Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a heterogeneous disease that is included in the group of spondyloarthritis. Although PsA has its own clinical characteristics, it has a relatively specific comorbidity in relation to the rest of the entities that make up the group. The most frequent comorbidities in PsA are emotional disorders (anxiety and depression) and obesity. Its presence implies a deterioration in the quality of life, an increase in mortality and constitutes a factor to be taken into account in the selection of treatment. However, the influence of these comorbidities on the activity of the disease is less known.
Purpose: To compare the presence of psycho-affective disorders and factors associated with obesity in patients with spondylitis and PsA. Relate them to the activity of the disease in patients with PsA.
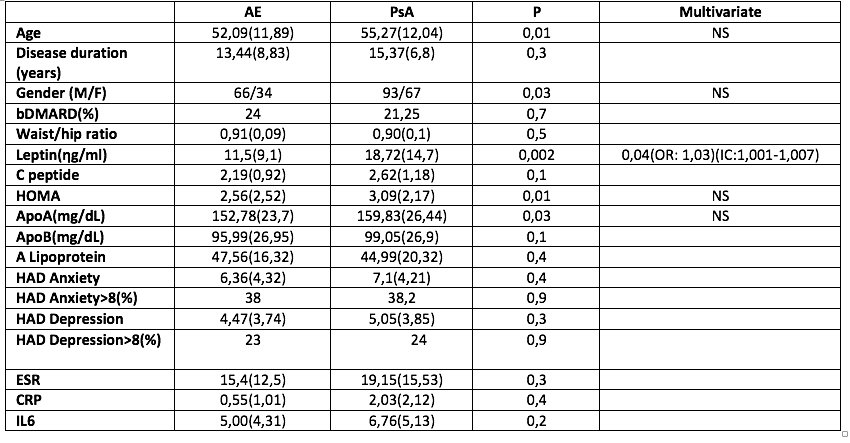
Methods: Prospective longitudinal study that included 100 patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AE) and 160 patients with PsA who attended the outpatient clinics of a tertiary hospital. Patients with PsA who had at least four assessments of the activity in one year, measured by the minimum disease activity (MDA), were included in the study. We compared those patients who met MDA criteria in the four visits compared to the rest of the patients. The tendency to anxiety and depression was evaluated using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) questionnaire. Regarding cardiovascular comorbidity, the waist / hip ratio and the analytical variables were measured: apolipoprotein A, apolipoprotein B, A lipoprotein, C peptide, insulin, insulin resistance (HOMA) and leptin. CRP, ESR and IL-6 were also measured. The age, the disease duration and the treatment used were collected basally. Due to the circadian variation of these determinations, all were collected at the same time. Patients with diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia in treatment or thyroid disease due to the influence on the parameters associated with cardiovascular comorbidity were excluded.
Results: The significant differences between the patients with ankylosing spondylitis and Aps are shown in Table 1. When comparing the patients with PsA that reached a MDA compared to the rest, the following significant differences were found Table 2. Among the variables that make up the MDA concept, only the number of swollen joints (r: 0.22, p < 0.009) and HAQ (r: 0.20, p < 0.01) were correlated with the concentration of leptin . There was no correlation between leptin levels and those of PCR, VSG or IL-6.
Conclusion: In our study, patients with PsA presented a higher concentration of several markers of vascular risk (insulin resistance, apoprotein A and leptin) compared to patients diagnosed with spondylitis. In the PsA, leptin influenced to a greater extent than the emotional factors (anxiety and depression) to reach a prolonged MDA. Leptin correlated with the number of swollen joints but not with acute phase reactants (ESR and CRP) or IL-6. These results could confirm that leptin would promote a low-grade inflammation not detected by the levels of ESR, CRP or IL-6.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gomez-Lechon L, Acosta M, Manzano Canabal G, Compan O, Hidalgo C, Martinez O, Turrión A, del Pino J, Montilla C. Comparison of Comorbidity in Spondyloarthritis: Influence on Inflammatory Activity in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-comorbidity-in-spondyloarthritis-influence-on-inflammatory-activity-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-comorbidity-in-spondyloarthritis-influence-on-inflammatory-activity-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/