Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular (CV) disease. The endothelium is a key regulator of vascular function. Subclinical CV disease and its progression are intimately related to endothelial dysfunction (ED), a preclinical marker of atherosclerosis. Endothelial function has been measured indirectly as the response to hyperemic flow in the peripheral vasculature to identify and monitor CV risk in RA. Positron Emission Tomography (PET/CT) with Cold Pressor Test (CPT) directly measures coronary artery endothelial cell function during sympathetic stimulation. This non-invasive index of coronary function predicts atherosclerosis. We evaluated the differences in large and small vessel coronary endothelial reactivity in early RA (< 2 years), established RA (> 2 years) and healthy subjects by PET/CT with CPT.
Methods: Delta percent Myocardial Blood Flow (Delta % MBF) was assessed by cardiac N-13 ammonia PET/CT scan. Myocardial perfusion (MP) was evaluated at baseline (BL) following intravenous (IV) administration of N-13 ammonia. After acquiring BL perfusion images with PET, cold pressor stress was assessed by immersing one hand in ice water while a second dose of N-13 ammonia was injected. MP and blood flow were determined from serially acquired images and left ventricular function was assessed from gated images. 15 non-smoking subjects (87% female) were studied: 5 early RA (mean age 60.8 y, mean disease duration 5.0 months), 5 established RA Methotrexate [MTX] inadequate responders (mean age 46.2 y, mean disease duration 153.6 months), and 5 healthy subjects (mean age 53.8 y). Means were calculated for demographic and physiologic characteristics, with one-way Anova and Kruskall-Wallis to compare differences across groups. Univariate correlations of Delta % MBF were also performed in the RA groups. Studies were controlled for age, body mass index (BMI), gender, and mean arterial blood pressure (MAP).
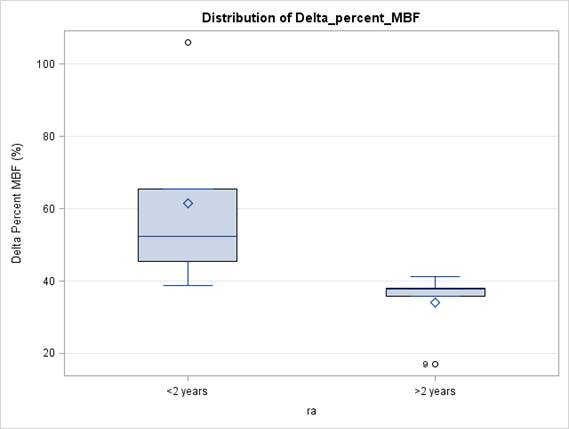
Results: Characteristics between groups were similar, except for sedimentation rate (P=0.003), and age (P=0.002). Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDLC), and MAP positively correlated with Delta % MBF (P<0.05). Delta %MBF was similar in normal and early RA subjects. However, RA > 2 years compared to RA <2years demonstrated markedly decreased endothelial reactivity (mean 34.0 (9.7) vs 61.6 (26.7); P=0.0001) when clinical disease activity index (CDAI) and vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM-1) were added to the model.
Conclusion: Premature coronary endothelial dysfunction is present in patients with established RA. CDAI and VCAM-1 impact the difference in endothelial function between established RA and early RA. These results raise the question of whether further disease modifying therapy beyond MTX will be useful to improve endothelial function in established RA patients.
Figure 1. Distribution of Delta % MBF across groups, adjusting for Age, Gender, BMI, MAP and CDAI
Disclosure:
O. Troum,
Bristol Myers Squibb,
2;
O. Pimienta,
None;
B. Hidalgo,
None;
W. Hsueh,
Bristol Myers Squibb,
2.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/coronary-endothelial-dysfunction-directly-measured-by-n13-positron-emission-tomography-pet-is-detected-in-established-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-but-not-early-ra/