Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rituximab (RTX) is often used to treat IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), but real-world data on clinical outcomes remain limited. Defining time to relapse and predictors of relapse in a large cohort would guide management strategies. We aimed to evaluate clinical outcomes of patients with IgG4-RD treated with RTX and identify baseline factors associated with risk of relapse.
Methods: We performed a cohort study based on a prospective IgG4-RD registry. We included patients who fulfilled the 2019 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria. Index treatment with RTX was defined as the first RTX administered after registry enrollment, between 1/1/08 and 10/31/23, for active disease (newly-diagnosed or relapsing) that met no exclusion criteria. Exclusion criteria were B cell depletion in the 6 months prior to index date, B cell depletion 6-12 months prior to index date without B cell repopulation, and malignancy or other autoimmune rheumatic disease treated with radiation, immunotherapy, or systemic immunosuppression in the 2 years prior to index date.
Demographics, disease features, and laboratory values at the index date and outcomes following RTX were extracted by medical records review. Among patients whose first-ever treatment with RTX was on the index date, a Cox proportional hazards model was used to estimate hazard ratios (HR) for relapse. Patients were censored at loss to follow-up or prophylactic re-treatment with RTX (e.g., remission maintenance or partial response to initial RTX course). For laboratory values (continuous predictors), HR for were calculated by comparing top quartiles to bottom quartiles.
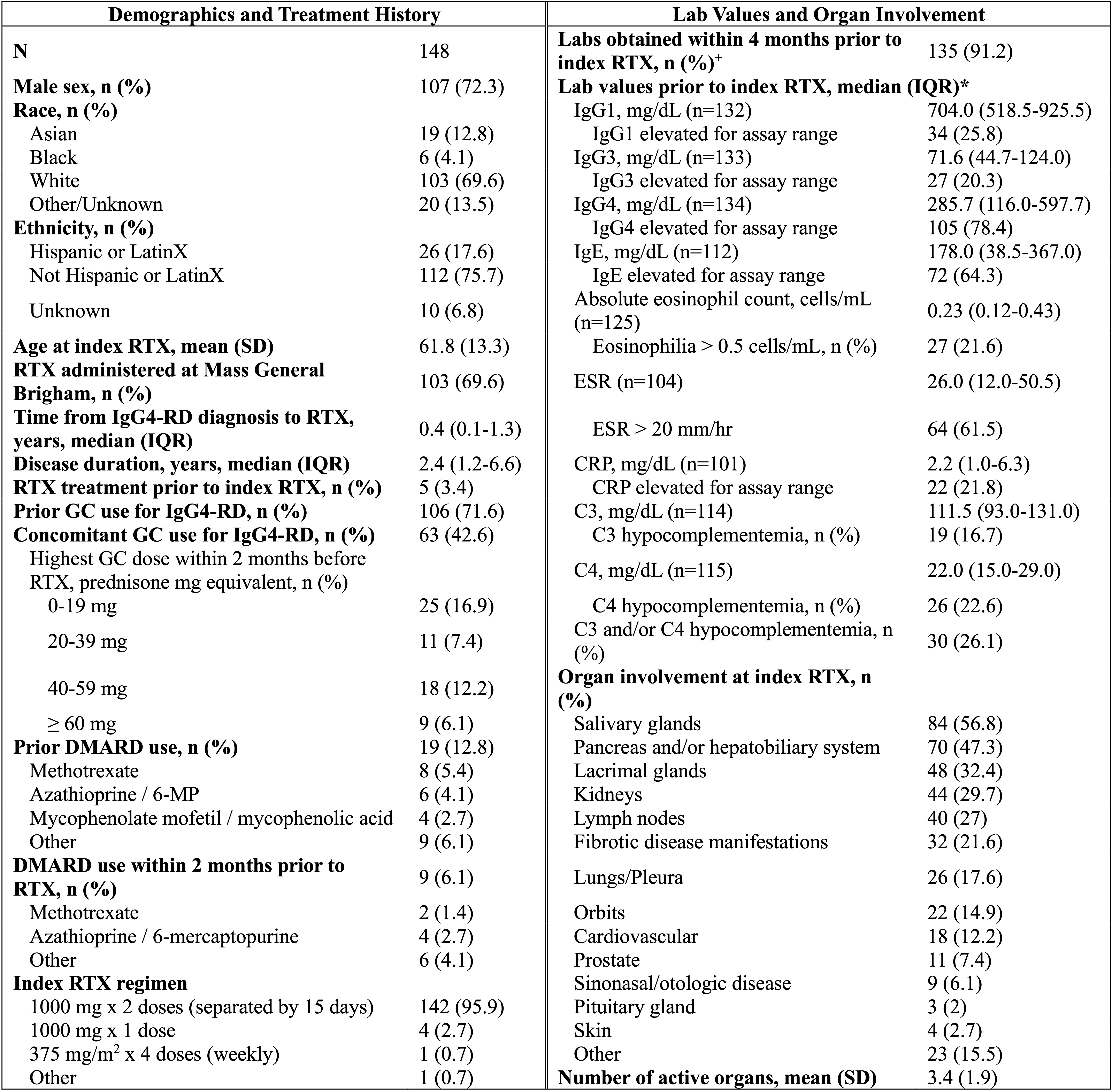
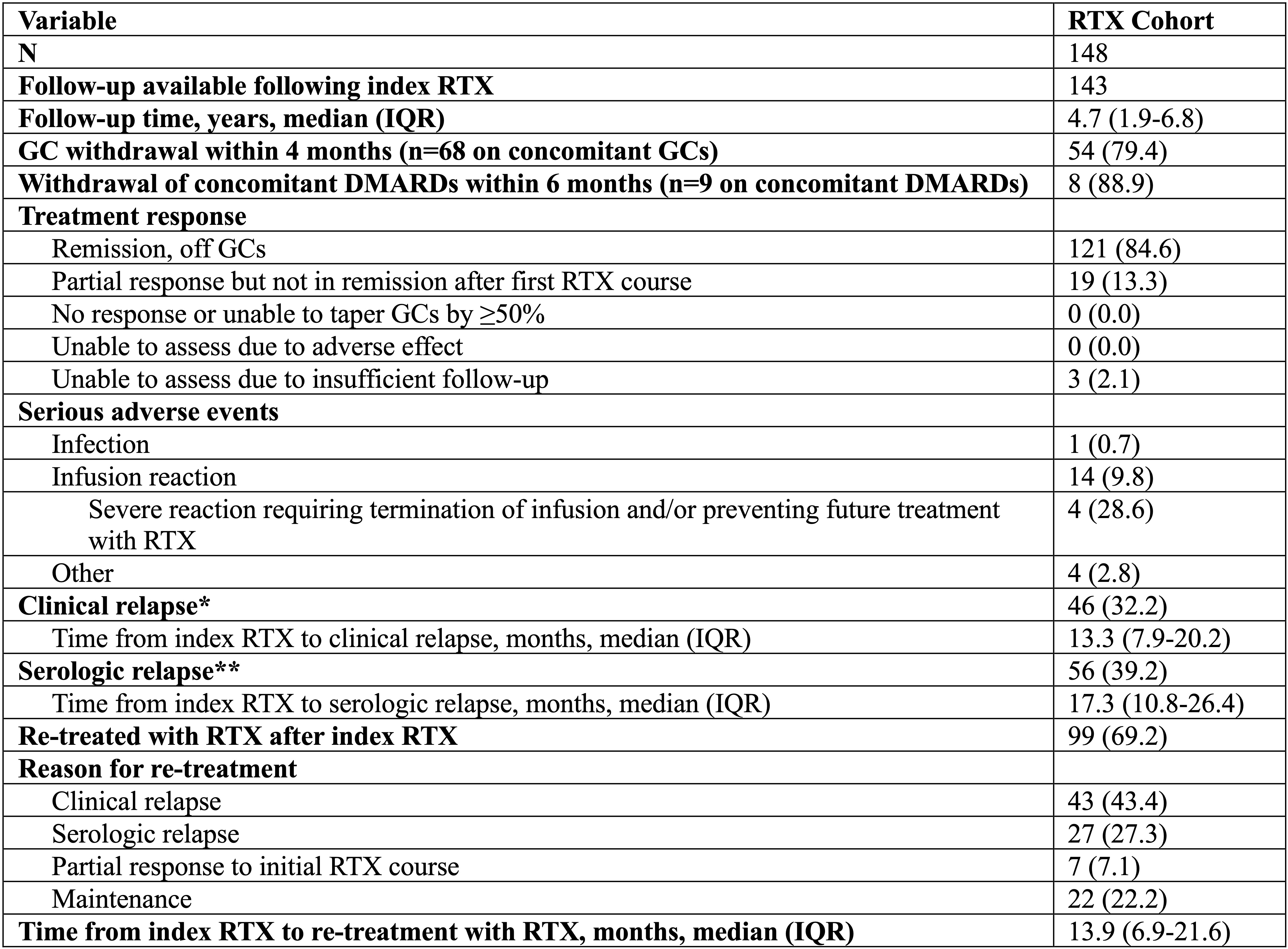
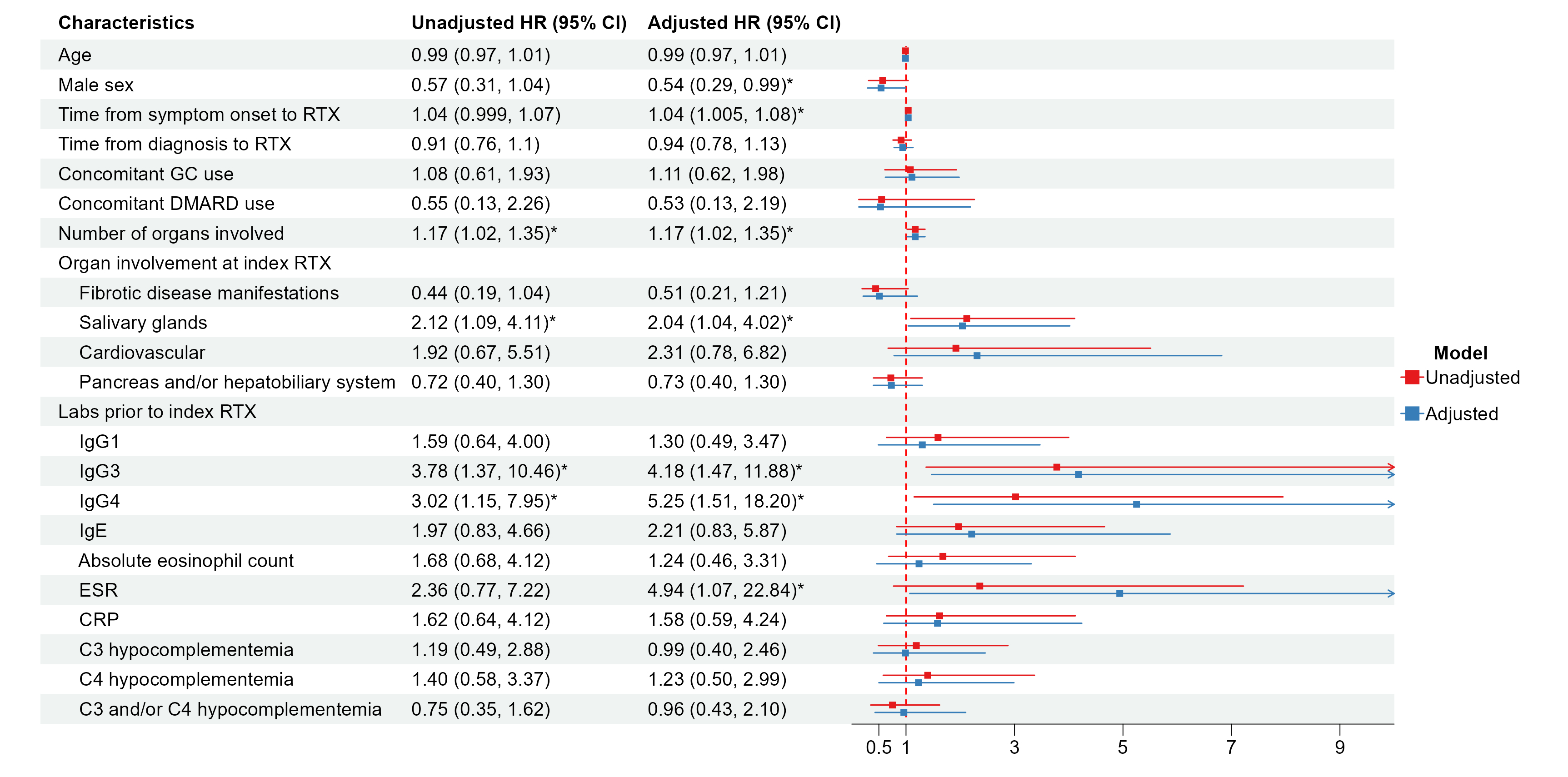
Results: 148 patients were included. Demographics and disease features are shown in Table 1. 107 (72%) were male, and median (IQR) disease duration was 2.4 (1.2-6.6) years. The most common organs involved at the time of index RTX were the salivary glands (57%), pancreas/hepatobiliary system (47%), lacrimal glands (32%), and kidneys (30%). Follow-up was available on 143/148 (97%) patients, with a median follow-up of 4.7 years after index treatment. Of these, 121 (85%) achieved complete remission and 19 (13%) achieved partial responses (Table 2). Clinical relapses occurred in 46 (32%) patients (median time to relapse: 13.3 months). 99 (69%) patients were re-treated with RTX (median time to re-treatment: 13.9 months). Baseline factors associated with relapse after RTX included disease duration (adjusted HR [95% CI] 1.04 [1.01, 1.08]), number of organs involved (1.17 [1.02, 1.35]), salivary gland involvement (2.04 [1.04, 4.02]), serum IgG3 (4.18 [1.47, 11.88]), serum IgG4 (5.25 [1.51, 18.20]), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (4.94 [1.07, 22.84]). Male sex was inversely associated with relapse (0.54 [0.29, 0.99]) (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Nearly all patients with IgG4-RD respond to RTX, but relapses are common. We confirmed prior observations and identified novel risk factors for relapse, including female sex and salivary gland disease. Given that IgG4-RD is more common and severe in males, the finding of a lower risk of relapse among male patients in this study is intriguing. These demographic and disease-specific features associated with relapse may guide management decisions following treatment with RTX.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Katz G, Wallace Z, McMahon G, Jha I, Fernandes A, Jiang B, Zhang Y, Choi H, Perugino C, Stone J. Clinical Outcomes and Predictors of Relapse in Patients with IgG4-Related Disease Treated with Rituximab: A Real-World Experience [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-outcomes-and-predictors-of-relapse-in-patients-with-igg4-related-disease-treated-with-rituximab-a-real-world-experience/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-outcomes-and-predictors-of-relapse-in-patients-with-igg4-related-disease-treated-with-rituximab-a-real-world-experience/