Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) is a complication of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) that occurs in 50 percent of patients. LN serves as an important predictor of mortality in SLE and is the most common cause of death in these patients. Despite recent guidelines and treatment options, 20 percent of patients progress to having end stage kidney disease. Additionally, patients with LN face a six-fold higher risk of mortality compared to the general population. The aim of this study is to compare clinical characteristics, readmission rates, and outcomes in SLE patients with and without LN using data from a national database.
Methods: We analyzed data from the National Readmission Database spanning the years 2016 to 2021, identifying cases of SLE and Renal involvement using ICD-10 codes M32 for SLE M3214 and M3215 for renal involvement. The primary objective of the study is to report outcomes. Subsequently, demographic and clinical characteristics, including age, gender, comorbidities, mortality rates, length of stay, and healthcare charges, were extracted and analyzed. Statistical analyses, including chi-square tests and t-tests, were performed to examine the association, with p-values < 0.05 considered statistically significant.
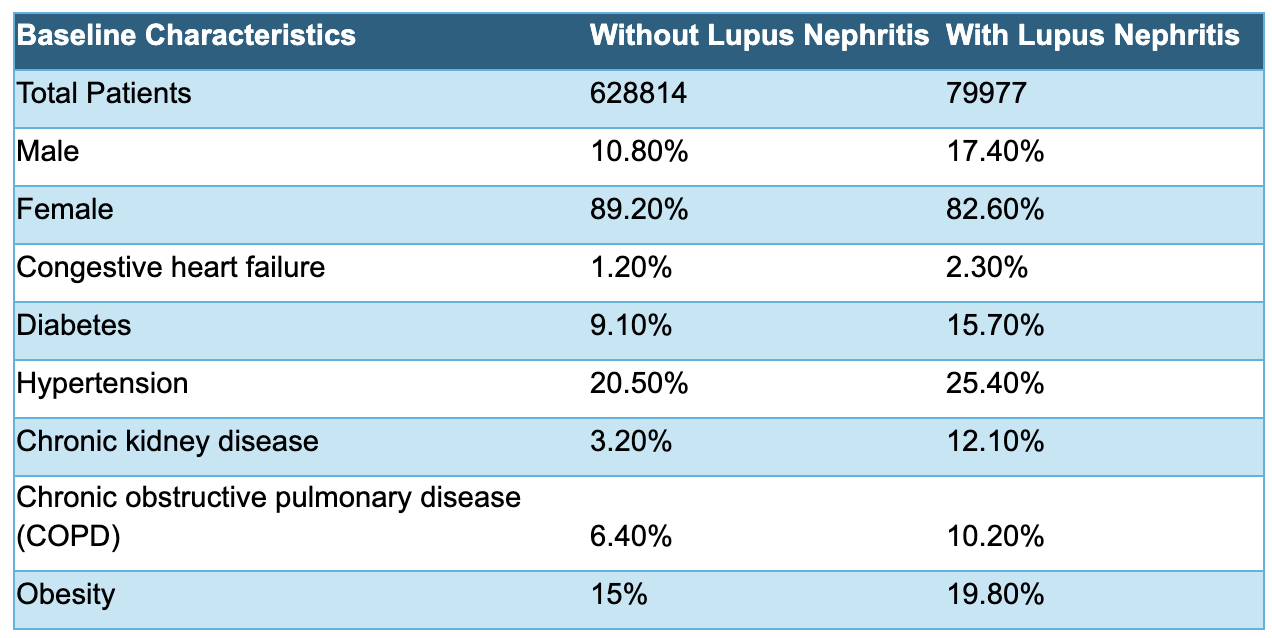
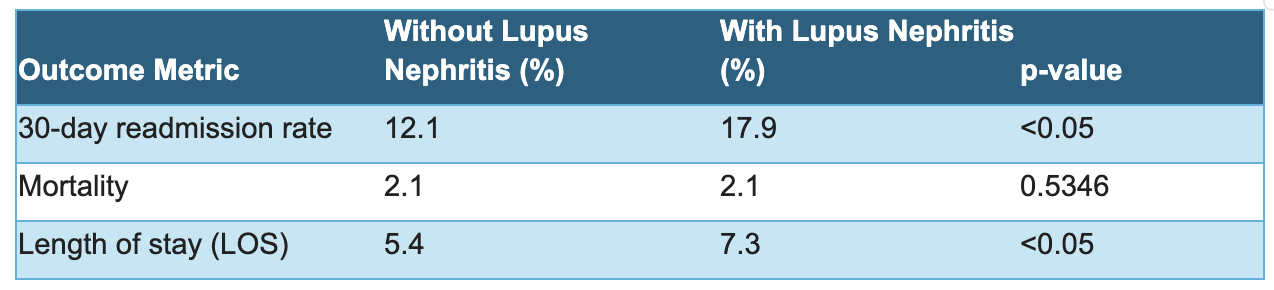
Results: We identified 79,977 patients with LN and 628,814 without LN. The majority in both groups were female ( >80%). The LN group had a higher incidence of medical comorbidities when compared to those without LN (congestive heart failure 2.3% vs 1.2%; diabetes 15.7% vs 9.1%; hypertension 25.4% vs 20.5%; chronic kidney disease 12.1% vs 3.2%; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 10.2% vs 6.4%; obesity 19.8% vs 15%). There was no statistically significant difference in mortality rates between both groups. The LN group experienced higher rates of 30-day readmission (17.9% vs. 12.1%; p < 0.05) and longer LOS (7.3 days vs. 5.4 days; p < 0.05) compared to those without LN.
Conclusion: Although there was no significant difference in mortality between those with LN vs those without LN, LN patients had both higher rates of 30-day readmission and longer LOS compared to those without LN. These patients may benefit from close monitoring; however, future studies are necessary.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Patel K, Chaudhary S, Bhimani S, Deshpande Y, Hope L, Rojulpote C. Clinical Characteristics, Readmission Rates, and Outcomes in Lupus Patients with and Without Nephritic Involvement: Analysis from a National Database [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-readmission-rates-and-outcomes-in-lupus-patients-with-and-without-nephritic-involvement-analysis-from-a-national-database/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-readmission-rates-and-outcomes-in-lupus-patients-with-and-without-nephritic-involvement-analysis-from-a-national-database/