Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Diagnosing arthritis remains challenging in a subset of patients despite advances in imaging, serological markers, and clinical scoring systems. Ultrasound-guided synovial biopsy (USG-SB) stands as a potentially valuable tool in clarifying diagnoses and guiding treatment in atypical or refractory joint presentations.The objective is to evaluate the clinical utility and patient-reported outcomes (PROMs) of USG-SB in patients with refractory arthritis in a real-world, secondary care setting.
Methods: We conducted a case series of seven patients who underwent knee USG-SB based on clinical indication by the treating rheumatologist. Histological samples were evaluated using the Krenn synovitis score, with scores < 5 indicating non-inflammatory or degenerative pathology, and scores ≥5 suggestive of active rheumatic disease. PROMs were assessed 7–10 days post-procedure via structured questionnaire.
Results: USG-SB provided diagnostic clarification or therapeutic guidance in 5 of 7 cases (71%). Inflammatory histological features (Krenn ≥5) were found in 4 patients and led to treatment adjustments in 3 cases. In one case, CD marker analysis guided selection of a biologic agent. Two patients were reclassified as having non-inflammatory arthritis, avoiding unnecessary immunosuppressive treatment. PROMs showed that 6 out of 7 patients (86%) reported clear and sufficient pre-procedure information, and 6 out of 7 experienced minimal or no pain during the biopsy, with a median visual analogic score (VAS) of 0. Median VAS in the first 24 hours was 1. No patients reported functional limitations or infection at the puncture site. Most patients (86%) resumed normal activities within 3 days. All patients rated healthcare staff attention as “excellent,” and 6 out of 7 (86%) indicated they would repeat the procedure if needed.
Conclusion: USG-SB is a safe, well-tolerated, and clinically useful procedure in patients with refractory arthritis. It contributed to diagnostic clarification and therapeutic decision-making in most cases, with minimal discomfort reported by patients. Its implementation in secondary care centers may help expand access to precision rheumatologic care.
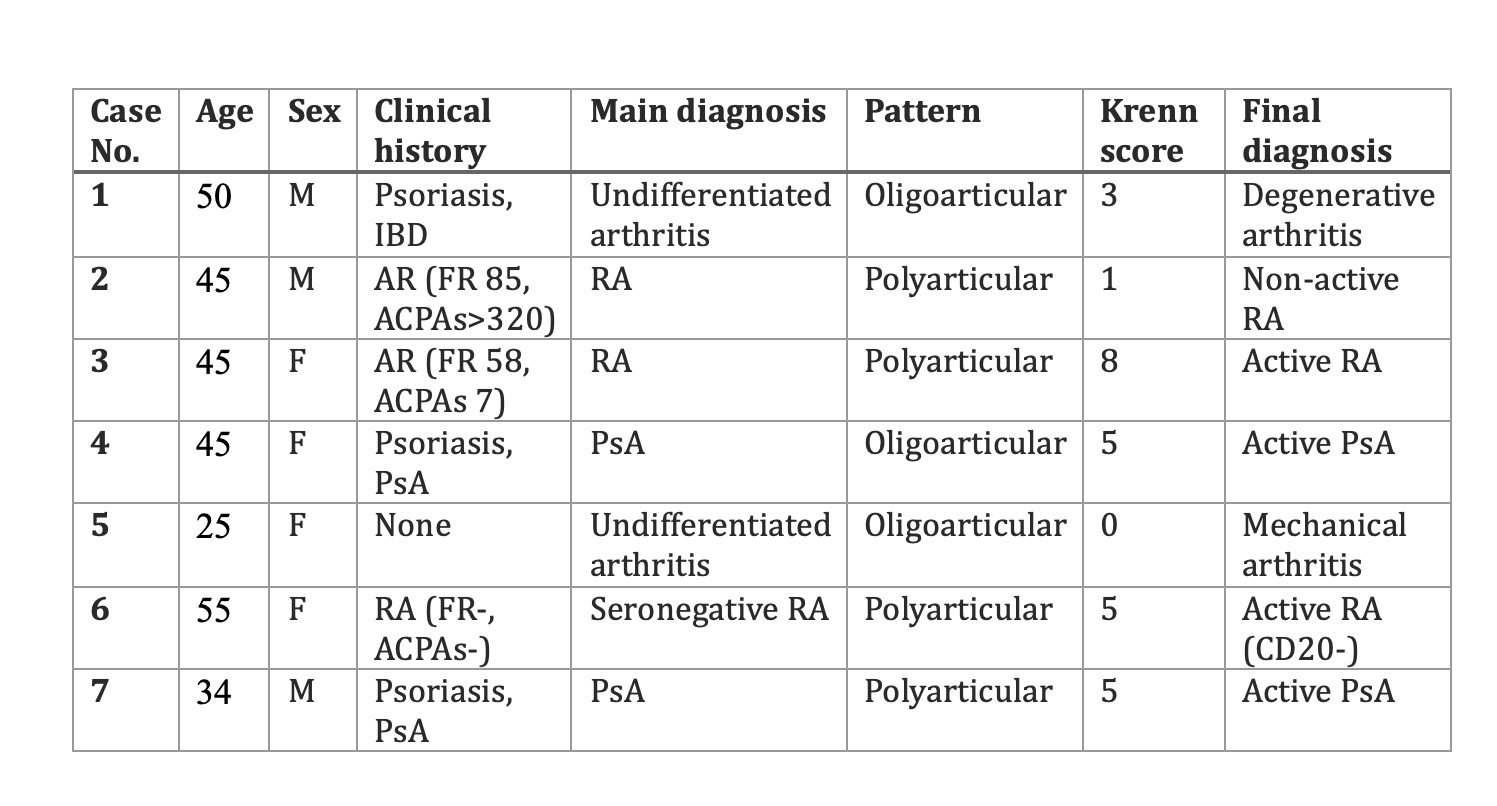 Figure 1. Clinical and histological features of patients undergoing ultrasound-guided synovial biopsy (SGB).
Figure 1. Clinical and histological features of patients undergoing ultrasound-guided synovial biopsy (SGB).
RA: Rheumatoid arthritis; PsA: Psoriatic arthritis; RF: Rheumatoid factor; ACPA: Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Paredes Romero M, Castañeda Estévez E, Steiner M, Algarra- San José M, Acosta A, Cobo-Ibáñez T, De la Cámara I, Esteban Vázquez A, Richi P, Romero-Bogado M, Trives L, Vergara-Dangond C, palomar-Ramos J, Muñoz S. Clinical Utility and Patient Experience of Ultrasound-Guided Synovial Biopsy in Refractory Arthritis: A Case Series from a Secondary Care Center [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-utility-and-patient-experience-of-ultrasound-guided-synovial-biopsy-in-refractory-arthritis-a-case-series-from-a-secondary-care-center/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-utility-and-patient-experience-of-ultrasound-guided-synovial-biopsy-in-refractory-arthritis-a-case-series-from-a-secondary-care-center/
