Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I: Patient Reported Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Involving patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in the assessment of their disease may increase adherence to treatment, improve disease outcomes and reduce consultation time. Concordance between Disease Activity Score (DAS-28) performed by physicians and patients was substantial in the phase 1 (baseline visit) of this prospective study.
The purpose of the study is to evaluate the persistence of the concordance between physician and patient assessment of disease activity in RA using DAS-28 after 3 months of the baseline visit.
Methods: At baseline visit, patients with RA from 7 Middle Eastern Arab Countries (MEAC) were briefed about DAS-28 by their rheumatologist and were given a smartphone access to a video in easy Arabic language explaining the performance of DAS-28. At visit 2, scheduled 3 months later, patients were asked to self-report DAS-28, blinded to the physician’s assessment. Concordance between DAS-28 at each visit was calculated using paired T-Test. Agreement between physician- and patient-DAS categories (remission, low-, moderate- and high disease activity) was calculated at baseline and at 3 months using weighted kappa for category comparison. Predictive factors of positive concordance between physician and patient-DAS were identified using logistic regression.
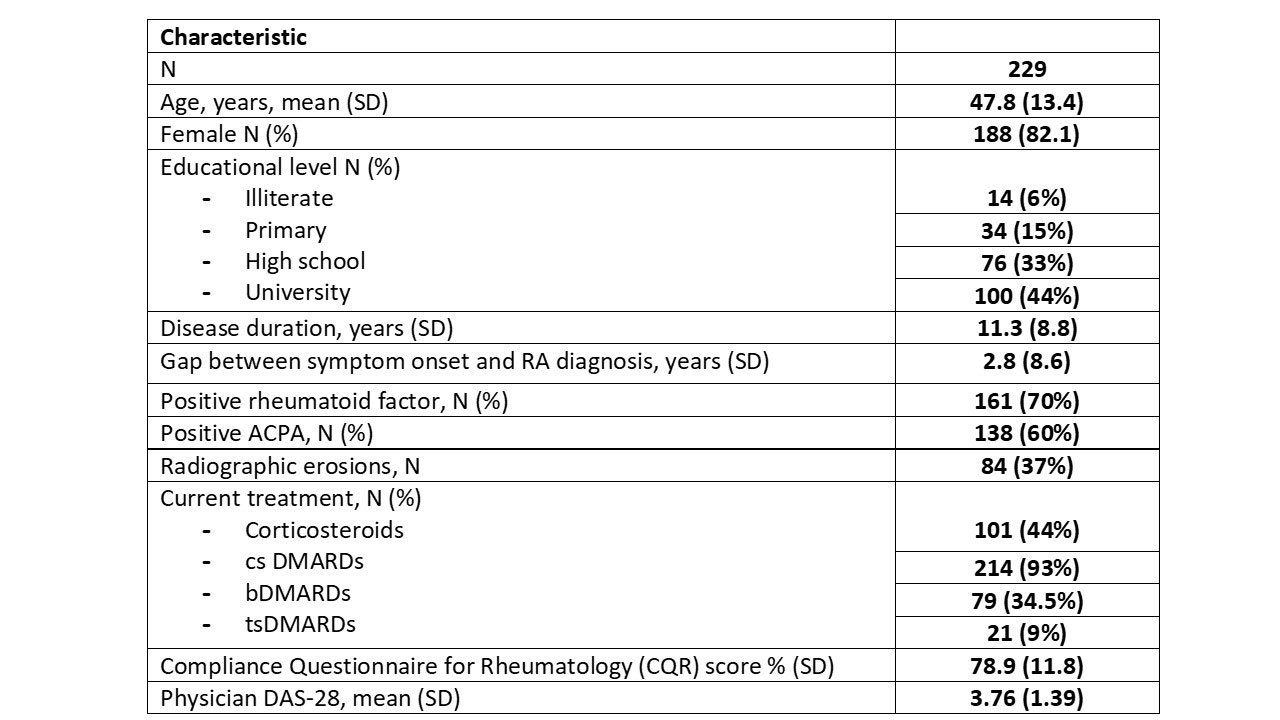
Results: Two hundred and twenty-nine patients were included in AUTODAS phase II (Characteristics in Table 1). At baseline, mean DAS-28 was 3.76 [SD 1.39] in physicians and 3.94 [SD 1.42] in patients, with a difference delta1 of -0.19 [95% CI -0.26; -0.11] (p < 0.0001). At 3 months, mean DAS-28 was 3.57 [SD 1.44] in physicians and 3.75 [SD 1.47] in patients, with a difference delta2 of -0.18 [95% CI -0.25; -0.11] (p< 0.0001). The difference between deltas was not statistically significant (p = 0.81). Agreement between physician- and patient-DAS categories was 76% at baseline (Weighted Kappa = 0.71), and 73% at 3 months (Weighted Kappa = 0.73). Concordance at 3 months was statistically associated with DAS-patient category (p = 0.045) and concordance at baseline (p = 0.036) and did not correlate with education, treatment or country.
Conclusion: DAS-28 is numerically slightly overestimated by patients compared to physicians but the concordance between DAS-28 categories was substantial and remained stable at the 3-months follow-up visit.
Self-assessment of disease activity should be decided according to the physician’s clinical judgment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ziade N, Alemadi S, Abu Jbara M, Saad S, El-Kibbi L, Al-Mashaleh M, El-Zorkany B, Merheb G, Alam E, Aiko A, Messaykeh J, Salloum N, Daher A, Halabi H, Mroue' K, Masri B, Badsha H, Harifi G, Arayssi T. Concordance Between Physician and Patient Assessment of Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Disease Activity Score: Phase II Results [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/concordance-between-physician-and-patient-assessment-of-disease-activity-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-using-disease-activity-score-phase-ii-results/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/concordance-between-physician-and-patient-assessment-of-disease-activity-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-using-disease-activity-score-phase-ii-results/