Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: A number of meta-analyses compare the efficacy of biologics for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, systematic reviews comparing the efficacy of biologics as monotherapy versus combination with DMARDs are rare,1 and none include all currently approved biologics. Our objective was to compare ACR response at 24 weeks in RA patients with an inadequate response to conventional DMARDs (DMARD-IR) receiving approved biologics as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate (MTX).
Methods: A systematic literature review was undertaken to identify RCTs that assessed approved biologic therapies as monotherapy or in combination with MTX in DMARD-IR RA patients. 22 RCTs were identified that evaluated tocilizumab (TCZ), adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, etanercept, golimumab, infliximab, abatacept, or anakinra. ACR responses at 24 weeks were extracted and combined by means of Bayesian network meta-analyses to obtain treatment effect estimates between all interventions included in the analysis, whether directly or indirectly compared. As shown elsewhere,1,2 an assumption was made that the effects of anti-TNF-α agents (aTNFs) are exchangeable. Given this, and the limited data identified for these therapies in monotherapy, aTNF data were pooled.
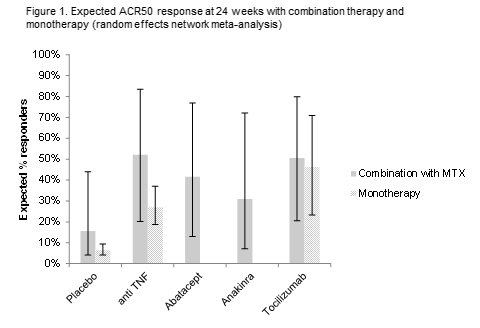
Results: Using random effects models, TCZ + MTX was shown to be comparable to other biologics + MTX across the ACR outcomes. A higher expected treatment effect was seen with TCZ + MTX for ACR70, in line with earlier analyses.3 When comparing biologic monotherapies with biologics + MTX, TCZ showed a comparable likelihood of ACR20, ACR50, and ACR70 response versus TCZ + MTX ([RR 0.98 (95% credible interval [CrI]: 0.70, 1.71)], [RR 0.92 [95% CrI: 0.62, 1.56)], and [RR 1.04 (95% CrI: 0.58, 2.08)], respectively). aTNF as monotherapy was likely to be less efficacious compared to aTNFs + MTX in terms of ACR20 and ACR50 response (probability better=13% [RR 0.71 (95% CrI: 0.48, 1.64)] and probability better=5% [RR 0.52 (95% CrI: 0.31, 1.25)], respectively). Between monotherapies, the chance of ACR20, ACR50, and ACR70 response for TCZ was found likely to be greater compared to responses for aTNFs (probability better=88%, 97%, and 96%, respectively), in line with recently reported outcomes of a trial4 comparing TCZ and adalimumab.
Conclusion: Our network meta-analysis, involving indirect comparison of trial findings, suggests that in DMARD-IR patients, TCZ + MTX shows comparable efficacy to other biologics + MTX. In monotherapy, TCZ is likely to have a greater efficacy than aTNFs and shows comparable efficacy compared to TCZ + MTX, whereas aTNFs are likely to show lower efficacy compared to aTNFs + MTX.
References
1. Nixon Rheumatology. 2007;46:1140; 2. Salliot Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:266; 3. Bergman Semin Arthritis Rheum 2010;39:425; 4. Gabay Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71(Suppl 3):152.
Disclosure:
F. Buckley,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
5;
A. Finckh,
BMS, Pfizer,
2,
BMS, Abbott, Roche Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer,
5,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
8;
T. W. Huizinga,
Merck, UCB, BMS, Biotest AG, Pfizer, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, Abbott, Crescendo Bioscience, Nycomed, Axis-Shield Diagnostics,
5,
Merck, UCB, BMS, Biotest AG, Pfizer, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, Abbott, Crescendo Bioscience, Nycomed, Axis-Shield Diagnostics,
8;
F. Dejonckheere,
F. Hoffman-La Roche,
3;
J. P. Jansen,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
5.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-efficacy-of-biologics-as-monotherapy-and-in-combination-with-methotrexate-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-an-inadequate-response-to-conventional-dmards-a-network-meta-analysis/