Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The frequency and types of comorbidities, causes of hospitalization, and the differences among clinical phenotypes in patients with IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) have not been explored thoroughly.
We aimed to disclose the types of comorbidities and causes of hospitalizations and their impact in a cohort of IgG4-RD patients.
Methods: We performed a retrospective study. IgG4-RD patients had to fulfill the Comprehensive Diagnostic Criteria for IgG4-RD and/or the Consensus Statement on Pathology and/or the 2019 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for IgG4-RD. Clinical variables, comorbidities and causes of hospitalizations were retrieved from the medical charts in a standardized manner. Patients were classified in clinical phenotypes: Group 1 (pancreato-hepato-biliary), Group 2 (retroperitoneal/aortic), Group 3 (head and neck-limited), Group 4 (Mikulicz/systemic) and Group 5 (undefined). The Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) and the Rheumatic Disease Comorbidity Index (RDCI) were calculated at last follow-up.
Results: We included 89 patients with a mean age at diagnosis of 49.6 ± 16 years, 47 (52.8) were male. Twenty-four (27%) belonged to Group 1, 9 (10.1%) to Group 2, 25 (28.1%) to Group 3, 24 (27%) to Group 4 and 7 (7.9%) to Group 5.
At least one comorbidity was detected in 85 (95.5%) patients (Table 1). Type 2 diabetes was more frequent in Group 4, type 3c diabetes in Group 1 and 4, obesity in group 3 and 5, thrombosis in Group 5 and malignancies in Group 1 (Table 2).
Forty-five (50.6%) patients were hospitalized during follow-up, 22 (24.7%) once, 15 (16.9%) twice and 8 (9%) ≥ 3 times. Causes of first hospitalization (non-exclusive) were: relapse in 28 (62.2%), infection in 16 (35.6), treatment complications in 5 (11.1%) and others in 5 (11.1%). The median days of hospitalization was 1 (IQR 0-11.5). Ten (22.2%) patients were taking prednisone at the time of hospitalization with a median dose of 20 mg (IQR 7.5-45) and 6 (14%) immunosuppressants. Only 4 patients required intensive care unit admission. Hospitalization was more common in patients from Group 1 and 5. Group 5 had the longest days of hospitalization.
The median score of the CCI and RDCI at last follow-up was 3 (IQR 1-4) and 1 (IQR 0-2), respectively. Patients who ever had a hospitalization were more likely to have damage attributed to IgG4-RD at last follow-up (OR 2.8, 95% CI 1.2-6.8, p=0.02). Two patients died during a median follow-up of 30 (IQR 18-63) months.
Conclusion: Comorbidities are very frequent in patients with IgG4-RD and differed according to clinical phenotype. Relapses were a common cause of hospitalization. Hospitalization was more frequent in patients from Group 1 and 5, and they were associated with damage accrual.
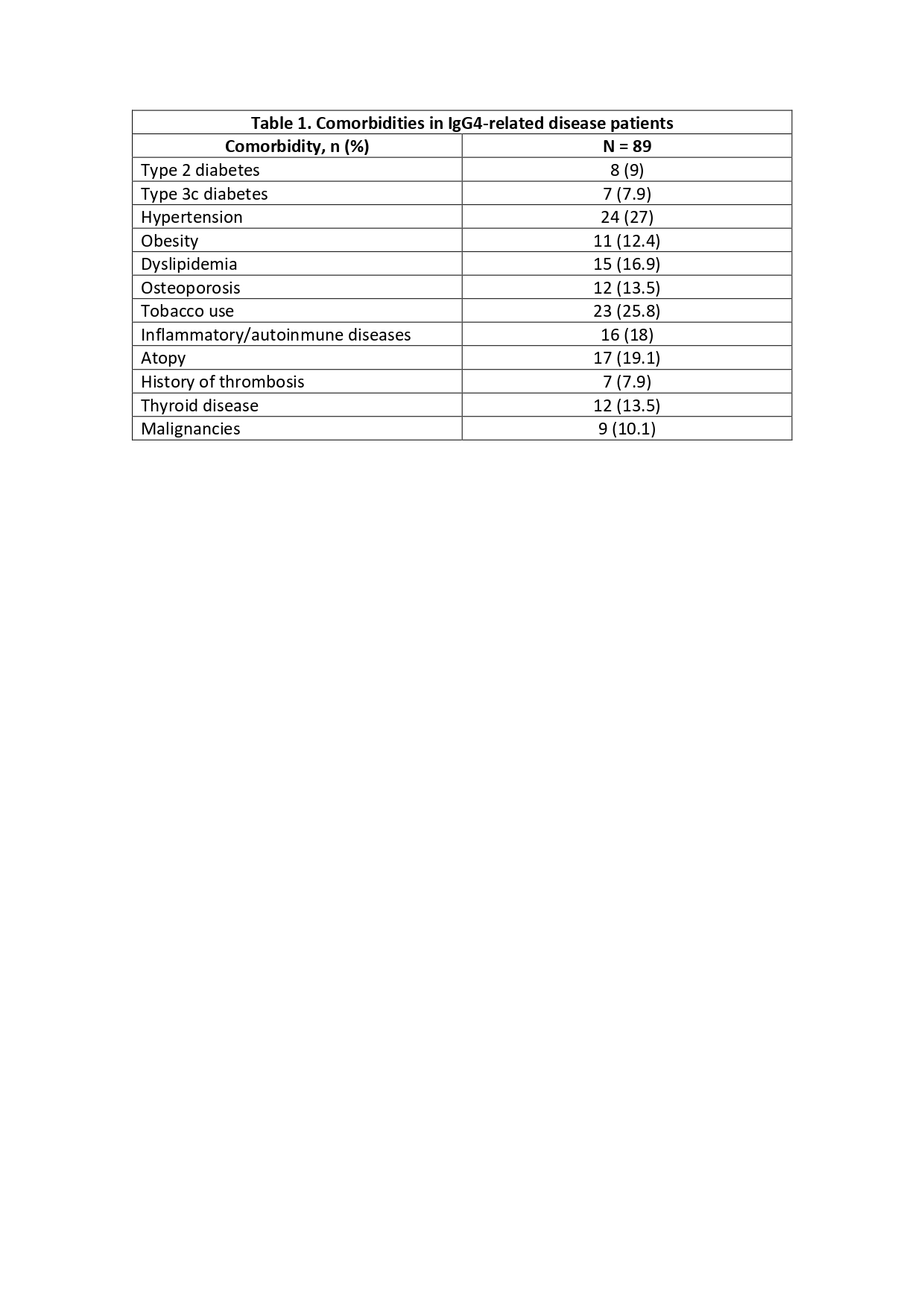 Table 1. Comorbidities in IgG4-related disease patients
Table 1. Comorbidities in IgG4-related disease patients
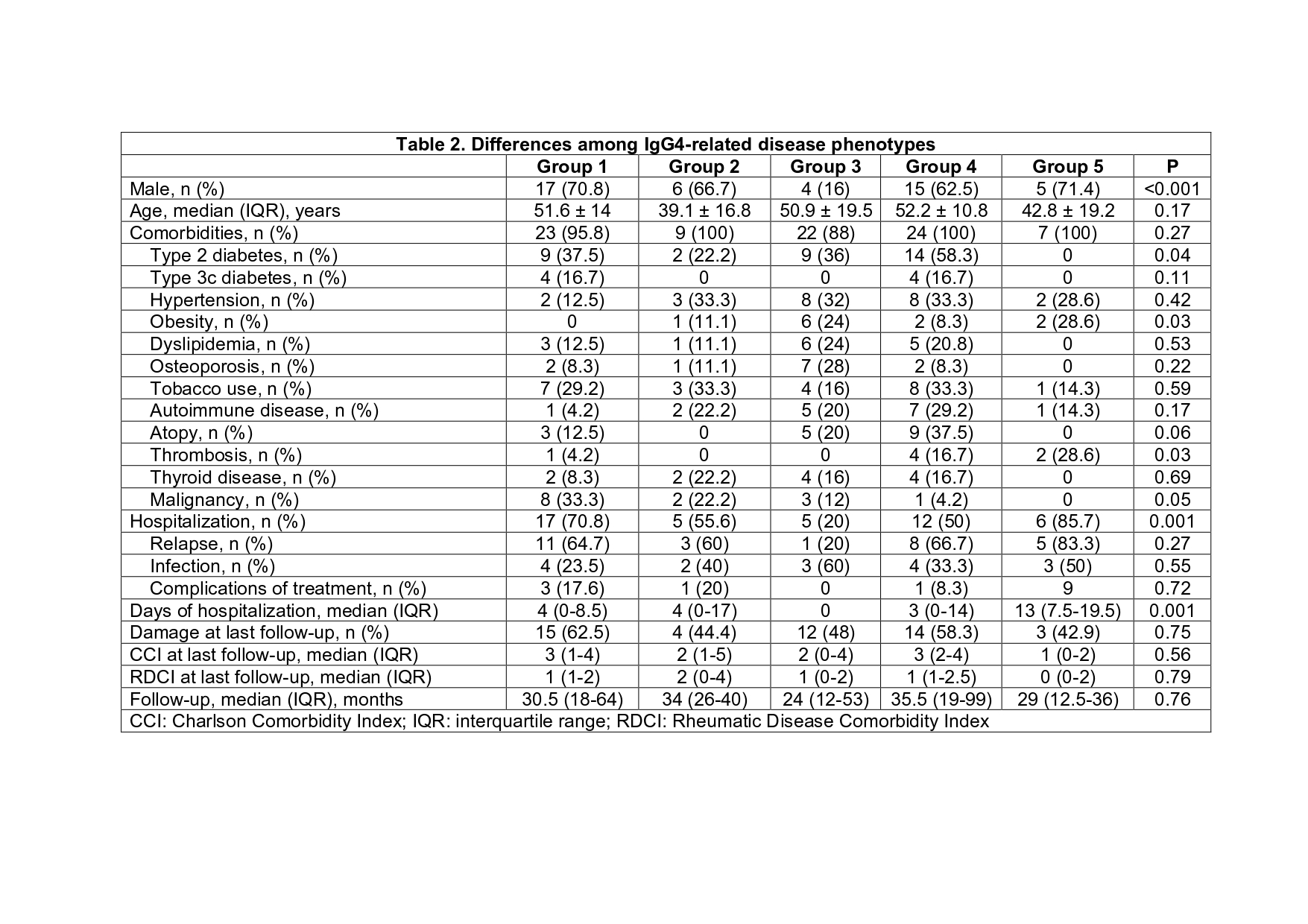 Table 2. Differences among IgG4-related disease phenotypes
Table 2. Differences among IgG4-related disease phenotypes
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Faz-Muñoz D, Martin-Nares E, Hernández-Delgado A, Hernandez-Molina G. Comorbidities and Causes of Hospitalizations in a Cohort of IgG4-Related Disease Patients from a Single Center [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comorbidities-and-causes-of-hospitalizations-in-a-cohort-of-igg4-related-disease-patients-from-a-single-center/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comorbidities-and-causes-of-hospitalizations-in-a-cohort-of-igg4-related-disease-patients-from-a-single-center/
