Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-3:30PM
Background/Purpose: The role of complement in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) has been increasingly appreciated and led to the use of complement system antagonists as a therapeutic strategy. However, it is unclear whether complement system activation occurs in affected organs such as the kidneys. This study aimed to characterize complement gene expression in patients with AAV with renal involvement (AAGN).
Methods: Whole-tissue RNA-sequencing was performed on kidney biopsy samples of 23 patients with AAGN, and 5 healthy kidney donors. After quality control, differential expression (DGE) analysis was performed using generalized linear models correcting for number of genes and batch effects. This abstract describes mRNA expression of 42 complement system proteins, receptors, and regulators. For this analysis, differential expression was considered statistically if the FDR-corrected p-value < 0.05, and the absolute value of log2 fold change between groups was > 0.6 (|log2FC| > 0.6).
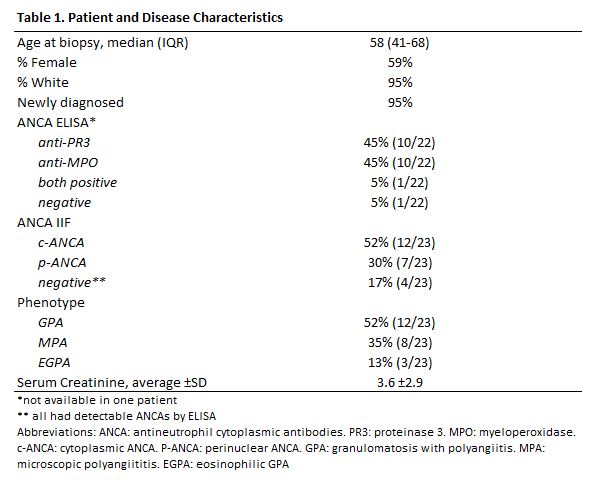
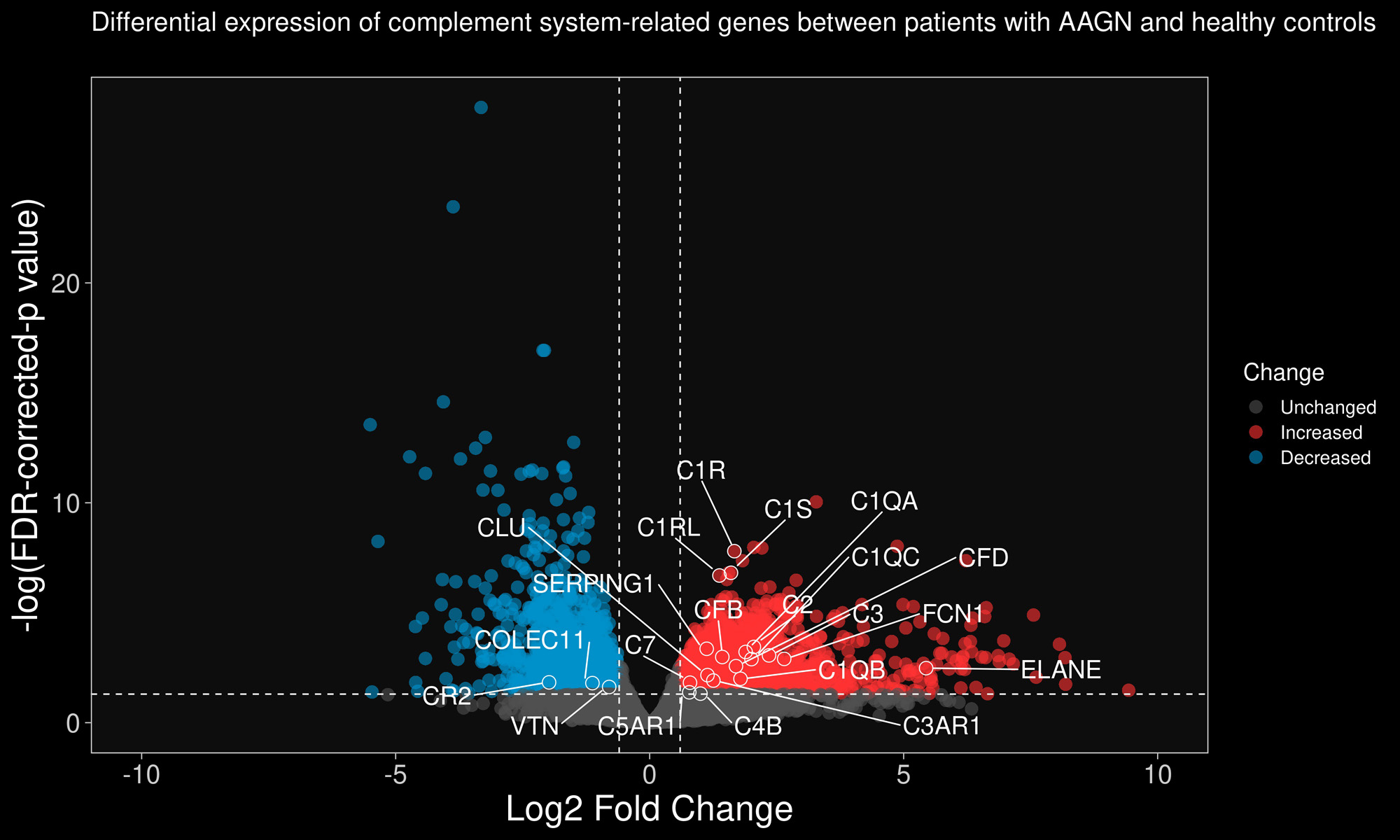
Results: Patients’ clinical and demographic characteristics are depicted in Table 1. Most patients were female (13/23), White (21/23), and had a median age of 58 years. Most patients had c-ANCAs and a granulomatosis with polyangiitis phenotype. DGE analysis (Figure 1) revealed increased abundance of mRNA coding for proteins participating in the classical (C1q, C1r, C1s, C2, C4B), alternative (CFB, CFD), and common (C3, C7) complement pathways. In addition, there was an increase in abundance of the anaphylatoxin receptors (C3AR, C5AR). mRNA abundance of complement regulators (CFH, CD55, CD46, CR1) were not different compared to controls except for CR2 which was decreased in patients with AAGN.
Conclusion: Analysis of mRNA expression in kidneys of patients with AAGN reveals increased abundance of members of the classical and alternative complement pathways, anaphylatoxin receptors, without a concomitant increase in mRNA expression of complement regulatory proteins. Along with our previous finding of increased complement activation products in urine of patients with active AAGN, these data strongly suggest intra-renal complement system activation in patients with AAGN.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Almaani S, Arazi A, Song H, Yan P, Puchulu-Campanella E, Wang H, Fussner L, Parikh S, Rovin B. Complement mRNA Expression in Patients with ANCA-associated Glomerulonephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/complement-mrna-expression-in-patients-with-anca-associated-glomerulonephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/complement-mrna-expression-in-patients-with-anca-associated-glomerulonephritis/