Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with psoriasis often present with musculoskeletal (MSK) symptoms, yet validated instruments to measure MSK symptoms in this population are limited. The IDEOM MSK-Q is a novel patient-reported outcome measure to evaluate MSK symptoms and their impact in individuals with psoriasis with or without concomitant psoriatic arthritis (PsA). The instrument has 3 subscores: Intensity of MSK Symptoms (3 items), Impact of MSK Symptoms (4 items), and Intensity of Fatigue (1 item). This study evaluated the construct validity of the IDEOM MSK-Q in a real-world cohort.
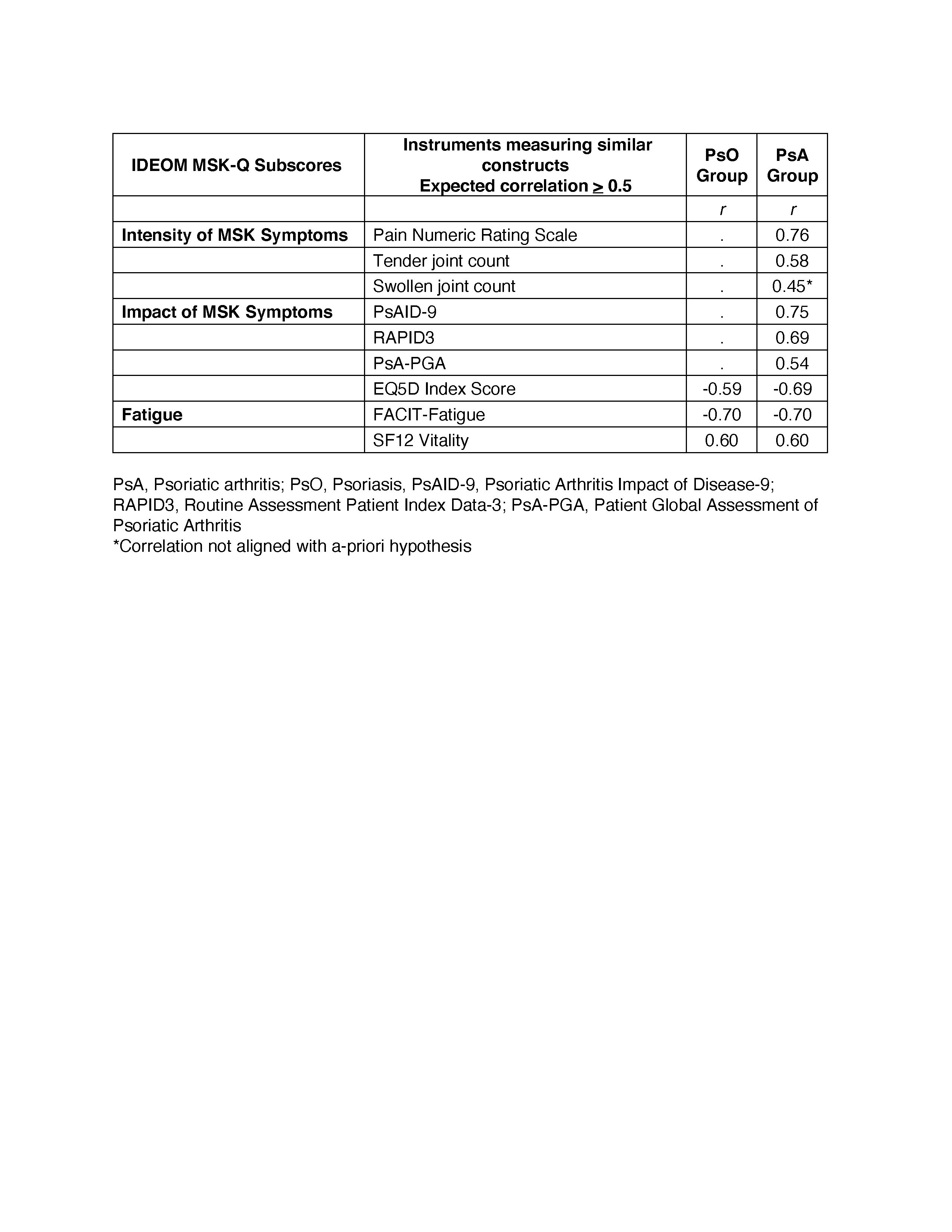
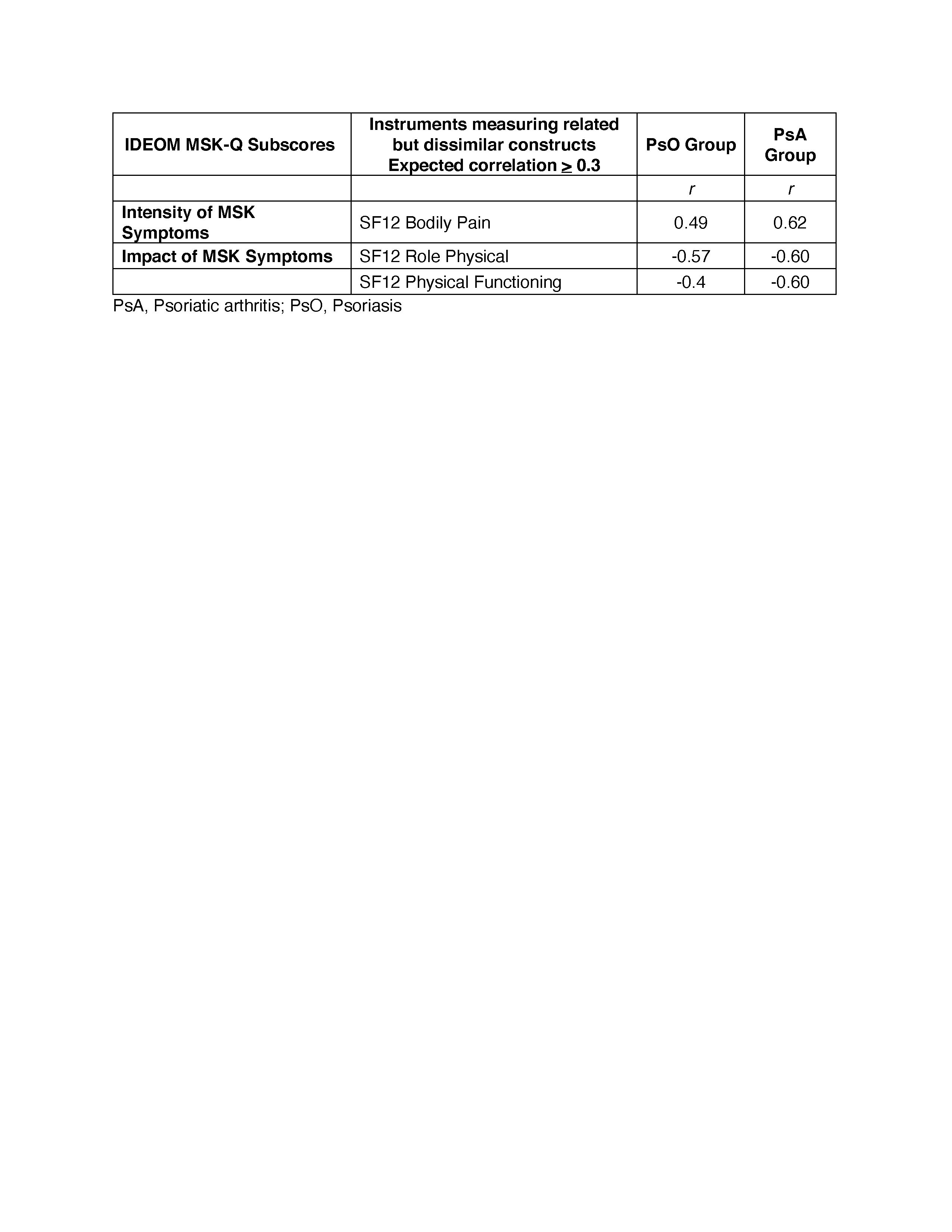
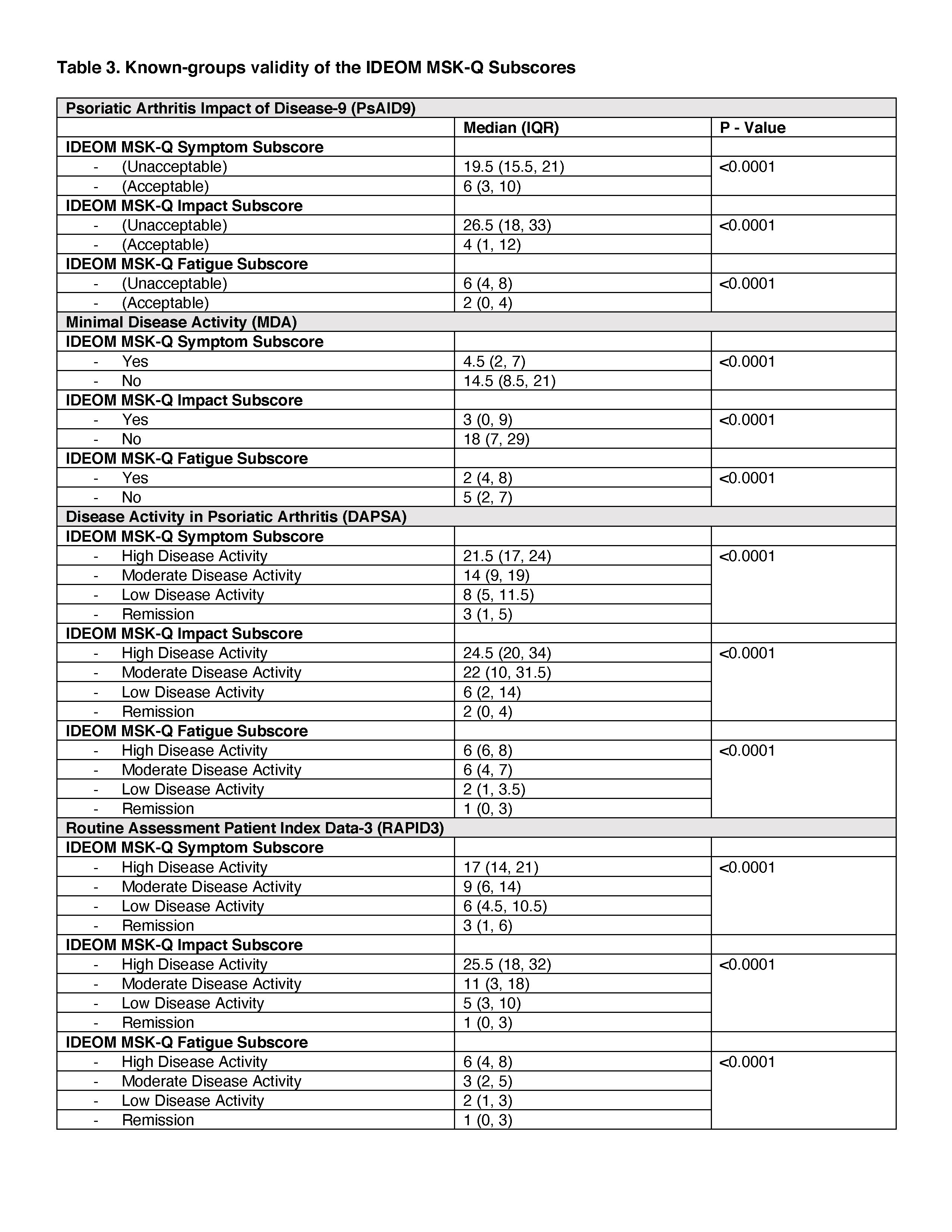
Methods: Data for analysis was obtained from the Cohort of Psoriasis for Psoriatic Arthritis Registry (COPPAR). We tested a-priori hypotheses about the correlation of the IDEOM MSK-Q subscores with scores of instruments measuring similar (r > 0.5) or related but dissimilar (r > 0.3) constructs (convergent validity) using Spearman’s rank correlation. To determine known-groups validity, we tested a-priori hypotheses about differences in the IDEOM MSK-Q subscores among groups based on disease severity as defined by the Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease (PsAID-9), Minimal Disease Activity (MDA), Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis (DAPSA), Routine Assessment Patient Index Data-3 (RAPID3). The median scores for each subscore of the IDEOM MSK-Q were compared among groups using Wilcoxon rank sum and Kruskal Wallis H tests. Construct validity was considered sufficient if at least 75% of the correlations aligned with the hypotheses.
Results: A total of 79 participants with psoriasis-only and 166 patients with psoriasis and concomitant PsA were included. In the psoriasis group, the mean age was 54.8 (SD 16.5), and 43% were female. In the PSA group, the mean age was 56.9 (SD 12.8), and 53.6% were female. Overall, more than 90% of correlations were aligned with hypotheses (Tables 1 and 2). Among patients with PsA, the Intensity of MSK Symptoms subscore strongly correlated with Pain Numeric Rating Scale (r=0.76) and tender joint count (r=0.58). The Impact of MSK Symptoms subscore strongly correlated with PsAID9 (r=0.75) and RAPID3 (r=0.69). Among patients with PsA and PsO, The Impact of MSK Symptoms subscore and the Fatigue subscore strongly correlated with EQ5D Index Score (r=-0.59 – -0.69) and FACIT-Fatigue (0.60-0.70), respectively. The IDEOM MSK-Q differentiated among individuals with different levels of PsA severity as defined by PsAID-9, MDA, DAPSA, and RAPID3 (Table 3).
Conclusion: Overall, the IDEOM MSK-Q has sufficient construct validity to assess musculoskeletal symptoms in patients with psoriatic disease. Assessments of other critical measurement properties, including test-retest reliability and responsiveness, are currently in progress.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Perez Chada L, Li R, feathers v, Schnock K, Early H, Carter G, Shahriari N, Zhang A, Cui J, Weinblatt M, Shadick N, Gottlieb A, Merola J. Construct Validity of the IDEOM Musculoskeletal Questionnaire (IDEOM MSK-Q) Using Data from the Cohort for Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Registry (COPPAR) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/construct-validity-of-the-ideom-musculoskeletal-questionnaire-ideom-msk-q-using-data-from-the-cohort-for-psoriasis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-registry-coppar/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/construct-validity-of-the-ideom-musculoskeletal-questionnaire-ideom-msk-q-using-data-from-the-cohort-for-psoriasis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-registry-coppar/