppression received, and the numbers of AIDs, using binary logistic regression. Statistically significant results following multivariate regression are reported.
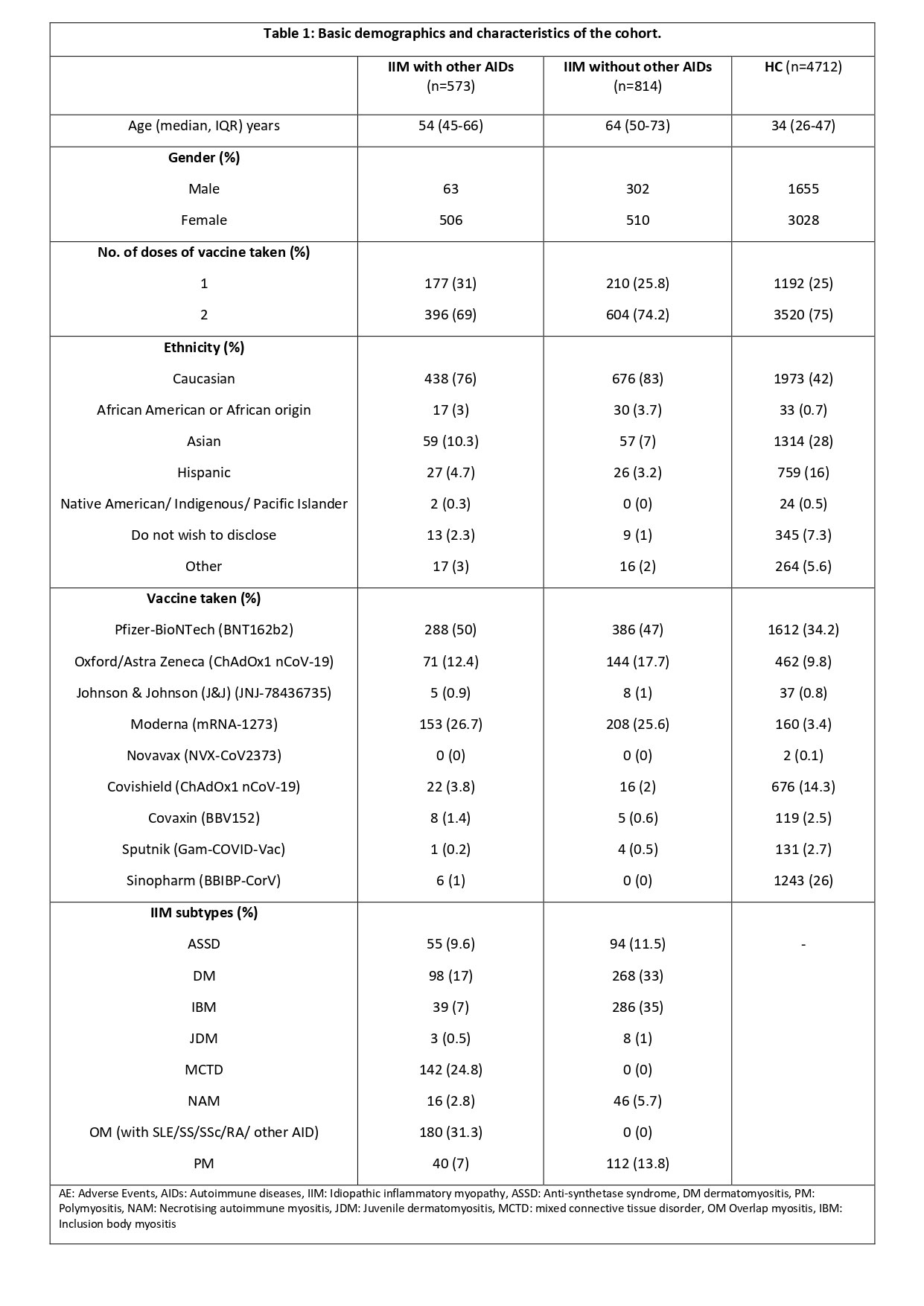
Results: Among 6099 participants, 1387 (22.7%) IIM, 4712 (77.2%) HC, 66.3% females, were included from a total of 18,882 respondents: 573 (41.0%) people with IIM-AIDs; 814 (59.0%) with IIM without other AIDs; and 4712 HCs (Figure 1). People with IIM were older [median age 54 (45-66) IIM-AIDs, 64 (50-73) IIM, 34 (26-47) HC years, p< 0.001]. BNT162b2 (Pfizer)(37.5%) and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (Oxford) (11.1%) were the most common vaccines received.
When compared to IIM alone patients, IIM-AID patients reported higher overall AEs [OR 1.5 (1.1-2.1)], minor AE [OR 1.5 (1.1-2.1)] and major AE [OR 3 (1.5-5.8)]. IIM-AIDs patients also reported higher body ache, nausea, headache, and fatigue (OR ranging 1.3-2.3, Table 2). After adjusting for the number of AIDs, the major AEs equalized but overall AEs, and minor AEs, such as fatigue remained higher in IIM-AIDs (Table 2).
When compared to HCs, IIM-AIDs patients reported similar overall AEs, minor AEs but higher major AEs [OR 2 (1.2-3.3)] nausea/vomiting [OR 1.4 (1.01-2)], headache [OR 1.2 (1.01-1.6)], and fatigue [OR 1.3 (1.03-1.6)].
Dermatomyositis (DM) patients with AIDs (n=183) reported higher major AEs [OR 4.3 (1.5-12)] compared to DM alone (n=293).
Active IIM with AIDs (n=482) reported higher overall AEs [OR 1.5 (1.1-2.2)], minor AEs [OR 1.5 (1.1-2.2)] and major AEs [OR 2.6 (1.2-5.2)] compared to active IIM alone (n=643).>
Conclusion: COVID-19 vaccination is safe with minimal to no risks of short-term AEs in patients with IIM without other concomitant autoimmune diseases. The presence of autoimmune multimorbidity conferred higher self-reported short-term risks of overall, major, and minor COVID-19 vaccination-related AEs seven days post-vaccination in IIM patients, particularly in those with active IIM.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dey M, R N, Nikiphorou E, Sen P, Lilleker J, Agarwal V, Kardes S, Day J, Milchert M, Joshi M, Gheita T, Salim B, Velikova T, Gracia-Ramos A, Parodis I, O’Callaghan A, Kim M, Chatterjee T, Tan A, Makol A, Nune A, Cavagna L, Saavedra Salinas M, Shinjo S, Ziade N, Knitza J, Kuwana M, Distler O, Chinoy H, Pauling J, Wincup C, Agarwal V, Aggarwal R, Gupta L. COVID-19 Vaccination-related Short-term Adverse Events in Patients with Idiopathic Inflammatory Myositis and Autoimmune Multimorbidity: Results from the COVID-19 Vaccination in Autoimmune Diseases Survey [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/covid-19-vaccination-related-short-term-adverse-events-in-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myositis-and-autoimmune-multimorbidity-results-from-the-covid-19-vaccination-in-autoimmune-diseases-sur/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/covid-19-vaccination-related-short-term-adverse-events-in-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myositis-and-autoimmune-multimorbidity-results-from-the-covid-19-vaccination-in-autoimmune-diseases-sur/