Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Periarticular trabecular bone loss and local cortical bone erosions are typical features of bone disease in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) 1 . Little, however, is known about the interactions between periarticular bone loss and local bone erosions. The purpose of this study was test whether bone mineral density (BMD) in metacarpophalangeal (MCP) head, radius or tibia are associated with cortical bone erosions in RA patients.
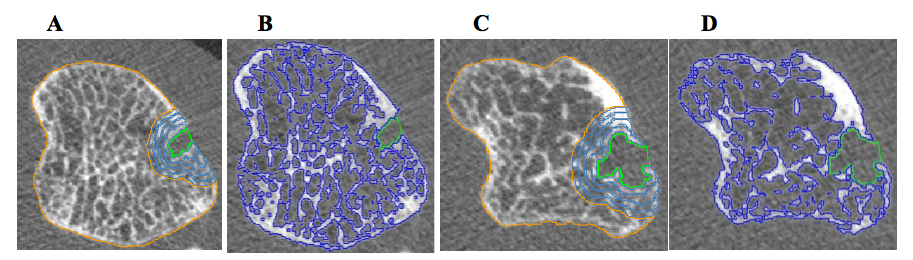
Methods: Forty-seven RA female patients underwent high-resolution quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) of 2 nd MCP joints of the dominant hand, and non-dominant distal radius and tibia in a cross-sectional study. Erosion volumewas assessed by the semi-automated Medical Image Analysis Framework (MIAF) software 2 . Clinical and laboratory variables were assessed, as well as Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) and Hand Grip test. Trabecular bone mineral density (BMD) was measured in 4 particular volumes of interest (VOI-1-4= 1 the nearest to erosion) around the bone erosions (Figure 1). Further, total BMD of metacarpal head was also analyzed. Univariate and multivariate analysis were done to find out a relationship between erosion volume and BMD of metacarpal head, radius and tibia.
Results: The mean age was 40.2±5.9yrs, mean of disease duration 10.9±4.8yrs, median of disease activity score-28 (DAS-28) 2.66(1.97, 3.00), mean of HAQ 0.88±0.70 and mean of hand grip was 18.1±7.1N. Current treatment: glucocorticoids: 61.7%(n=29), conventional DMARDs (Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs): 80.9%(n=38) and biological DMARDs: 48.9%(n=23). There were found 43 erosions (0.9±1.2/patient) and 14 osteophytes (0.3±0.7/patient) in the 2ndMCP head. The joint gap mean was 80.6±34.9mm3, and erosion volume median was 0.26(0, 16.16) mm3. Volume of cortical bone erosions was negatively correlated with BMD in 2ndMCP head (r= -0.53, p< 0.001), VOI-4 (r= -0.48, p=0.017) and joint gap (r= -0.40, p=0.005); and it was positively correlated with number of erosions (r= 0.82, p< 0.001) and number of osteophytes (r= 0.32, p= 0.026). Furthermore, after the sample was categorized by absence or presence of erosion in 2ndMCP head it was found a significant difference between number of osteophyte (0.10±0.41vs.0.50±0.88, p=0.028), BMD of MCP head (321.53±37.12 vs.281.38±67.69mg/cm3, p=0.043) (Figure 2) and joint gap (93.59±36.94 vs.68.20±28.31, p=0.025), respectively. The multiple linear regression showed that BMD of 2ndMCP head was negatively associated with its volume of erosion (B= – 0.813, p=0.003, adjusted R2= 0.32), adjusted by number of erosions, number of osteophytes, joint gap, VOI-4 and volumetric trabecular BMD of radius.
Conclusion: Cortical bone erosions volume were associated with low BMD in the 2 nd MCP head, suggesting that this variable should also be included as an outcome parameter in the follow-up of RA patients.
Funding:Camille P. Figueiredo was supported by FAPESP (2018/01315-9). This work was supported by FAPESP 2016/00006-7.
References:
1-Tam LS. J Rheumatol 2016;43(10):1911-3.
2-Figueiredo CP, et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2017;47(7):611-8.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Figueiredo C, Perez M, Ribeiro A, Caparbo V, Pereira R. Cortical Bone Erosion in the 2nd Metacarpal Bone Head: Association with Its Bone Mineral Density by HR-pQCT in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cortical-bone-erosion-in-the-2nd-metacarpal-bone-head-association-with-its-bone-mineral-density-by-hr-pqct-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cortical-bone-erosion-in-the-2nd-metacarpal-bone-head-association-with-its-bone-mineral-density-by-hr-pqct-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/