Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2095–2140) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The risk of mortality is increased in patients with RA compared to the general population. Different non-invasive surrogate markers of atherosclerosis have been implemented to identify RA patients who are at high risk of cardiovascular (CV) disease.
In the present study, we aimed to establish the predictive capacity of the following surrogate markers: Coronary calcium (CAC) and carotid pulse wave velocity (PWV) to predict CV events and all-cause mortality in a cohort of RA patients prospectively followed.
Methods: We conducted a prospective longitudinal study that included 126 patients with RA. The patients were recruited in 2011 and followed-up for 10 years. All patients had undergone baseline CAC score, and carotid PWV by US. Multivariate Cox regression analysis was performed to identify the predictive ability of these surrogate markers for CV events and all-cause mortality.
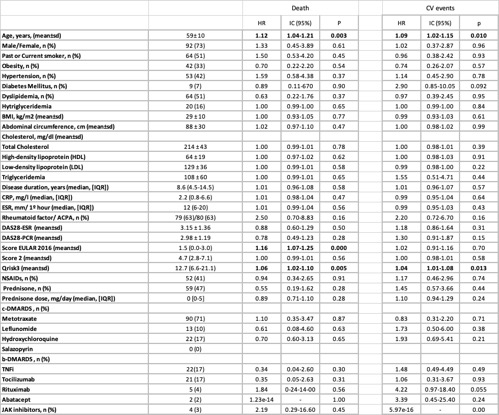
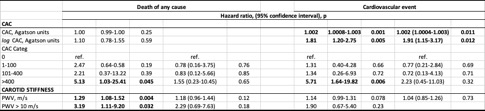
Results: A total of 126 patients were included, 92 women (73%), with a mean age of 59±10 years. The main baseline characteristics, CV risk factors, disease activity data and treatments are detailed in Table 1, as well as the baseline parameters that showed statistically significant association with mortality and CV events. After a follow-up of 14,479 person-months, there were 15 deaths and 24 cardiovascular events in 18 patients. The main causes of mortality were infections (n=7, 46.7%) and neoplasms (n=5, 33.3%). In univariate analysis, CAC values above 400 Agatston units were associated with a statistically significant increased risk of overall mortality (HR 5.13 (1.03-25.41 95% CI), p=0.045) (Table 2). However, in multivariate analysis adjusted for classical CV risk factors, the results obtained were not statistically significant. Increasing CAC value as a continuous variable was significantly associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular event in both univariate (HR 1.002 (1.0008-1.003 95% CI), p=0.001) and multivariate (HR 1.002 (1.0004- 1.003), p=0.011) analyses. The increase in carotid arterial stiffness value measured by PWV was statistically significantly related to overall mortality in the univariate analysis. The same was observed when categorizing this variable, as values higher than 10 m/s in the univariate analysis were statistically associated with overall mortality. However, this relationship did not maintain in the multivariate analysis, nor could it be demonstrated for CV events.
Conclusion: CAC measurement in RA patients is predictive of CV events. In our cohort of 126 RA patients, increased PWV values did not correlate with overall mortality or CVD after 10 years of follow-up.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Corrales Selaya C, Vegas Revenga N, Parra J, Portilla V, Blanco R, Gonzalez-Gay M, Ferraz Amaro I, Corrales A. Coronary Calcium and Carotid Artery Stiffness as Predictors of Cardiovascular Events and Mortality in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A 10-year Prospective Follow-up Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/coronary-calcium-and-carotid-artery-stiffness-as-predictors-of-cardiovascular-events-and-mortality-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-10-year-prospective-follow-up-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/coronary-calcium-and-carotid-artery-stiffness-as-predictors-of-cardiovascular-events-and-mortality-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-10-year-prospective-follow-up-study/