Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Studies of dermatomyositis (DM) are frequently limited to single center cohorts at academic centers. We aimed to use two large nationally representative US cohorts to describe common patient characteristics, treatments, and outcomes of patients with incident DM.
Methods: This retrospective study aimed to identify two inception DM cohorts using 1) commercial claims (derived from Komodo Healthmap data) 1/1/2016 and 12/31/2023 and 2) electronic health record (EHR) data 10/1/2014 to 9/30/2023 from the Excellence Network in RheumatoloGY (ENRGY), a community rheumatology practice-based research network (PBRN) of >700 rheumatology providers. DM patients had to have one inpatient or two outpatient DM ICD-10 codes (M33.1* or M33.9*, which are more specific than codes for polymyositis). For outpatient DM, the 2nd diagnosis code was the index date. Those with other myositis diagnoses or immunomodulatory therapy other than hydroxychloroquine prior to the first DM diagnosis or with malignancy prior to index were excluded. Patient characteristics, treatments, and healthcare utilization were assessed using the 18 months before and 12 months after index in claims and using the 12 months before and after index in EHR data. Time-to-event analyses assessed incidence of outcomes (e.g., hospitalization, malignancy) after index in claims data.
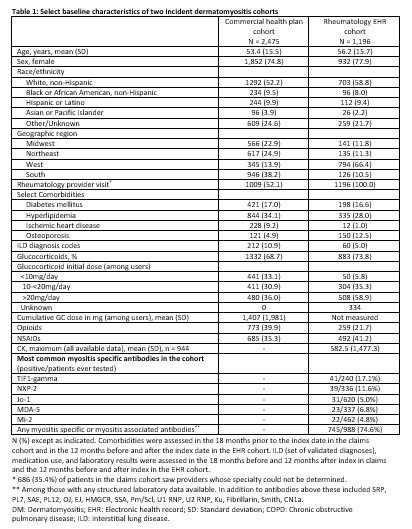
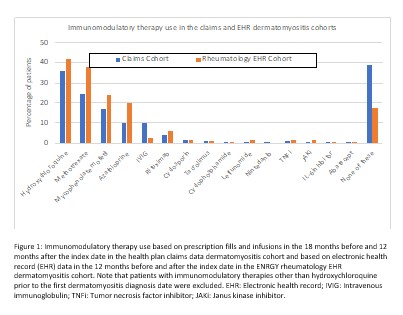
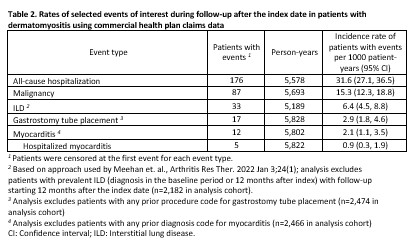
Results: We identified 2,475 patients with incident DM (claims data) and 1,196 patients (EHR cohort) after applying exclusions (12.7% and 4.3% in each cohort excluded for malignancy prior to the index date, respectively). In both cohorts, patients were predominantly female with 52.2% and 58.8% non-Hispanic White, respectively (Table 1). Interstitial lung disease diagnoses were present for 10.9% in the claims and 5.0% in the EHR cohort. In the EHR cohort, the most frequent myositis specific antibodies were TIF-1 gamma (41 positive/240 tested), NXP-2 (39/336), and Jo-1 (31/620). Among 998 patients with any laboratory results available, 745 (74.6%) had a positive myositis-specific or myositis-associated antibody. Glucocorticoid use was common, 68.7% and 73.8% in the two cohorts respectively, with initial doses most often > 20mg/day (Table 1). HCQ, methotrexate, and mycophenolate were the most commonly used immunomodulatory therapies (Figure 1). Intravenous immunoglobulin was used by 10.0% of the health claims cohort and 2.3% of the EHR cohort, although with potential for under-ascertainment the EHR cohort. In the claims cohort, incidence of patients with events per 1000 person-years for outcomes of interest were 31.6 for hospitalization, 15.3 for malignancy, 6.4 for ILD, 2.9 for gastrostomy tube, and 2.1 for myocarditis (Table 2).
Conclusion: Augmented claims data and rheumatology EHR data can be successfully leveraged to assess comorbidities, glucocorticoid use, hospitalizations, and other important DM-associated events in incident DM cohorts. These cohorts provide complementary perspectives of treatment patterns and long-term outcomes among a representative sample of real-world DM patients nationwide. Glucocorticoid burden and varied treatment approaches highlight the need for more effective therapies for DM.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
George M, Riley T, Romich E, England B, Chung J, Masri K, Daigle S, Holladay E, Su Y, xie F, Curtis J. Characteristics, Treatments, and Outcomes of Patients with Dermatomyositis from Two Large, Nationwide US Cohorts [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characteristics-treatments-and-outcomes-of-patients-with-dermatomyositis-from-two-large-nationwide-us-cohorts/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characteristics-treatments-and-outcomes-of-patients-with-dermatomyositis-from-two-large-nationwide-us-cohorts/