Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) have reported chronic pain despite having normal serum muscular enzymes, physician global assessment (PhGA) and MMT8 scores, thus becoming a priority in treatment and research. The prevalence, clinical and immunological factors associated with fibromyalgia (FM), a condition known for chronic pain in patients with IIM have not been previously addressed.
Methods: We performed a case-control study in a third-level referral center in Mexico City. We included patients from the institutional myositis cohort MYOTReCSZ who fulfilled EULAR/ACR 2017 criteria for IIM and had complete clinical response / remission for 6 months; patients with other autoimmune diseases were excluded. All subjects answered the PROMIS Pain Interference Short Form 8a; in case of a score >11, WPI and SSS were used for FM classification according to EULAR/ACR 2010 criteria. Activity and damage were evaluated by IMACS core set measurements. Peripheral blood mononuclear subsets were assessed by multiparametric flow cytometry and serum cytokines were measured by a multiplex luminometry assay.
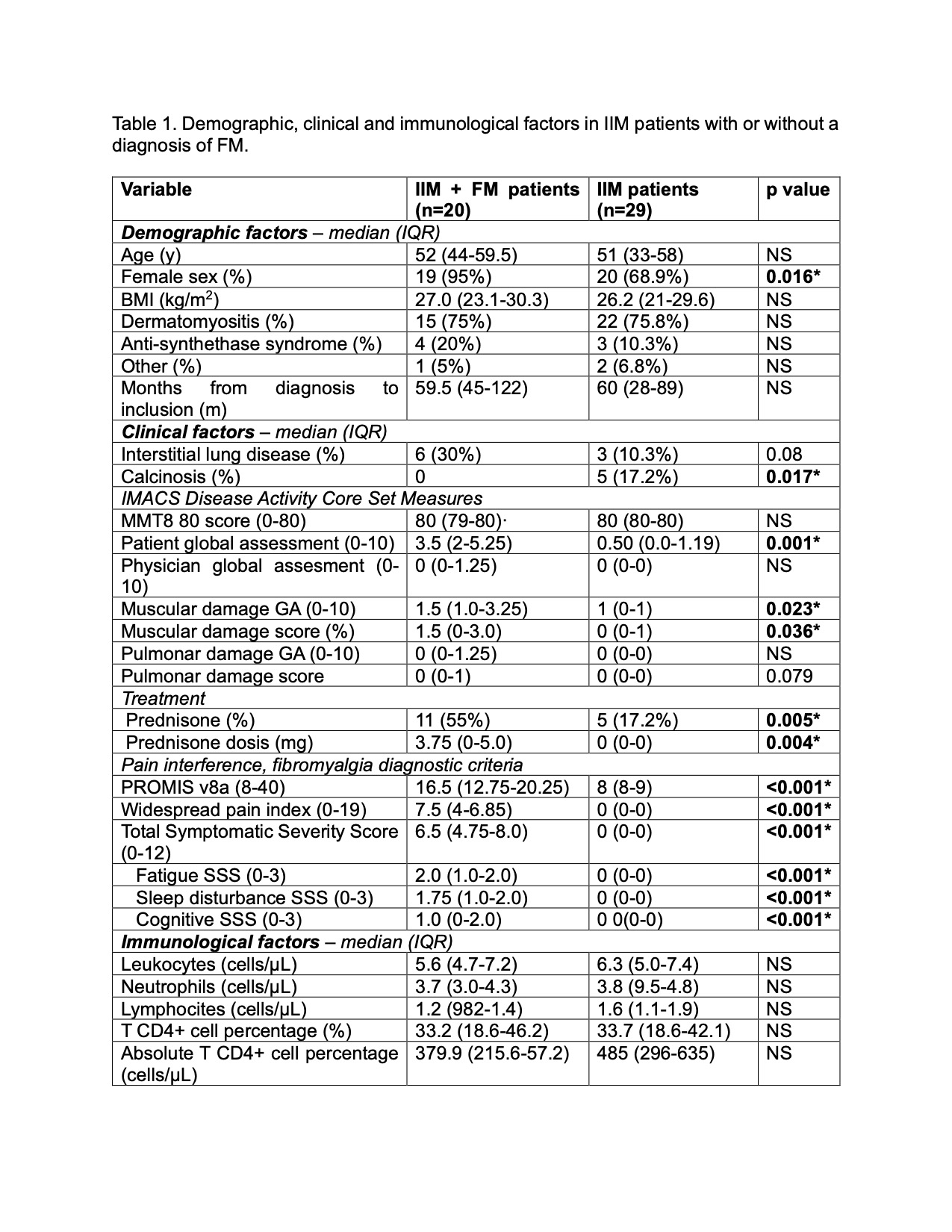
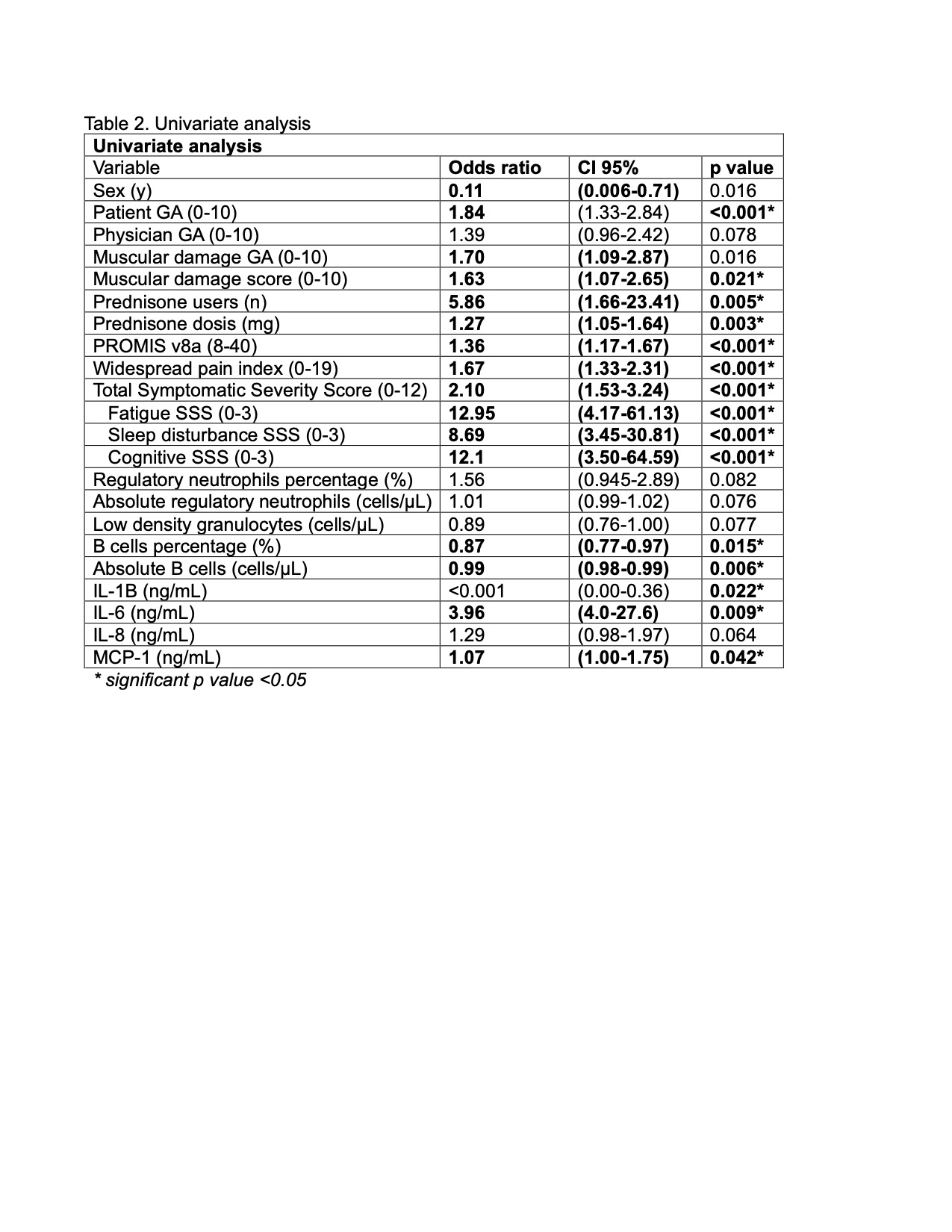
Results: We included 49 IMM patients in complete clinical response; the prevalence of FM was 40.1% (20/29) and female sex was predominant (95% vs 68.9%, p=0.016). Main demographic, clinical and immunological features and depicted in Table 1. Dermatomyositis was the most prevalent subtype in both groups. We did not find any differences in MMT8 and PhGA scores. Interestingly, patients with IMM and FM displayed higher PtGA (3.5 vs 0.50, p=0.001), as well as muscular damage (1.5 vs. 1.0, p=0.023). Furthermore, the percentage and dosis of prednisone usage was more prevalent in IIM + FM (55% vs 17.2%, p=0.005). Immunologically, patients with IIM+ FM were characterized by lower amounts of T CD8+ cells (0.04 vs 0.13, p=0.045), B cells (58.4 vs. 152, p=0.052), and non classial monocytes (16.4 vs 28.5, p=0.027), as well as higher levels of serum IL-6 (0.111 vs. 0.003, p=0.232). Accordingly, the univariate analysis showed the following variables to be associated with FM in IIM patients: ptGA (OR 1.84, CI 95% 1.33-2.84), muscular damage score (OR 1.63, CI 95% 1.07-2.65), use of prednisone (OR 5.86, CI 95% 1.66-23.41), levels of IL-6 (OR 3.96, CI 95% 4.0-27.6) and MCP-1 (OR 1.07, CI 95% 1.0-1.75) and B cell count (OR 0.99, CI 95% 0.98-0.99). The univariate analysis showed a positive association between the presence of FM and the patient’s GA.
Conclusion: Our data suggests a high prevalence of FM in patients with IIM in complete clinical response, which might be a source of chronic pain and decreased quality of life in this population. The main risks factors associated with FM in IIM are PtGA, muscular damage score, use of prednisone as well as higher serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and MCP-1 and lower amounts of B cells, despite of being classified as complete clinical responders. Our findings suggest that persistent pain in patients with IIM should raise a suspicion for a diagnosis of fibromyalgia, remarking the importance of PROs for the comprehensive evaluation of this population, since it could suggest prescription of unnecessary therapy, thus translating in higher comorbidity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Govea-Peláez S, Alcalá-Carmona B, Balderas Miranda J, Reyna-Juárez Y, Ostos-prado M, Mejía-Domínguez N, Juarez-Vega G, Torres Ruiz J, Gomez-martin D. Clinical and Immunological Risk Factors Associated with Fybromialgia in Patients with Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-and-immunological-risk-factors-associated-with-fybromialgia-in-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-and-immunological-risk-factors-associated-with-fybromialgia-in-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies/