Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Upadacitinib (UPA) is a selective and reversible Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor with an approved dose of 15 mg once daily (QD) for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Patients (pts) receiving JAK inhibitors have been reported to be at increased risk of developing serious infection events (SIE) and opportunistic infections (OI). We evaluate the incidence of SIEs and OIs in pts with RA receiving UPA and active comparators in the Phase 3 SELECT clinical trial program.
Methods: The exposure-adjusted event rate (EAER) per 100 patient-years (E/100 PY) of SIEs and OIs was determined in pts receiving UPA in five randomized Phase 3 trials (SELECT-EARLY, SELECT-MONOTHERAPY, SELECT-NEXT, SELECT-COMPARE, and SELECT-BEYOND), of which four evaluated both UPA 15 mg and 30 mg QD doses and one (SELECT-COMPARE) evaluated only UPA 15 mg QD. Incidences of SIEs and OIs were also determined in pts receiving adalimumab (ADA) + methotrexate (MTX) in SELECT-COMPARE and MTX monotherapy in SELECT-EARLY. Data were analyzed descriptively, with no statistical comparisons between groups or doses. Risk factors for SIEs were determined using a univariate Cox regression model. The data cut-off was June 30, 2019.
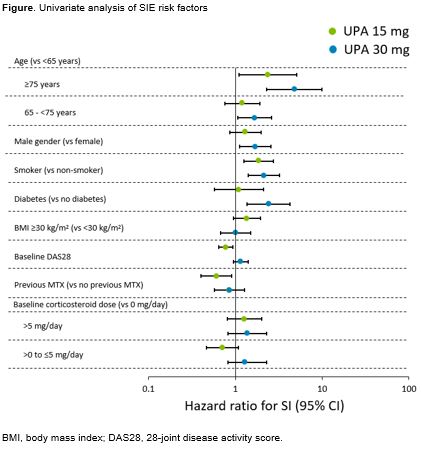
Results: Overall, 2629 pts who received UPA 15 mg, 1204 pts who received UPA 30 mg, 579 pts who received ADA + MTX, and 314 pts who received MTX monotherapy were included in this analysis. The EAERs (E/100 PYs [95% CI]) of SIEs were 3.2 (2.7–3.7) in the UPA 15 mg group, 5.7 (4.8–6.8) in the UPA 30 mg group, 3.9 (2.6–5.6) in pts receiving ADA + MTX, and 3.1 (1.7–5.2) in pts receiving MTX monotherapy. Pneumonia was the most common SIE, with EAERs (E/100 PYs [95% CI]) of 0.7 (0.5–1.0), 1.3 (0.9–1.9), 0.7 (0.2–1.5), and 0.7 (0.1–1.9) in the UPA 15 mg, UPA 30 mg, ADA + MTX, and MTX monotherapy groups, respectively. Rates of OIs (including oral candidiasis and disseminated herpes zoster [HZ]) (E/100 PYs [95% CI]) were 0.7 (0.5–1.0), 1.3 (0.9–1.9), 0.4 (0.1–1.1), and 0 (0–0) in the UPA 15 mg, UPA 30 mg, ADA + MTX, and MTX monotherapy groups, respectively. Oral candidiasis was the most frequent OI with EAERs (E/100 PYs [95% CI]) of 0.4 (0.2–0.6) in the UPA 15 mg group, 0.6 (0.3–1.0) in the UPA 30 mg group, 0.4 (0.1–1.1) in the ADA + MTX group, and 0 (0–0) in the MTX monotherapy group. Serious adverse events of HZ were only reported in the UPA groups (0.2 E/100 PYs [95% CI: 0.1–0.3] and 0.6 E/100 PYs [95% CI: 0.4–1.1] in the UPA 15 mg and 30 mg groups, respectively). Overall, there were 3 (4 coded events), 3, 1, and 0 pts who had active tuberculosis events in the UPA 15 mg, UPA 30 mg, ADA + MTX, and MTX monotherapy groups, respectively. Risk factors for SIEs are shown in the Figure. For both UPA doses, age ≥75 years and smoking were noted to have hazard ratios >1.
Conclusion: The incidence rate of SIEs and OIs was higher in the UPA 30 mg group than the UPA 15 mg group. SIEs observed with UPA 15 mg were similar to that seen with ADA although the rates of HZ were higher on UPA. Pts with RA who are ≥75 years old and/or smokers may be at higher risk than other pts with RA for SIEs while receiving UPA.
Reference:
Original abs: Ann Rheum Dis. 2020; 79(S1):650.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Winthrop K, Calabrese L, Van den Bosch F, Yamaoka K, Selmi C, Song Y, Hendrickson B, Lagunes-Galindo I, McInnes I. Characterization of Serious Infections with Upadacitinib in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-serious-infections-with-upadacitinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-serious-infections-with-upadacitinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/