Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1013–1032) Healthcare Disparities in Rheumatology Poster II: Socioeconomic Determinants
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a multi-organ fibroinflammatory disease with an autoimmune basis that can affect essentially any organ. Differences in phenotypic expression between males and females have been observed in case series features of individual organ involvement. We aimed to characterize sex differences in IgG4-RD using baseline data from the Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) IgG4-RD cohort.
Methods: Subjects were recruited between 2008 and 2023 and classified by ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria. Age at diagnosis, disease activity, treatment status, organ involvement, pre-treatment laboratory values, and blood plasmablast concentrations were collected at baseline. Active disease was defined as IgG4-RD-associated inflammation in at least one organ, such that the IgG4-RD Responder Index score was > 0. Laboratory values are reported only on patients who had active IgG4-RD and were untreated at baseline. The study was approved by the MassGeneral Brigham IRB.
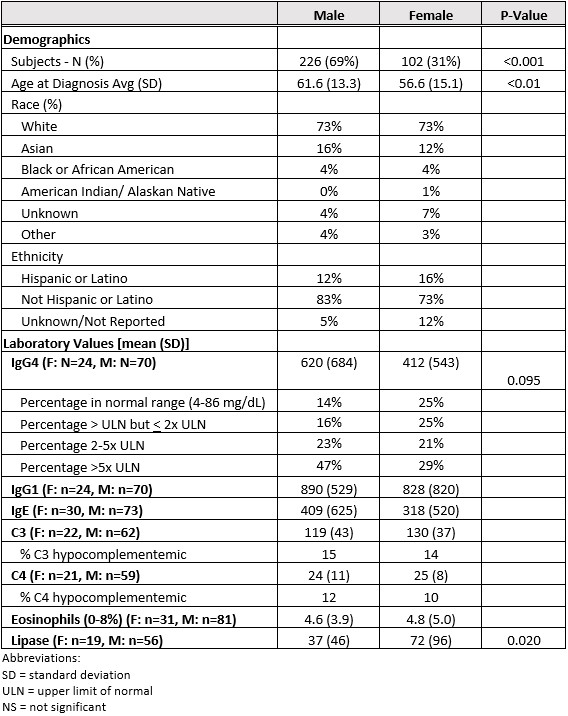
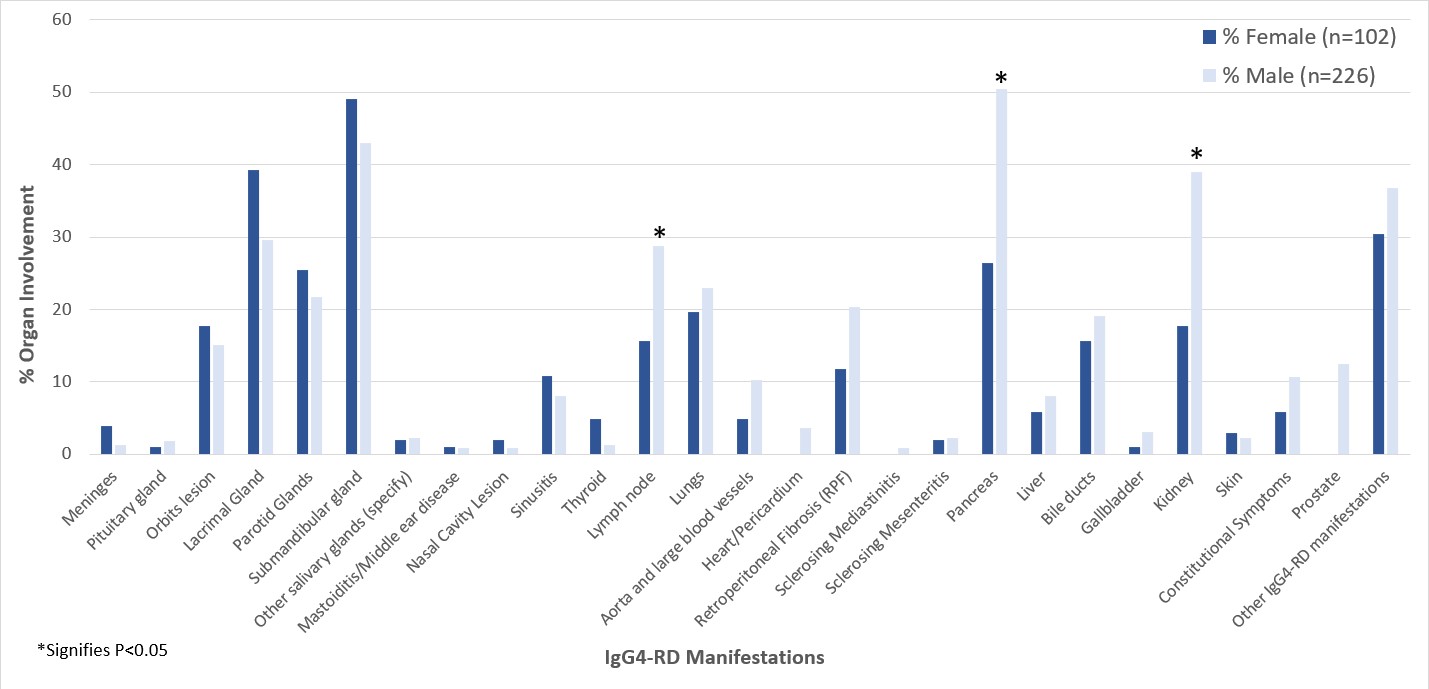
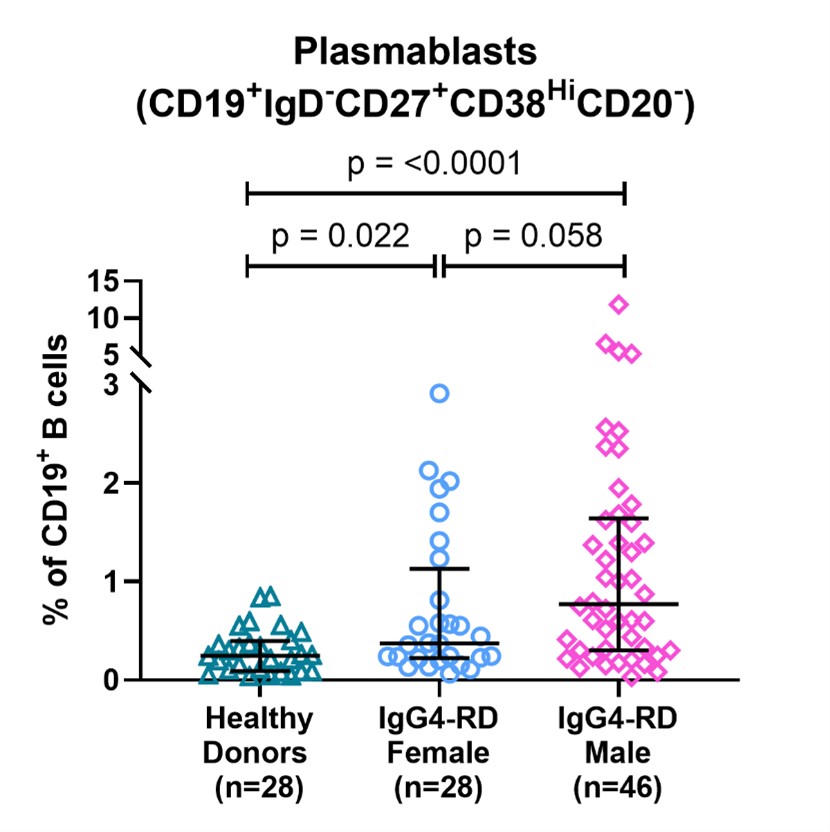
Results: Of the 564 participants enrolled in the MGH Registry for IgG4-RD, 328 fulfilled ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria and were included. There was a strong male predominance: 226 males (69%) versus 102 (31%) females [Table 1]. This M:F ratio of 2.2:1.0 contrasts markedly with both that of the general population (1:1) (P < 0.001) and our general clinic population (0.4:1.0) (P < 0.001). Male patients were five years older on average at the time of diagnosis (61.6 vs 56.6; P < 0.01) and disproportionately more likely to have involvement of the pancreas, kidneys, lymph node, aorta, large blood vessels, coronary arteries, and retroperitoneum. Females had higher involvement in the lacrimal and submandibular glands than males (for all organ involvement comparisons, P < 0.05) [Figure 1]. We examined laboratory values in 127 (39%) subjects who had active IgG4-RD and were untreated at baseline. Males were more likely to be serologically active at baseline as defined by serum IgG4, IgG1, and IgE concentrations. The mean serum IgG4 concentration in males was 620 mg/dl (±684) versus 412 mg/dl (±543) for females (P = 0.095). Forty-seven percent of males had serum IgG4 concentrations 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN), compared with 29% of the female subjects. Male subjects also had higher mean concentrations of IgE and IgG1 [Table 1]. Mean serum lipase values were lower among the male subjects (P = 0.020). A greater degree of plasmablast expansion was observed in males [Figure 2].
Conclusion: In its predilection for affecting males more often than females, IgG4-RD bears a striking contrast to most other forms of autoimmune disease, which typically have strong female predilections. Male patients with IgG4-RD also appear more likely than females to have multi-organ involvement, to have disease affecting major organs, and to be serologically active as defined by immunoglobulin concentrations in the blood. The lower lipase levels observed in males are consistent with greater degrees of pancreatic damage. Further study is required to understand these sex differences.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
McMahon G, Jha I, McMahon A, Fernandes A, Wallace Z, Katz G, Perugino C, Stone J. Characterization of Phenotypic Differences in IgG4-Related Disease Across the Sexes [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-phenotypic-differences-in-igg4-related-disease-across-the-sexes/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-phenotypic-differences-in-igg4-related-disease-across-the-sexes/