Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (1990–2014) Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Pegloticase significantly reduces serum uric acid (sUA) values in patients with refractory gout. Co-use of methotrexate (MTX) improves efficacy and safety of pegloticase by reducing the development of anti-drug antibodies1. Because MTX is primary excreted through the kidney, there has been concern that MTX use may increase adverse effects in patients with renal impairment. The present study was designed to examine effects of co-using pegloticase with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), another immunomodulatory (IMM) proven to extend pegloticase efficacy2.
Methods: This is a longitudinal analysis using the Optum Clinformatics® DataMart®, 2016-2024. The study participants included new users of pegloticase; the first pegloticase infusion defined the index date. Based on the presence of IMM treatment ±90 days from the index date, we defined three exposure groups: MTX co-therapy group, MMF group and pegloticase monotherapy (IMM nonusers). We described pegloticase duration of use, patterns of sUA values and estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR). Analyses were stratified by baseline eGFR (60+ vs. < 60 ml/min/1.73m2).
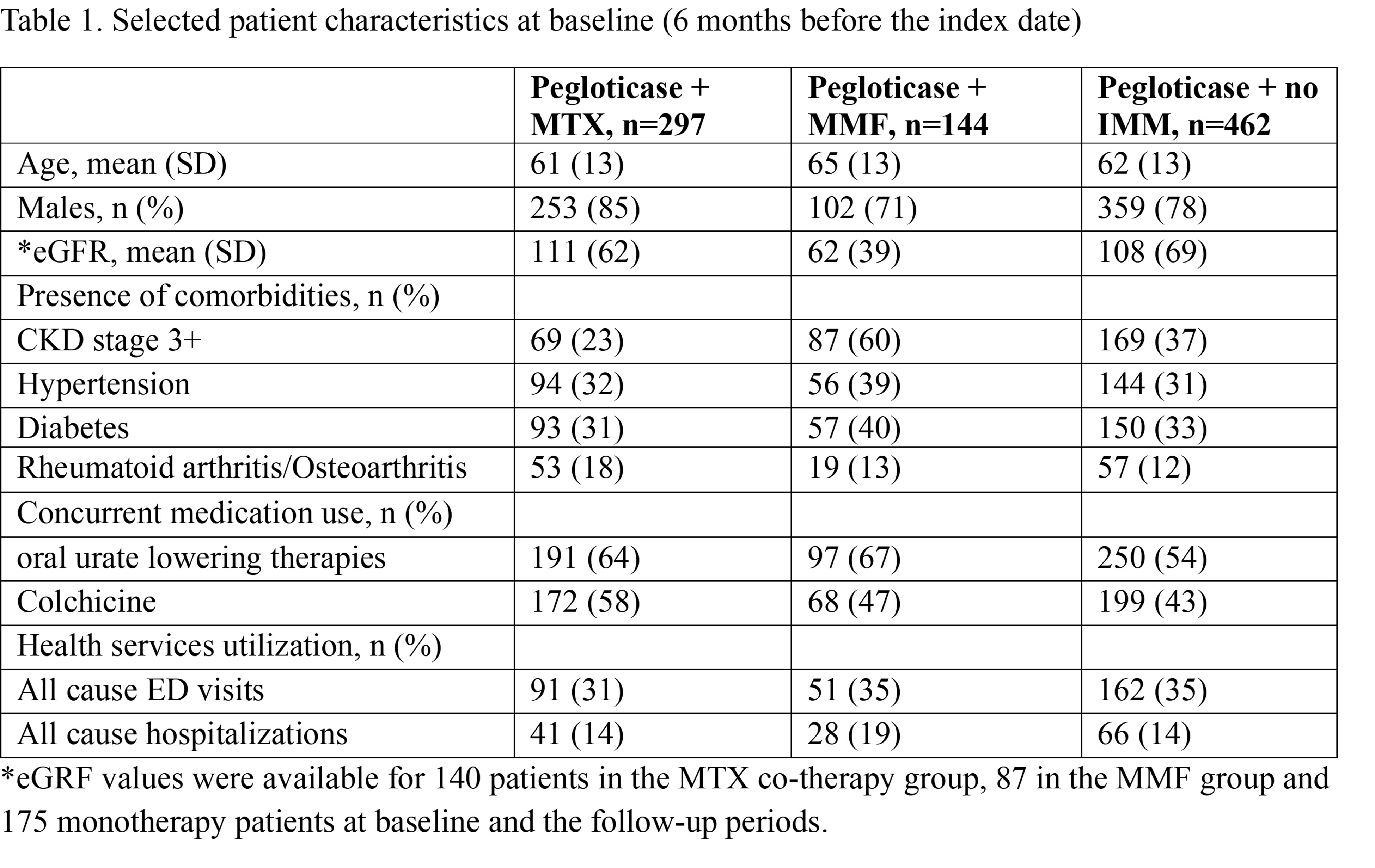
Results: We identified 903 pegloticase new users who met the inclusion criteria (297 in the MTX co-therapy group, 144 in the MMF group and 462 monotherapy group). The MMF co-therapy group was older, had a high prevalence of comorbid CKD stages 3+ (60%), as well as higher proportions of all-cause hospitalizations and comorbidities than the other two groups (Table 1). By comparison, the MTX group had 23% and the monotherapy group had 37% with advanced CKD. The median number of pegloticase infusions was 11 for the MMF group (IQR: 4-18), 8 for the MTX group (IQR: 3-15) and 6 for the immunomodulator nonusers (IQR: 2-14). The mean sUA levels changed from over 7 mg/dL at baseline, to ~2 mg/dL between 1-6th infusions and ~1mg/dL between 7th infusion and follow-up end (Figure 1). The mean eGFRs were stable [MTX group: 111 (SD: 62) ml/min/1.73m2 at baseline to 105 (SD: 53) during the follow-up; MMF group: 62 (39) to 60 (34); monotherapy: 108 (69) to 108 (71)]. Stratified analyses produced consistent findings.
Conclusion: 49% of pegloticase patients were treated with immunomodulating co-therapy, among which MMF was 33% of IMM use, with most patients going on MMF having advanced CKD. Pegloticase duration, effectiveness in terms of sUA reduction and eGFR stability in the MMF group were similar to the MTX group. The co-therapy of MMF and pegloticase may be an option for patients with pre-existing renal impairment. Reference: 1Botson et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2023. 2Khanna et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2021.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhang T, Saag K, Qazi Y, Marder B, Lamoreaux B. Co-Use of Mycophenolate Mofetil with Pegloticase Yielded Similar Clinical Outcomes as the Co-Use of Methotrexate [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/co-use-of-mycophenolate-mofetil-with-pegloticase-yielded-similar-clinical-outcomes-as-the-co-use-of-methotrexate/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/co-use-of-mycophenolate-mofetil-with-pegloticase-yielded-similar-clinical-outcomes-as-the-co-use-of-methotrexate/

.jpg)