Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Soluble checkpoint molecules (sCM) may be involved in the pathophysiology of autoimmune diseases by inhibiting the suppressive signals of immune cell activation through binding to membrane-bound checkpoint molecules. The serum levels of soluble programmed death-1 (sPD-1) and soluble programmed death ligand 1 (sPD-L1) have been reported to correlate with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) , but their dynamics in other autoimmune diseases remain unclear.
Methods: Plasma from healthy controls (HC) and patients was used. The plasma concentrations of sPD-1, sPD-L1, and soluble cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (sCTLA-4) were measured (pg/ml) by a fully automated immunoassay (HISCL system). If possible, samples at multiple timepoint were collected from the same patient with different disease states. Disease activity was assessed using Simplified Disease Activity Index (SDAI) for RA, SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) for SLE, Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (BVAS) for AAV and Myositis Intention To Treat Activity Index (MITAX) for Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM). Other clinical evaluation items, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), were also compared.A patent application has been filed related to the methodology described in this study.
Results: There were 29 HC (44% female, median age 35 years), 30 RA patients (59 samples, 81% female, median age 66 years), 42 SLE patients (84 samples, 94% female, median age 43 years), 20 AAV patients (41 samples, 70% female, median age 75 years), and 21 IIM patients (49 samples, 59% female, median age 58 years). In the present patient cohort, untreated patients generally showed higher levels of sCM compared to HC. The SDAI had no correlation with sCM. SLEDAI and BVAS showed mild correlations with sCM ( rs=0.48-0.55; p< 0.001). MITAX showed high correlations with sCM (sPD-1, sPD-L1, sCTLA-4; rs=0.76, 0.75, 0.81; p< 0.0001), In particular, sCM showed a stronger correlation with MITAX (rs > 0.8) in cases of anti-ARS antibody or anti-MDA5 antibody positive. And when calculating the AUC using ROC curves, sCTLA-4 (0.97) were able to distinguish between pre- and post-treatment more effectively than CRP (0.86) and ESR (0.67) in IIM patients. Even after performing multivariate analysis with age, sex, sPD-L1, and sCTLA4, sCTLA-4 and sPD-L1 remained independent factors associated with MITAX, regardless of age and sex.
Conclusion: The correlation between disease activity and sCM varied among autoimmune diseases. sCM may be useful as evaluation parameters, especially in IIM patients.
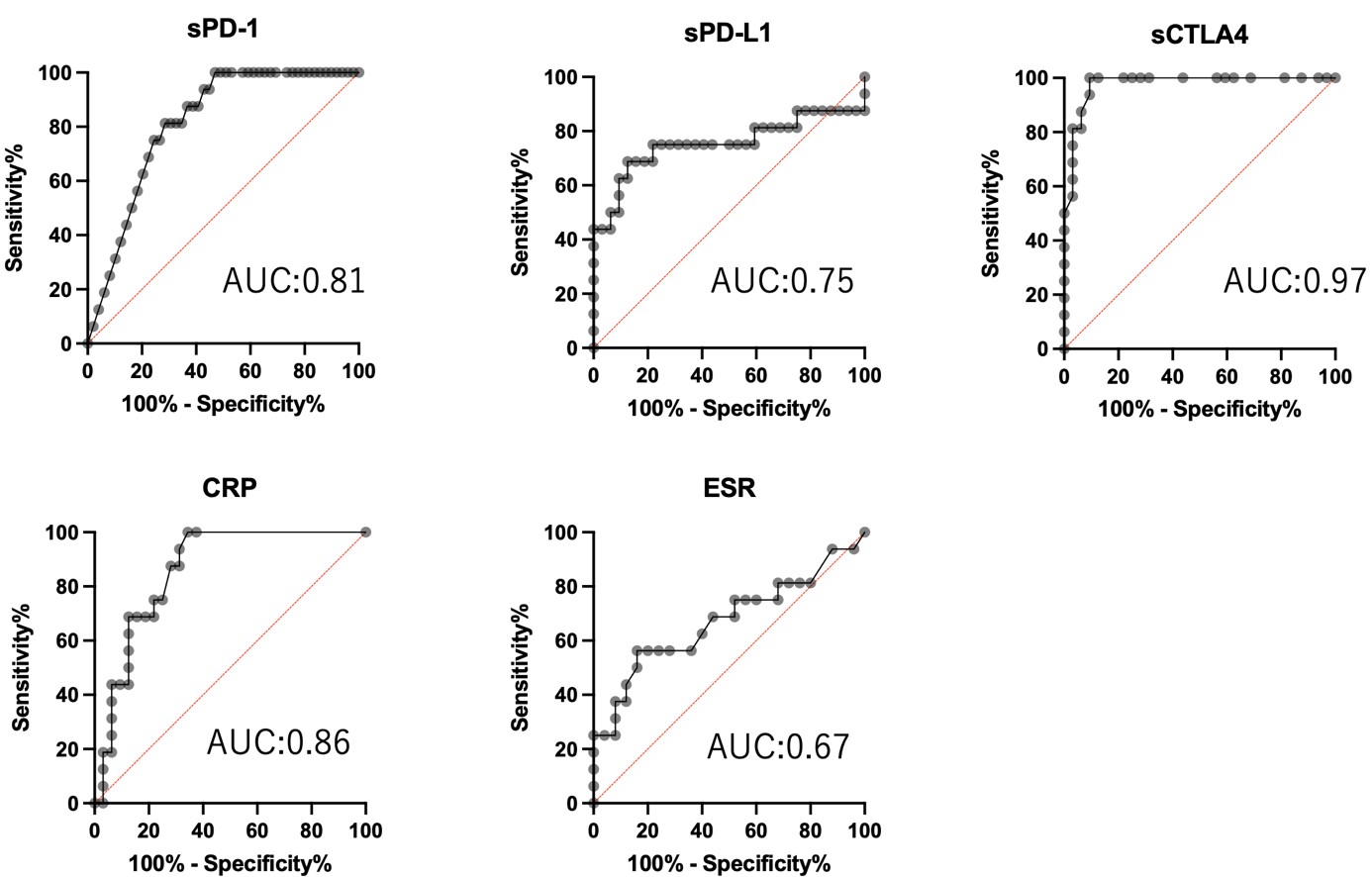 figure1. Plasma sCM in healthy individuals and autoimmune disease patients before treatment.
figure1. Plasma sCM in healthy individuals and autoimmune disease patients before treatment.
.jpg) figure 2. The correlation of each assessment parameter with MITAX.
figure 2. The correlation of each assessment parameter with MITAX.
.jpg) figure 3. Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (ROC) of plasma sCM in IIM patients before and after treatment.
figure 3. Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (ROC) of plasma sCM in IIM patients before and after treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Murakami K, Yoshida A, Uga H, Sumitomo S, Ohmura K, Hiwa R, Kozuki T, Kuroishi M, Suminaka C, Shirakashi M, Tsuji H, Akizuki S, Nakashima R, Yoshifuji H, Onishi A, Tanaka M, Morinobu A, Chamoto K, Honjo T. Correlation between Soluble Checkpoint Molecules and Disease Activity in Autoimmune Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/correlation-between-soluble-checkpoint-molecules-and-disease-activity-in-autoimmune-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/correlation-between-soluble-checkpoint-molecules-and-disease-activity-in-autoimmune-diseases/
