Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2227–2264) Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by chronic inflammation of synovial joints with extra articular manifestations. Disease activity indices in Rheumatoid arthritis are composite tools to assess disease activity and ascertain if treatment targets are met. Patient reported outcomes are increasingly recognized in medicine and have been incorporated in RA treatment guidelines. Routine Assessment of Patient Index3 (RAPID3) is a validated patient reported outcome measure calculated in less than 10 seconds, with no need for acute phase reactants. Previous studies comparing RAPID3 with the traditional physician measured disease activity indices have all been outside sub-Saharan Africa. We compared RAPID3 with physician measured indices in RA patients attending the Lagos State University Teaching Hospital (LASUTH) Rheumatology clinic.
Methods: A comparative study of 72 Rheumatoid Arthritis patients who presented to the outpatient Rheumatology clinic. Consenting patients who fulfilled the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis were recruited consecutively. Each participant was required to fill out the Multidimensional Health Assessment Questionnaire (MDHAQ), from which the RAPID3 score was calculated. For the physician-measured disease activity, the DAS 28 ESR, DAS 28 CRP, Simplified Disease Activity Index, and Clinical Disease Activity Index were calculated by the investigator following clinical and laboratory evaluations, then disease activity determined. Historical data about the disease and patient demographics were recorded in a proforma. Data was analyzed with SPSS version 25, using Spearman’s correlations and kappa statistics. A p-value of < 0.05 was considered significant for statistical tests.
Results: The mean age of the study participants was 48.40 ± 14.46 years, with a median of 50 years and a range of 18-79 years. There was a female-to-male ratio of 17:1. There was fair to moderate agreement between RAPID3 and the physician-driven indices in classifying participants into four disease activity categories (k=0.27- 0.52; p< 0.001). This increased to substantial agreement when disease activity was dichotomized into active versus inactive (k=0.63-0.71; p=0.0001). Overall, 83.3%–92.1% of patients who met moderate/high activity criteria according to the physician-measured indices met similar RAPID3 criteria, and 70.6%–100% who met remission/low disease activity criteria according to the physician-measured indices also met similar RAPID3 criteria. Patient-reported disease activity correlated significantly with the physician-measured indices. (r > 0.79, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: RAPID3, although not a perfect substitute for the traditional indices, provides an alternative for Rheumatoid arthritis disease activity assessment, with potential usefulness in busy clinic settings and areas with paucity of Rheumatologists like Nigeria. It has shown significant correlation and substantial agreement with the traditional indices in classifying as active versus inactive disease.
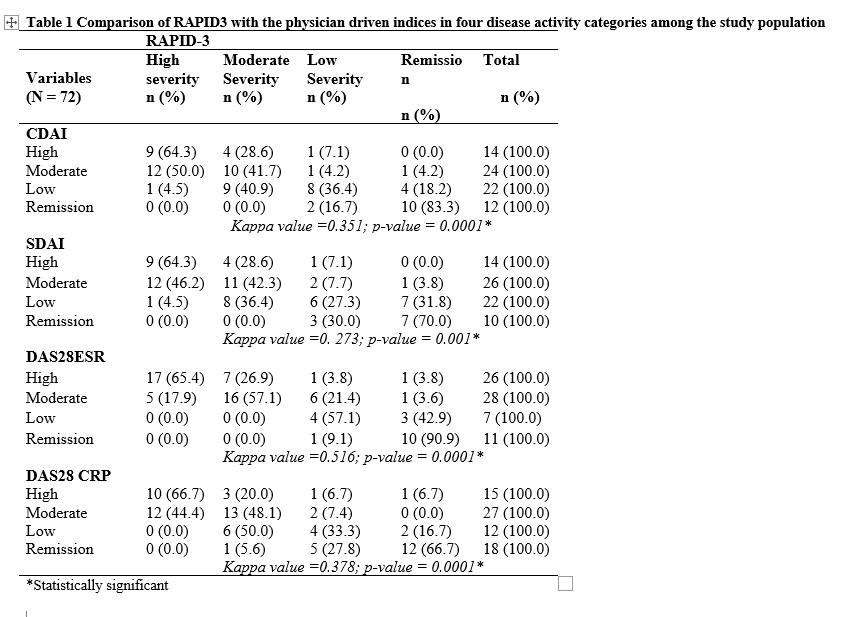 Comparison of RAPID3 with the physician driven indices in four disease activity categories among the study population
Comparison of RAPID3 with the physician driven indices in four disease activity categories among the study population
.jpg) Comparison of RAPID3 with Physician measured indices in classifying as active versus inactive disease in the study population
Comparison of RAPID3 with Physician measured indices in classifying as active versus inactive disease in the study population
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tralagba U, Uhunmwangho C, Adelowo O, Nwankwo H, Altraide D, Aigbokhan E, Itam A, Asekhame O, Olaosebikan H. Comparison of a Patient-Reported Disease Activity Measure with Physician-Based Indices in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients in Nigeria [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-a-patient-reported-disease-activity-measure-with-physician-based-indices-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-in-nigeria/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-a-patient-reported-disease-activity-measure-with-physician-based-indices-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-in-nigeria/
