Session Information
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Diurnal variations are observed in symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Among them, “morning stiffness of joints” is closely reflects the daily medical condition of RA patients. The diurnal variation is also present in the production of inflammatory cytokines that interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) or interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) show peak concentrations in sera of RA patients during mid night, and similarly, those of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mice are reported to increase from morning to evening. A Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor Baricitinib, orally administrated once a day, competitively inhibits phosphorylation of JAK1/2 bound of type 1/2 cytokine receptors, and suppresses productions of wide range of inflammatory cytokines derived from JAK/ signal transducers and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway. As reference to a recent report that chronotherapy using modified-release prednisone effectively suppresses “morning stiffness” of RA patients, in this study, differences in efficacy according to oral administration time of Baricitinib, targeting peaks of cytokine secretion, were examined in CIA mice.
Methods: CIA mice were administered a dose of 3 mg/kg of Baricitinib once a day at zeitgeber time (ZT) 0 or ZT12 for 21 days. Mice paws and ankles were scored on a scale from 0-4, as the cumulative value for all paws with a maximum possible score of 16, every third day. On day21, Hind limbs were examined by hematoxylin eosin staining. Hepatic proteins at ZT2, 6, 10, 14, 18 and 22 were analyzed for phosphorylation of STAT3 by western blotting. Splenic lymphocytes were isolated at ZT2, 6, 10, 14, 18 and 22 to measure expressions of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17A, TNF, IFN-γ and Granulocyte Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) by Real-time PCR.
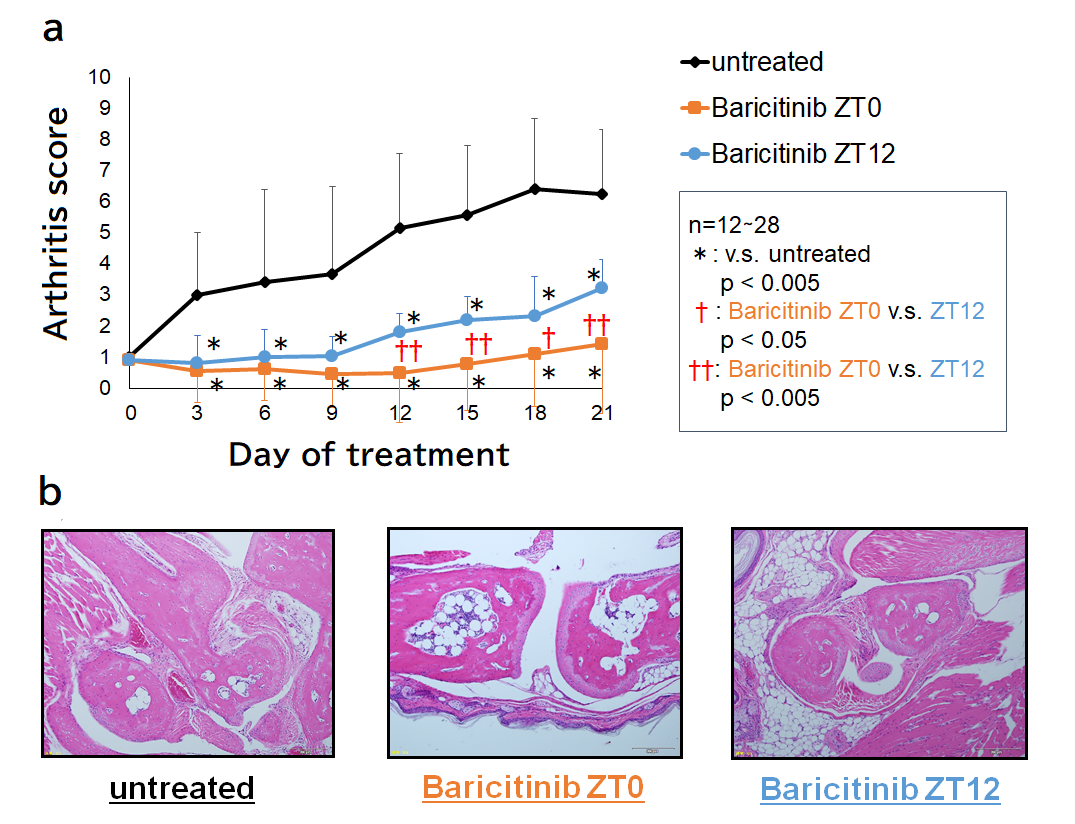
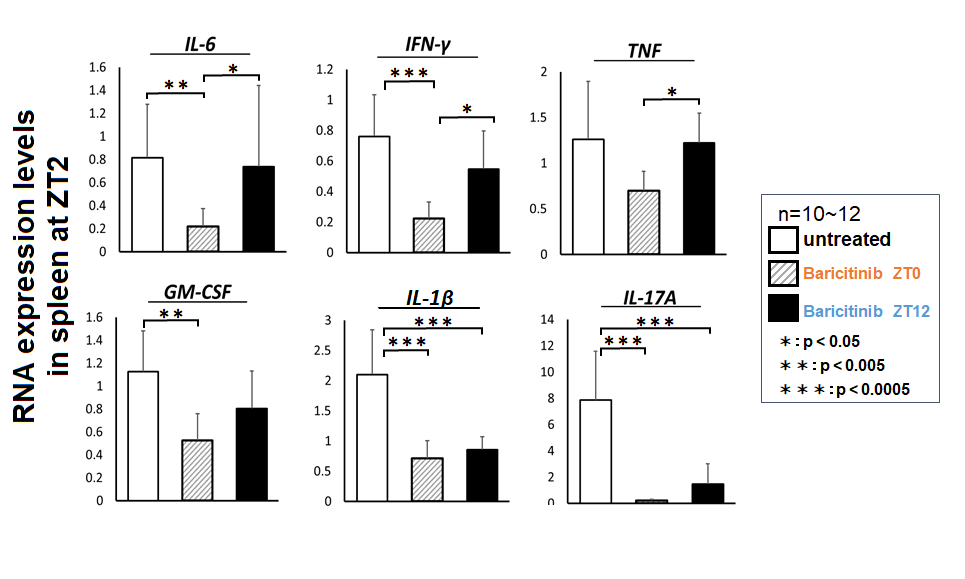
Results: Arthritis score of ZT0/12 group decreased from day3 as compared to the untreated group, and those of ZT12 group rose significantly higher than those of ZT0 group from day12 (Fig. 1a). Joint destructions with synovial hyperplasia were observed in untreated group and ZT12 treated group, while those were suppressed in ZT0 group (Fig. 1b). In CIA mice, STAT3 was highly phosphorylated from ZT22 to ZT10 (Fig. 2a), and it was suppressed in ZT0 group (ZT2) (Fig. 2b). The expressions of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF, and GM-CSF reached maximum levels at ZT2 in untreated group, and that of IFN-γ reached maximum level at ZT22. At ZT2, the expressions of IL-6, IFN-γ, TNF and GM-CSF in ZT0 treated group were significantly decreased as compared to untreated mice, whereas those of ZT12 group were not. The expressions of IL-1β, IL-17A in lymphocytes were significantly decreased by Baricitinib treatment as compared to untreated group (Fig. 3).
Conclusion: Administration of Baricitinib at ZT0 significantly attenuated the progression of arthritis in CIA mice. Results show that chronotherapy targeting cytokine secretions is far more effective than previously considered, and clinical application of chronotherapy using Baricitinib can be expected to enhance the drug efficacy by appropriate administration.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yaekura A, Morii K, Oketani Y, Okumura I, Kaneshiro K, Yoshida K, Kawasaki Y, Shibanuma N, Sakai Y, Hashiramoto A. Chronotherapy Using Baricitinib Attenuates Collagen-induced Arthritis in Mice [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/chronotherapy-using-baricitinib-attenuates-collagen-induced-arthritis-in-mice/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/chronotherapy-using-baricitinib-attenuates-collagen-induced-arthritis-in-mice/