Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The application of molecular targeted drugs has been expanding in vasculitides. Takayasu arteritis (TAK) frequently relapses and tocilizumab (TCZ) and tumor necrosis factor inhibitors are used for resistant cases. Although the use of these drugs enabled the tapering of corticosteroids, it is still unclear whether corticosteroid withdrawal (CW) is feasible. Recently, we identified two autoantibodies (Abs), anti-endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR) Abs and anti-scavenger receptor class B type 1 (SR-BI) Abs in TAK. Patients presented specific clinical characteristics according to the Ab profile, which suggested different response to treatments. Therefore, this study prospectively evaluated the possibility of CW in patients with relapsed TAK using TCZ and its association with the Ab profile.
Methods: This study was a prospective, single-arm, multicenter trial. Participants who fulfilled the following five criteria were included; age ≧20 years old, diagnosed with TAK based on respective criteria, absence of inflammatory markers, prednisolone (PSL) < 20 mg/day, and previous relapse with >7.5 mg/day of PSL. All patients received 162 mg of weekly subcutaneous (sc) TCZ. The total length of study was 24 weeks, and PSL were tapered according to the scheduled protocol; CW at week 20. The primary endpoint was the difference in the rate of A remission, defined by CW and the absence of inflammatory markers, according to the Ab profile at week 24. Other endpoints were also set, and factors influencing CW were investigated.
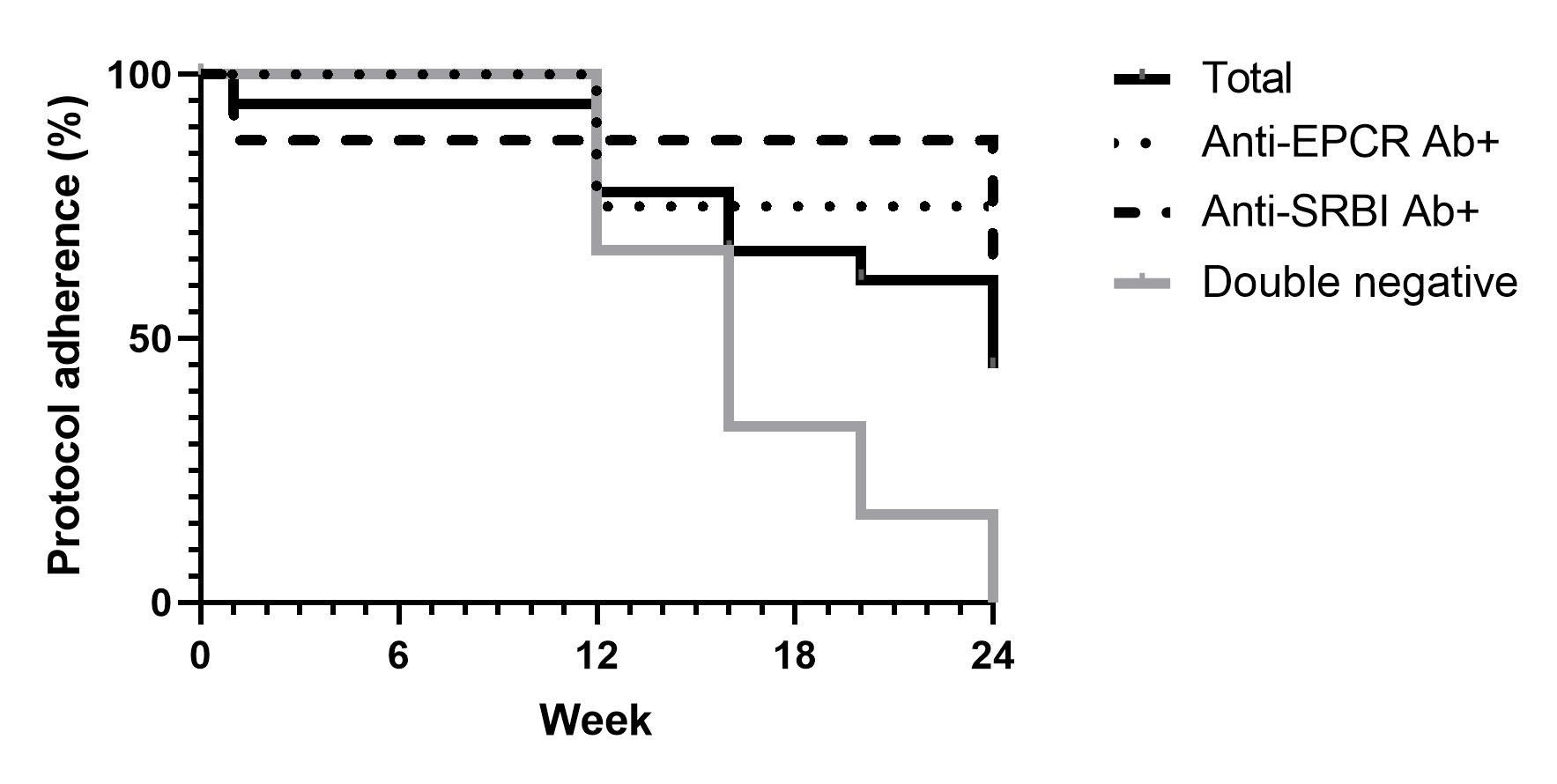
Results: 20 patients were enrolled and one patient dropped out. One patient was excluded because of the double positivity of Abs and 18 patients were analyzed. 16 patients (89%) were female. The mean age and disease duration were 49.7±15.3 and 18.7±9.3 years, respectively. All patients were on scTCZ, and five patients used other immunosuppressants. Mean dose of PSL was 4.9±2.8 mg/day and type V artery lesion was observed in nine patients. The number of anti-EPCR Ab-positive (E+), anti-SRBI-positive (S+), and double negative (DN) patients was four (22.2%), eight (44.4%), and six (33.3%), respectively. At 24 weeks, the mean dose of PSL was reduced to 2.0±2.7 mg/day The A remission was observed in eight patients (44.4%) and was significantly different according to the Ab profile; three (75%), five (62.5%), and zero (0%) in E+, S+, and DN group, respectively (P=0.018). Therefore, CW was feasible in patients with positive Abs and difficult in DN patients. The rate of protocol adherence is shown in Figure 1. CW tended to be difficult in the following patients; older age, longer duration, higher dose of PSL, type V artery lesion, presence of dilated artery, and the levels of CRP >0.1 mg/dL. Worsening of vascular lesion was not documented in this study. Three patients developed arthralgia after CW at week 20, and PSL was restarted.
Conclusion: In this prospective study, CW using TCZ was achieved in 44.4% of patients with TAK who experienced relapse. Ab profile was associated with the achievement of CW, which was significantly higher in E+ and S+ group compared with DN group. Furthermore, other factors which could influence CW were clarified. These results would help to minimize the adverse effects of corticosteroid in TAK.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shirai T, Ishii T, Okazaki S, Shirota Y, Ishii Y, Sato H, Fujii H. Corticosteroid Withdrawal Using Tocilizumab and Its Association with Autoantibody Profile in Takayasu Arteritis: A Multicenter, Single-arm, Prospective Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/corticosteroid-withdrawal-using-tocilizumab-and-its-association-with-autoantibody-profile-in-takayasu-arteritis-a-multicenter-single-arm-prospective-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/corticosteroid-withdrawal-using-tocilizumab-and-its-association-with-autoantibody-profile-in-takayasu-arteritis-a-multicenter-single-arm-prospective-study/