Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Many patients suffering from knee OA show swelling, warmth along with pain which are features of inflammation. There are no accepted pharmacological therapy for osteoarthritis that target inflammation though inflammation plays a crucial role in pain generation and progressive joint damage.
There are some evidence that Methotrexate may be useful in knee osteoarthritis. The latest ACR recommendation for OA is not in favour of MTX, but it seems they have more weight to the evidence in case of hand OA than knee OA. ACR recommendation found no evidence of usefulness of glucosamine also, another very commonly used drug for knee OA.
We decided to evaluate the effect of methotrexate in primary knee OA with inflammation in comparison with glucosamine as placebo.
Methods: Primary knee OA of both sex, aged 40-65 years, having swelling and pain of both knee joints for at least six months with radiographic OA and consent to study were recruited. Exclusion criteria consisted of KL grade 4, secondary OA, arthroscopy or intra articular injections in last three months, uncontrolled Diabetes, renal, hepatic diseases or gout.
Patients with signs of local inflammation i.e. pain swelling of whole knee and warmth were checked for ESR and CRP.
If there was increase in both in one occasion or either of them in two occasions 1 month apart (ESR >30mm/1st Hr and CRP >1.5 times of reference), they were placed in systemic Inflammatory group.
Others were placed in non-inflammatory group.
Blood was collected from all patients and healthy controls for testing of selected biomarkers.
Patients in the inflammatory group were stringently screened for Inflammatory arthritis by clinical examination, blood tests, Musculoskeletal ultrasound, X-ray..
MRI of knee was done in all patients of Inflammatory group.
Then, patients of inflammatory group were randomly allocated to receive Methotrexate (15-20 mg/week) or Glucosamine (placebo) and followed monthly for three months.
All patients were allowed to take paracetamol and tramadol on as needed basis. NSAIDs were given in the beginning for 7-10 days to improve compliance.
WOMAC (CRD Pune version) was measured at beginning and end of three months.
Results: Total 344 primary knee OA patients who fulfilled the inclusion and exclusion criteria, were examined from July 2016 to June 2019 in Department of Rheumatology, IPGME&R and SSKM Hospital, Kolkata.
249 patients had local inflammation (swelling of both knees). 172 patients of them had elevated ESR/CRP, both in one occasion or either of them in two occasions 1 month apart.
Table 1: Demography
Table 2: Patients suffering from primary knee OA with inflammation receiving MTX
Table 3: Patients suffering from primary knee OA with inflammation receiving Glucosamine
Conclusion: We found significant improvement in WOMAC, ESR and CRP in patients suffering from primary knee OA with inflammation after three months of taking methotrexate while there was insignificant effect with glucosamine, used as placebo. Our study provides proof that oral Methotrexate may be an important intervention in primary knee osteoarthritis with inflammation.
 Patients suffering from primary knee OA with inflammation receiving MTX
Patients suffering from primary knee OA with inflammation receiving MTX
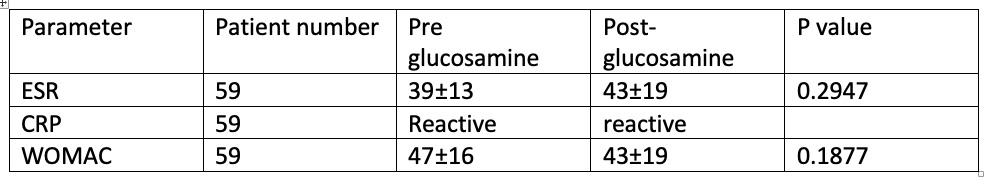 Patients suffering from primary knee OA with inflammation receiving Glucosamine
Patients suffering from primary knee OA with inflammation receiving Glucosamine
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ghosh B, Haldar S, Saha M. Comparison of Methotrexate and Glucosamine in Primary Knee Osteoarthritis with Inflammation [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-methotrexate-and-glucosamine-in-primary-knee-osteoarthritis-with-inflammation/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-methotrexate-and-glucosamine-in-primary-knee-osteoarthritis-with-inflammation/

