Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Abstracts: Osteoporosis & Metabolic Bone Disease – Basic & Clinical Science (0445–0448)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:45AM-10:00AM
Background/Purpose: This study is an ongoing USFDA post-marketing requirement (2020-2024) to assess the impact of boxed warning on romosozumab (romo) treatment and the feasibility of future comparative safety analysis using real-world data. As of March 2021, about 14,958 person-years of exposure to romo have been reported in US. Results from the first interim report utilized Optum claims and supplemental EHR data covering the period between April 2019–March 2020.
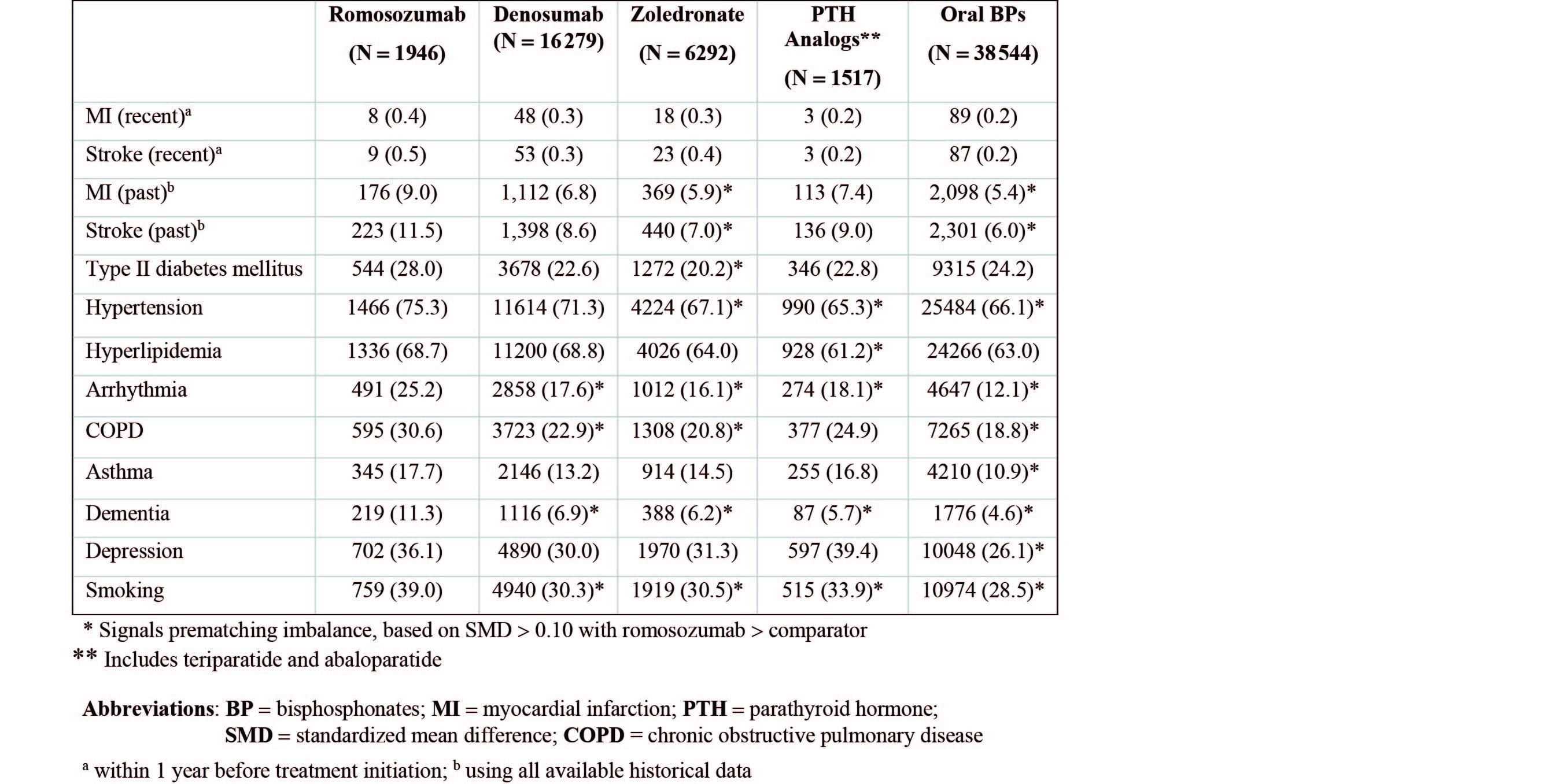
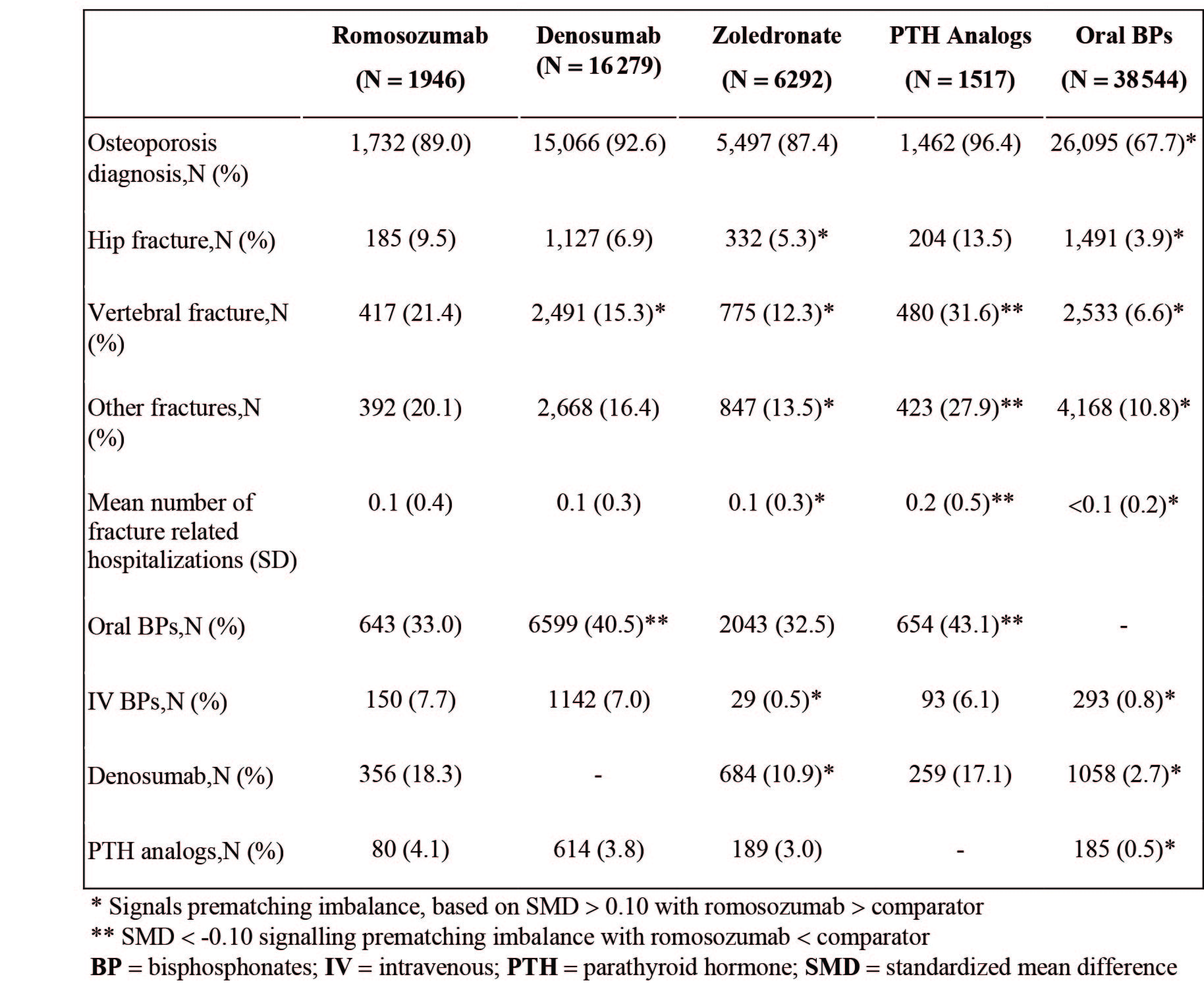
Methods: This is a retrospective, repeated analysis within five 1-year (yr) blocks of calendar time following marketing approval of romo in 2019. Women at least 55 yrs old who had newly initiated romo, denosumab (dmab), zolendronate (zol), PTH analogues, or oral bisphosphonates (BPs) were included. We describe the proportion of women who experienced a myocardial infarction (MI) or stroke in the year before drug initiation, as well as history of cardiovascular (CV) diseases, osteoporosis, other comorbidities and concomitant medications, and healthcare utilization using all available historical data up to 19 years. Four pairwise comparisons were conducted to describe the differences in the above histories compared with romo, before and after propensity score (PS) matching. Standardized mean differences (SMD) >0.1 indicated imbalance between groups.
Results: Patients newly initiating romo (N=1,946; mean age 74.8 yr) were older than zol (N=6,292; 72.9 yr), PTH (N=1,517; 70.7 yr), and oral BPs (N=38,544; 72.1 yr). Romo patients had increased prevalence of chronic diseases (eg, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, type II DM) and healthcare utilization, and had more prior fractures and OP treatments (Table 1-3). Using all available historical data, the proportion of patients with MI/stroke history was higher in romo patients (9%/11.5%) than dmab (6.8%/8.6%), PTH (7.4%/9.0%), zol (5.9%/7.0%) and oral BPs (5.4%/6.0%) (Table 2). When limited to 1 yr before treatment initiation, the proportions of patients with MI/stroke in romo were very low (MI: 0.4%, N=8; stroke: 0.5%, N=9) and similar to other OP treatments (all SMDs< 0.1). All baseline characteristics were balanced after PS matching.
Conclusion: Patients who initiated romo were a high OP-risk population and generally had more comorbidities including CV risk factors. Nevertheless, the low proportion of patients who had a MI/stroke within 1-yr prior to treatment initiation suggests the label boxed warning language may have had the intended effect on patient selection.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lin J, Nielson C, Oates M, Deignan C, Yu Z. Clinical Characteristics, Including History of Myocardial Infarction and Stroke, Among US PMO Women Initiating Treatment with Romosozumab and Other Anti-osteoporosis Therapies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-including-history-of-myocardial-infarction-and-stroke-among-us-pmo-women-initiating-treatment-with-romosozumab-and-other-anti-osteoporosis-therapies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-including-history-of-myocardial-infarction-and-stroke-among-us-pmo-women-initiating-treatment-with-romosozumab-and-other-anti-osteoporosis-therapies/