Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Multimorbidity
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patient registries have become a common approach to learn from patient-related data by prospectively including large numbers of individuals into a sample followed over some time. Data quality improves by semi(automated) input of laboratory values or patient input by using apps.
Methods: The RHADAR framework is a network of currently 25 rheumatologists in Germany supplying pseudonymized data for aggregation into a joint database. Every patient, except the patients not consenting, is documented. The growing data input is conducted by physicians, nurses and patients using personal computers, tablets, and apps. Laboratory values are included (semi)automatically. Comorbidities are documented using the diagnoses in the patients’ records. The database is regularly analysed, lastly after March 31st 2020, using statistical software R and RStudio. (1, 2)
Results: 4962 patients had rheumatoid arthritis (RA), 1009 psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and 1013 axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). The minimum data set consisted out of age, sex, and symptom duration. Different disease specific scores were present in subsets of patients (table 1).
Chronic renal disease was documented in 252 (8.7%) RA patients, 33 (5.5%) PsA patients, and 16 (3.8%) of axSpA patients. Further cardiovascular diseases and risk factors are displayed in figure 1.
Laboratory results regarding estimated renal function (GFR) by the CKD-EPI equation (3) revealed a higher percentage of renal impairment (table 2) in RA patients, but not in SpA or PsA patients. A grad 3 renal impairment was present in 389 (13 %) RA patients, 29 (4.8 %) PsA patients, and 20 (3.8%) of axSpA patients
Conclusion: Real world data revealed a higher percentage of chronic kidney disease by laboratory values than recognized by the treating physician in RA patients.
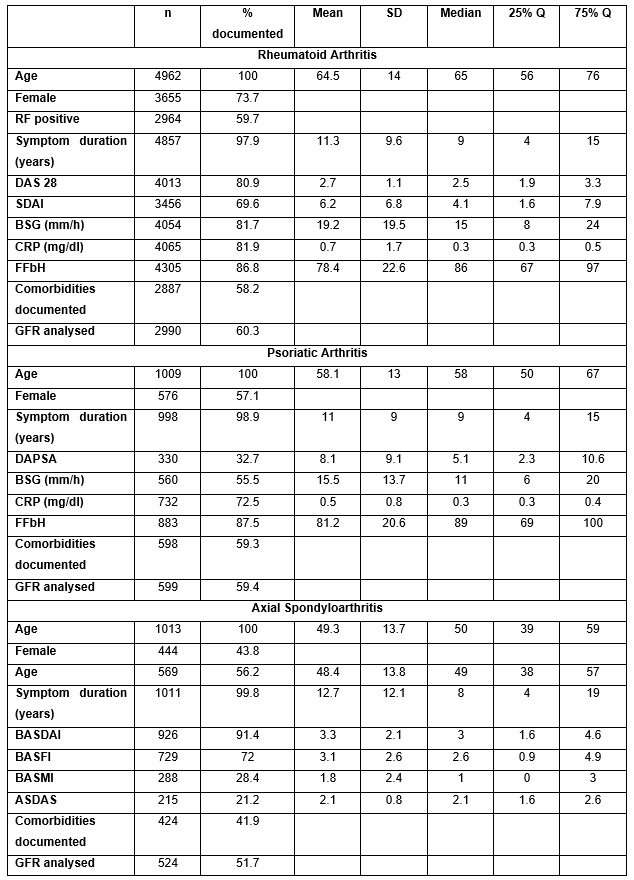 Table 1: Patients’ characteristics with different rheumatic diseases (GFR: Glomerular filtration rate; FFbH: Funktionsfragebogen Hannover, range 0-100 (100 normal function), equivalent to Health assessment questionnaire (HAQ-DI) range 3-0).
Table 1: Patients’ characteristics with different rheumatic diseases (GFR: Glomerular filtration rate; FFbH: Funktionsfragebogen Hannover, range 0-100 (100 normal function), equivalent to Health assessment questionnaire (HAQ-DI) range 3-0).
 Figure 1: Cardiovascular and renal comorbidities in patients with RA, PsA, and AS as documented by the treating physician.
Figure 1: Cardiovascular and renal comorbidities in patients with RA, PsA, and AS as documented by the treating physician.
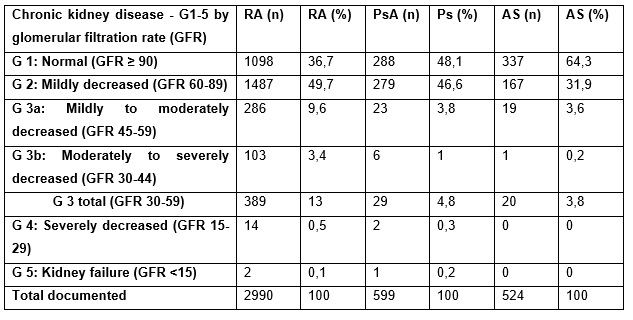 Table 2: Chronic kidney disease analysed by using the laboratory value “estimated glomerular filtration rate”.
Table 2: Chronic kidney disease analysed by using the laboratory value “estimated glomerular filtration rate”.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kleinert S, Bartz-Bazzanella P, von der Decken C, Karberg K, Schuch F, Gauler G, Wurth P, Spaethling-Mestekemper S, Kuhn C, Englbrecht M, Vorbrueggen W, Welcker M. Chronic Kidney Disease Is Underestimated in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis – Real World Data Gathered from a Network of Rheumatologists [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/chronic-kidney-disease-is-underestimated-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-real-world-data-gathered-from-a-network-of-rheumatologists/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/chronic-kidney-disease-is-underestimated-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-real-world-data-gathered-from-a-network-of-rheumatologists/
