Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
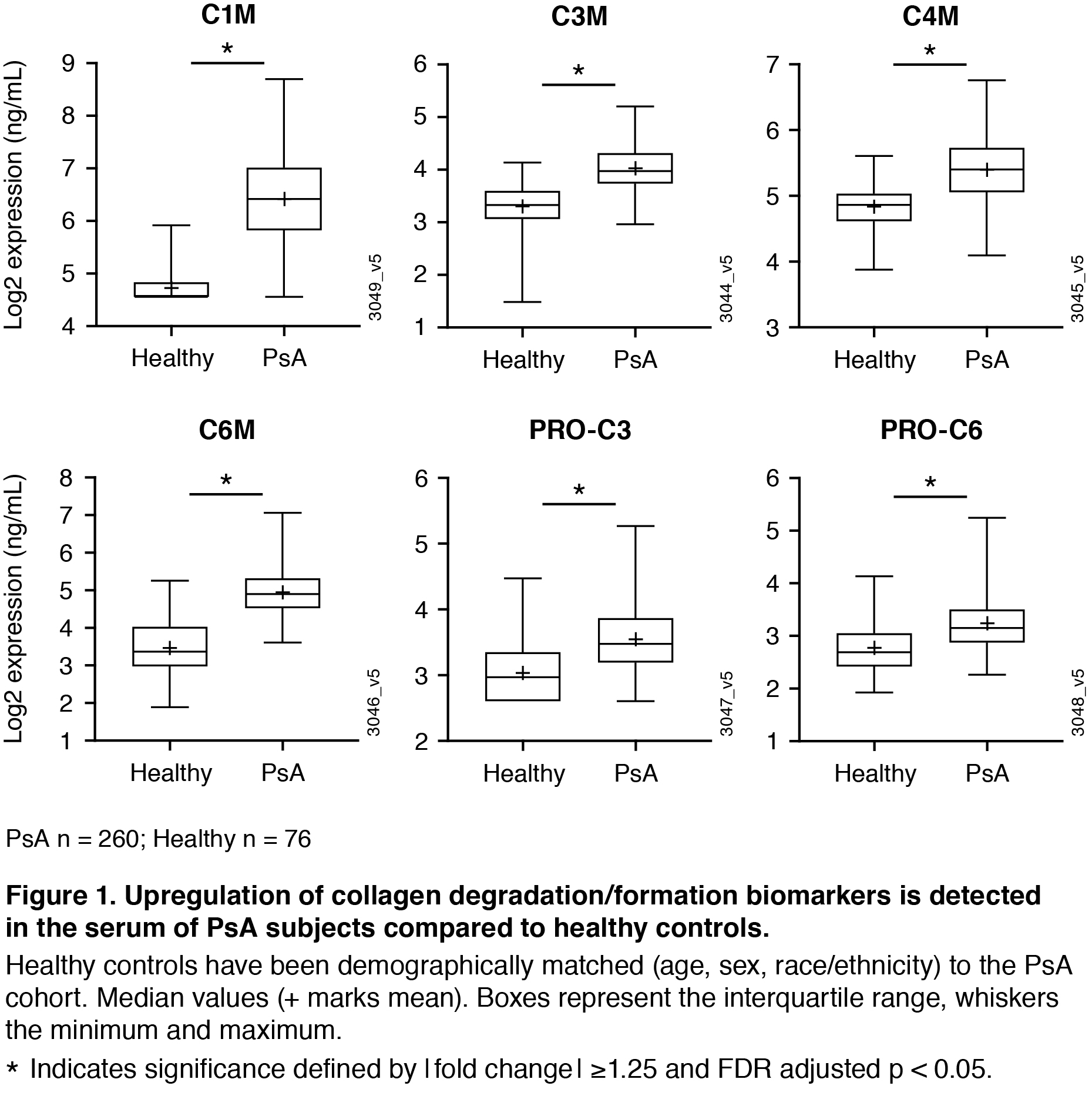
Background/Purpose: Guselkumab (GUS), an interleukin-23p19-subunit monoclonal antibody, demonstrated efficacy compared to placebo (PBO) in reducing skin and musculoskeletal signs and symptoms in patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in two phase-3 studies, DISCOVER 1 & 2, and in retarding structural damage in DISCOVER 2.1,2 Here we evaluate tissue-derived extracellular matrix (ECM) products3,4 in serum of PsA patients in the DISCOVER 2 study and their relationship with radiographic damage, clinical response, and impact of treatment.
Methods: In DISCOVER 2, patients were treated with GUS 100 mg at Week (w) 0, 4, then every 8w (q8w); GUS 100mg every 4w (q4w); or matching PBO. At w24, PBO subjects were crossed-over to GUS q4w. 11 serum biomarkers of ECM collagen formation (PRO-C1, PRO-C2, PRO-C3, PRO-C4, PRO-C6) and degradation (C1M, C2M, C3M, C4M, C6M, and COL10) were measured (by Nordic Bioscience) in a subset of 260 patients from the DISCOVER 2 program at Weeks 0, 4, 24, & 52 and in 76 healthy controls matched for age, sex, and ethnicity. PsA patients were selected randomly, though enriching for subjects with greatest radiographic changes, at Weeks 24 and 52. Significance defined by P< 0.05 and |fold difference| ≥ 1.25.
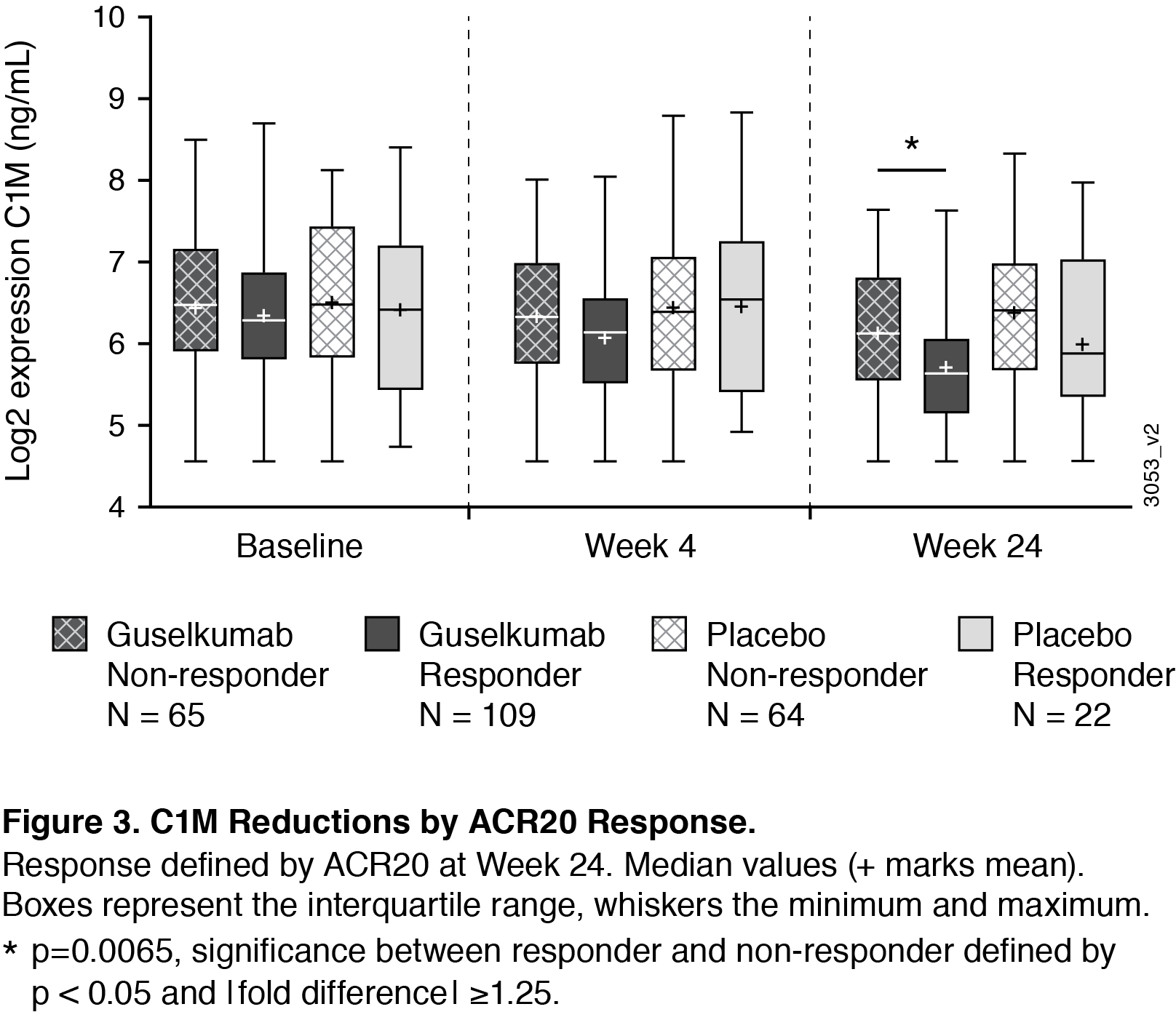
Results: At baseline, collagen degradation markers C1M, C3M, C4M, C6M and collagen formation markers PRO-C3 and PRO-C6 were significantly higher in PsA patients compared to matched healthy controls (Figure 1). Baseline C3M, C4M, and C6M were positively correlated to baseline skin and joint disease; baseline C1M, C3M, C4M, C6M, and PRO-C1 were positively correlated to baseline radiographic damage (data not shown). Levels of C1M (a maker indicating breakdown of collagen type I, the major collagen subtype in the bone) were significantly decreased after 24w treatment with GUS (Figure 2), reaching significant differences from placebo with the GUS 100 mg q4w group. For the PBO patients who crossed over to GUS at w24, there was also a reduction in this marker observed at w52 (Figure 2). In patients treated with GUS or PBO, there were not significant differences in baseline expression levels of the analytes in responders (patients achieving ACR20 at w24) compared with non-responders. However, ACR20 responders in the combined GUS group had a significantly greater reduction in C1M levels compared to non-responders (Figure 3).
Conclusion: This work provides evidence that collagen biomarkers in serum are dysregulated in patients with PsA compared to healthy controls, and that GUS impacts levels of these proteins. Importantly, C1M serves as a biomarker that tracks with joint response. We observed a greater reduction in C1M in ACR responders compared to non-responders, providing insight into how GUS may be working to protect from degradation of bone in PsA.
References:
- Deodhar A et al. Lancet. 2020;395:1115
- Mease P et al. Lancet. 2020;395:1126
- Gudmann N. S. et al. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017;35: 653–659
- Sardar S et al. Annals of the Rheum Dis 2019;78 (Suppl 2): https://ard.bmj.com/content/78/Suppl_2/867.1
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schett G, Loza M, Palanichamy A, FitzGerald O, Ritchlin C, Baribaud F, Sweet K. Collagen Turnover Markers Are Associated with Active Psoriatic Arthritis and Decrease with Guselkumab Treatment in a Phase-3 Clinical Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/collagen-turnover-markers-are-associated-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-and-decrease-with-guselkumab-treatment-in-a-phase-3-clinical-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/collagen-turnover-markers-are-associated-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-and-decrease-with-guselkumab-treatment-in-a-phase-3-clinical-trial/