Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (1895–1912) Measures & Measurement of Healthcare Quality Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Hypertension is the most common modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular diseases among all adults. Studies have shown that single blood pressure (BP) measurements vary in an unpredictable way in clinics, and up to one-third of patients initially categorized with high BP were subsequently reclassified into lower BP categories upon confirmatory readings.
This quality improvement project aimed at improving the rate of checking BP a second time (confirmatory reading) if the initial BP was high (systolic ≥140 mmHg or diastolic ≥90 mmHg) by implementing a staff-driven workflow with a goal to improve accuracy of clinic BP values.
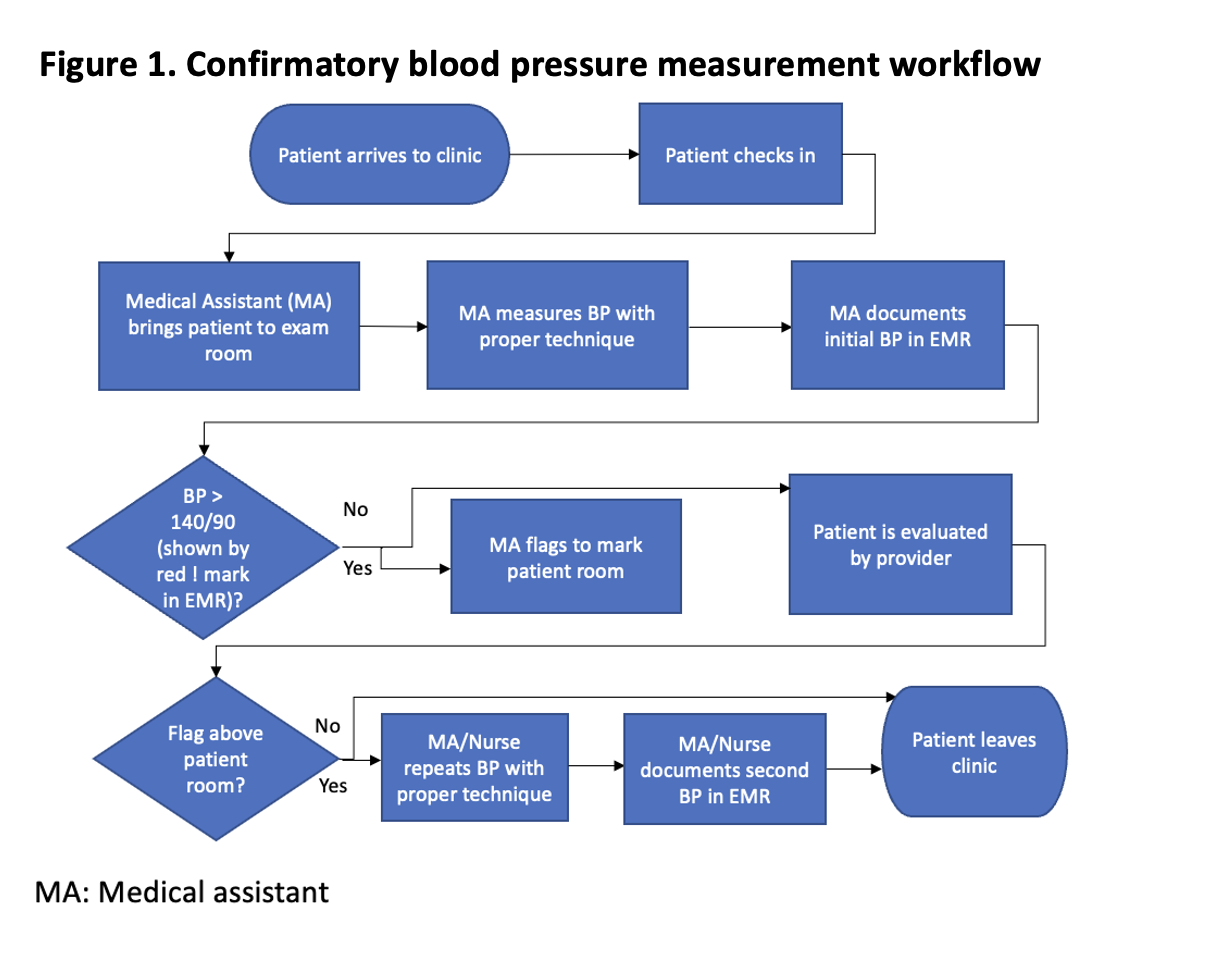
Methods: This study was conducted at a large quaternary care academic center.We included patients from internal medicine subspecialty clinics (IMSS), which includes rheumatology, seen between June 2022 and April 2023 with initial high BP (systolic BP ≥140 mmHg or diastolic BP ≥90 mmHg). We created a new workflow (Figure 1) to standardize the process of obtaining confirmatory readings for initial high BP. Nurses and medical assistants (MAs) received education on accurate BP measurement techniques, the workflow, the importance of confirmatory readings and accurate documentation within EMR. Upon check-in, medical assistants escorted patients to the exam room, where they measured BP using proper techniques and recorded in the EMR. If the initial BP was high, the MAs flagged the patient’s room accordingly. After the flagged patients were evaluated by the healthcare provider, MAs or nurses repeated the BP measurement using proper techniques and documented the results in the EMR. To collect and track the BP data, we developed a Tableau software dashboard that was updated monthly. The Department of Internal Medicine sent monthly quality improvement newsletter to all clinic leadership, serving as a reminder of clinic performance, which is then shared with the clinic staff to further reinforce adherence to the established workflow.
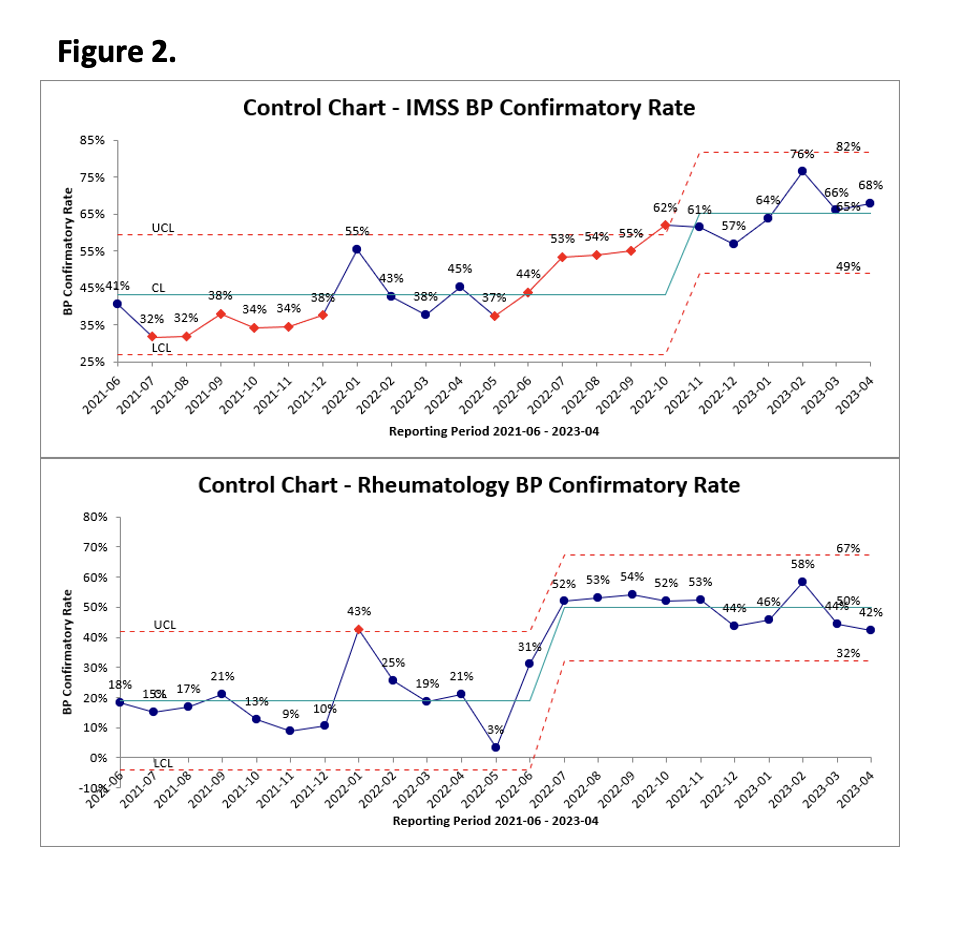
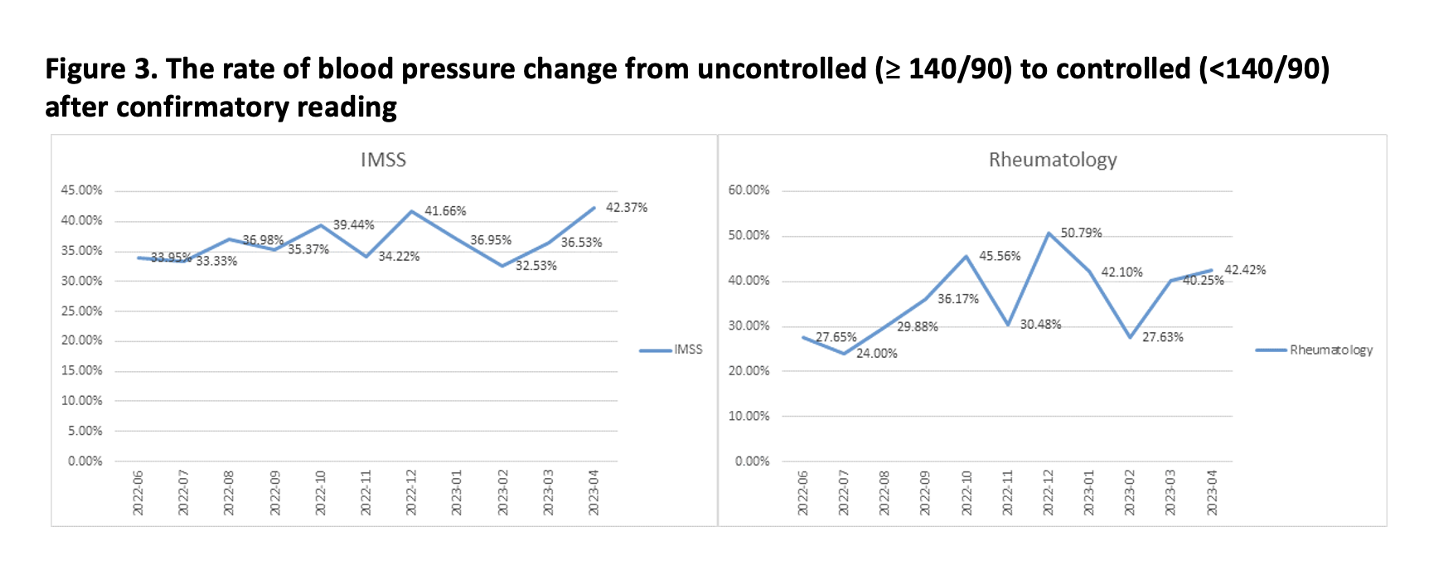
Results: Between June and December 2022, the IMSS clinics had a total of 18,390 encounters, of which 4,009 (21.8%) were eligible for confirmatory reading due to high initial readings. The confirmatory rate increased from a baseline of 38% between June 2021 to May 2022 to 55% between June to December 2022. In the rheumatology clinics, out of a total of 4,371 encounters, 1,073 (24.5%) were eligible for confirmatory reading. The clinic’s confirmatory rate improved from a baseline of 17.6% between June 2021 to May 2022 to 48% between June to December 2022 as seen in the control charts (Figure 2). The confirmatory rate remained stable at 48% in the rheumatology clinics, while in the IMSS clinics, it improved to 60% by April 2023. Among patients who had confirmatory readings, 36% (Figure 3) showed an improvement in blood pressure to below 140/90 mmHg.
Conclusion: It is feasible to increase the rate of BP confirmatory readings within a clinic using a staff-driven workflow. We were able to improve the rate of confirmatory reading over 20% in the IMSS clinics and over 30% in the rheumatology clinics within eleven months. Additionally, 36% of the patient who underwent repeat BP checks had improved BP, underscoring the importance of confirmatory readings for accurate measurement.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bugdayli K, Meyer A, Keith A, Dirisala K, Quiceno G, Bajaj P. Clinic Protocol Boosts Blood Pressure Confirmatory Readings and Accuracy in an Academic Medical Center [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinic-protocol-boosts-blood-pressure-confirmatory-readings-and-accuracy-in-an-academic-medical-center/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinic-protocol-boosts-blood-pressure-confirmatory-readings-and-accuracy-in-an-academic-medical-center/