Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Multiple patient-reported outcomes (PROs) have been utilized to capture the burden of Systemic Sclerosis (SSc), including the Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI), Cochin Hand Function Scale (CHFS), Borg, and the UCLA gastrointestinal tract 2.0 (GIT 2.0). The EULAR Systemic Sclerosis Impact of Disease (ScleroID) questionnaire is a comprehensive PRO that includes Raynaud, hand function, upper gastrointestinal, pain, fatigue, lower gastrointestinal, life choices and activity limitation, body mobility, dyspnea, and digital ulcer. ScleroID captures all the disease manifestations that matter the most to patients and symptoms frequently responsible for disease burden (1). The aim of the study is to determine the distribution of ScleroID and its domain questions among different disease subsets and whether they correlate with clinical findings and PROs cross-sectionally and over time.
Methods: Patients with ScleroID questionnaires from the observational cohort STRIKE were included in the study. Patients with other chronic pain syndromes were excluded. The Mann-Whitney U or One-way ANOVA was used to compare subgroups as appropriate. Wilcoxon ranked test was used to assess the differences between baseline and follow-up scores. Spearman’s rank correlation was used to analyze cross-sectional and over-time correlations between ScleroID and its dimensions and clinical findings or other PROs. Changes (Δ) in scores were calculated as the difference between 12-month follow-up and baseline scores.
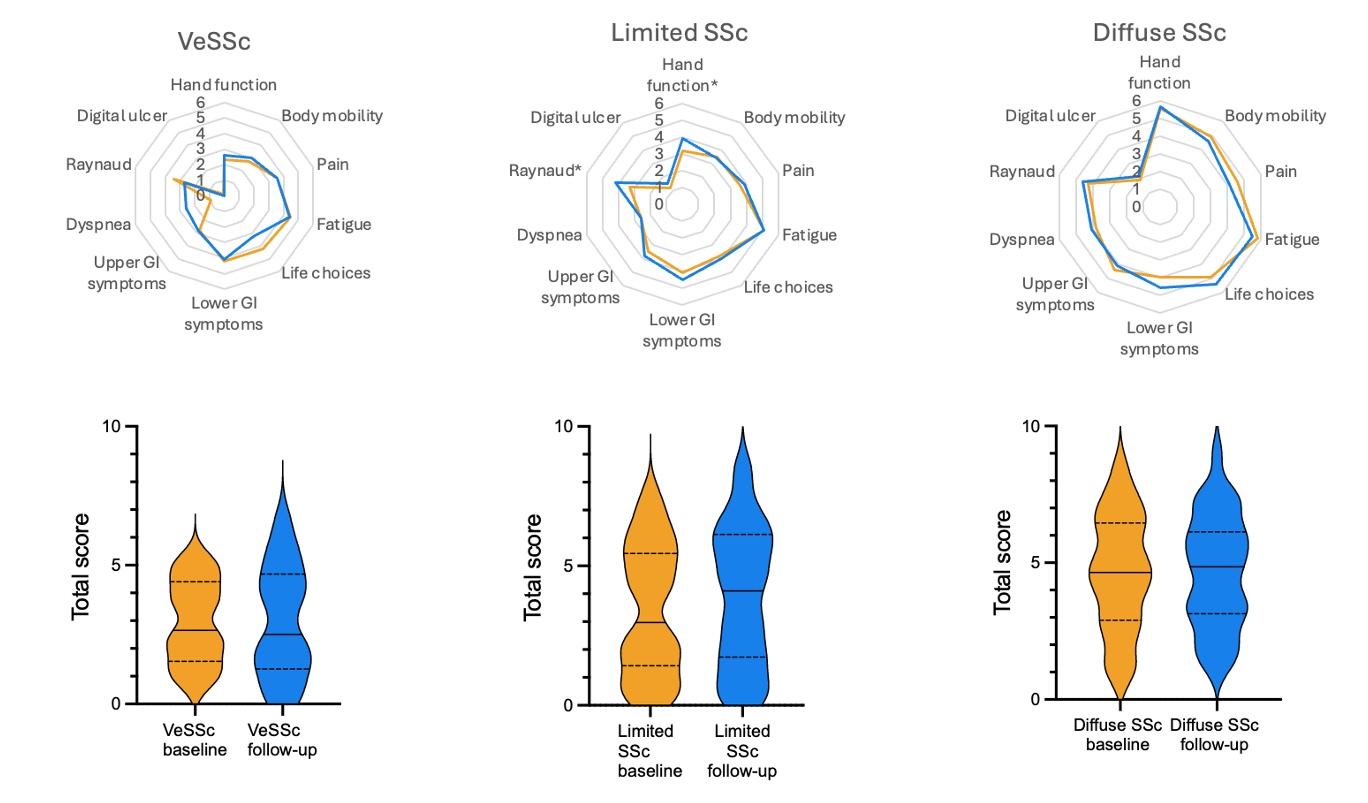
Results: We administered ScleroID to 271 patients (245 Female/26 Male) between January 2022 and February 2024. Mean age was 54.8±13.9 years. At baseline, 69 (25.5%) patients had a very early diagnosis of SSc (VeSSc), 139 (51.3%) limited cutaneous (lcSSc), and 63 (23.2%) diffuse cutaneous SSc (dcSSc). ScleroID distribution was not normal with median (IQR) score of 3.4 (4.2). ScleroID was significantly different in the 3 subsets: 2.1 (3.6) in VeSSc, 3.4 (4.4) in limited SSc, and 4.7 (4) in diffuse SSc (p< 0.001), with lower GI domain being the only constant domain within the subsets.
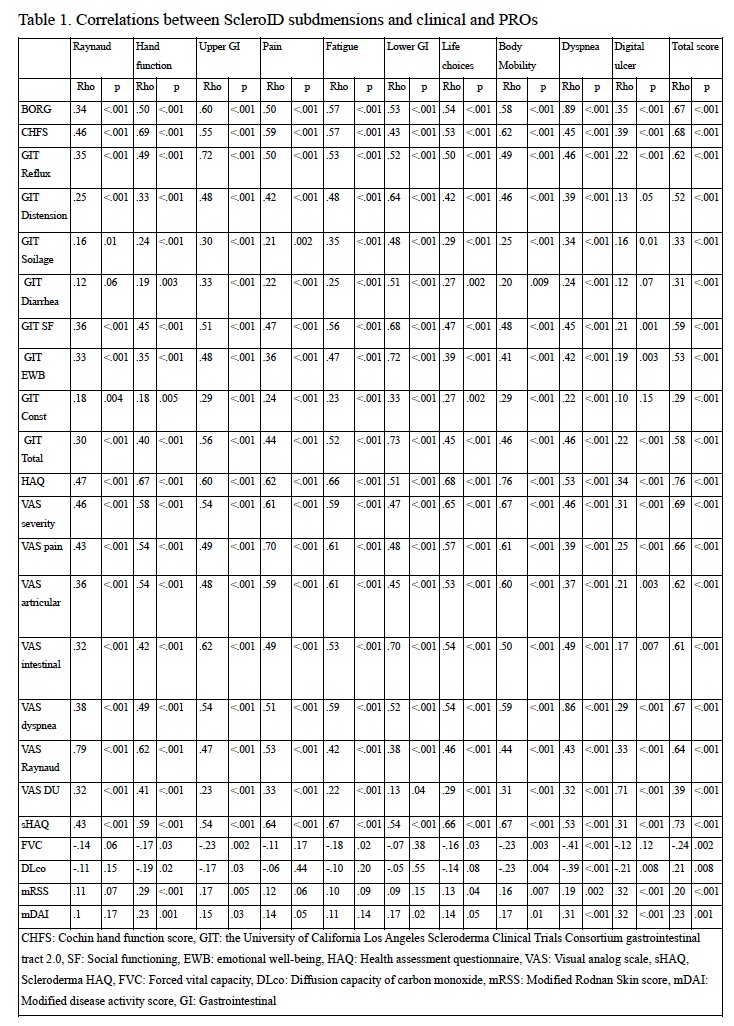
ScleroID domains and total ScleroID scores showed highly significant correlation with all the other PROs (p< 0.001 for all) with the strongest correlation for scleroderma HAQ-DI, confirming the comprehensive face and content validity of Sclero-ID (Table 1). Importantly ScleroID total score also correlated with clinical measures of disease severity including mRSS, FVC and DLCO (p< 0.05 for all) and with the modified Disease activity Index (2). Longitudinal measures were available for 114 patients (17 VeSSc) (Figure 1). ΔScleroID total correlated with ΔSHAQ (r=.465) (p< 0.05). ΔScleroID dyspnea was correlated with ΔBORG (r=.334), ΔScleroID hand function was correlated with ΔCOCHIN (r=.418), ΔScleroID upper and lower GI scores correlated with ΔGIT 2.0 scores (p< 0.05).
Conclusion: EULAR ScleroID is a comprehensive, easy to perform PRO able to capture the overall impact of SSc on patients across different disease subsets. ScleroID correlation with validated clinical measures and its sensitivity to change in standard of care setting, support its use as a key composite PRO in clinical practice and clinical trials.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Colak S, Di Donato S, Bixio R, Bissell L, Barnes T, Denton C, Nisar M, Del Galdo F. Content Validity and Sensitivity to Change of ScleroID Through the Natural History of Scleroderma. a Validated Tool to Measure the Impact of SSc on How Patients Feel and Function [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/content-validity-and-sensitivity-to-change-of-scleroid-through-the-natural-history-of-scleroderma-a-validated-tool-to-measure-the-impact-of-ssc-on-how-patients-feel-and-function/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/content-validity-and-sensitivity-to-change-of-scleroid-through-the-natural-history-of-scleroderma-a-validated-tool-to-measure-the-impact-of-ssc-on-how-patients-feel-and-function/