Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: A large proportion of patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) are considered difficult to treat (D2T).The study aimed to compare baseline characteristics, extra-articular manifestations (EAM), and co-morbid conditions between two groups of AS patients: those considered difficult-to-treat (D2T) and those not difficult-to-treat (ND2T).
Methods: We performed a retrospective study using a de-identified federated database with 89 contributing healthcare organizations (HCO), including over 125 million patients (TriNetX Research Network, Cambridge, MA; date of data access: May 28, 2024)
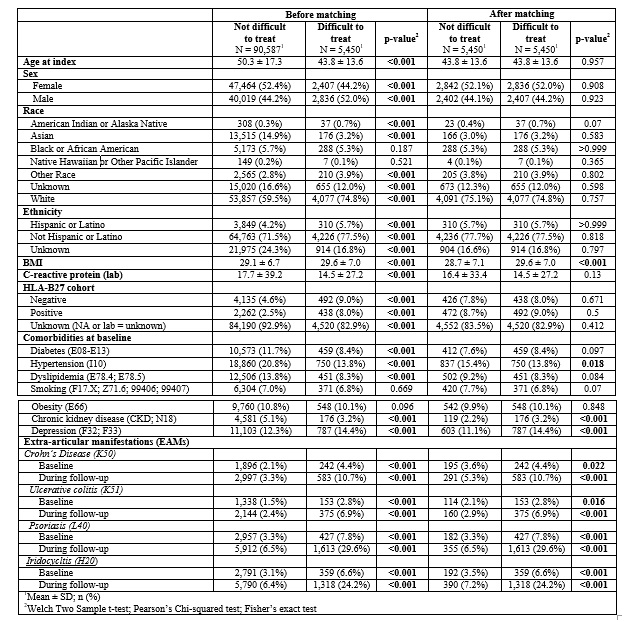
All adult patients with a diagnosis of AS (ICD-10: M45.9) 1) ≥ 18 years at the index date of diagnosis and 2) had at least one follow-up after their index date were identified between the years of 1953 and 2024. The use of biologic/targeted synthetic DMARDs (b/tsDMARDs) was assessed after the index date. There is no consensus definition for D2T AS, but we proposed this definition: using 3 or more b/ts DMARDs or 2 b/ts DMARDS from the same class. We collected demographic information, comorbid conditions, and EAMs at baseline and follow-up. To control for potential confounding variables, we performed 1:1 greedy nearest neighbor propensity score matching based on demographic and HLA-B27 status (Table 1). Continuous variables are presented as means ± SD and analyzed using independent t-tests. Categorical variables are presented as counts or frequencies and were analyzed using chi-squared tests or Fisher’s Exact test for smaller samples. All tests were two-tailed, and an alpha level of .05 was considered statistically significant.
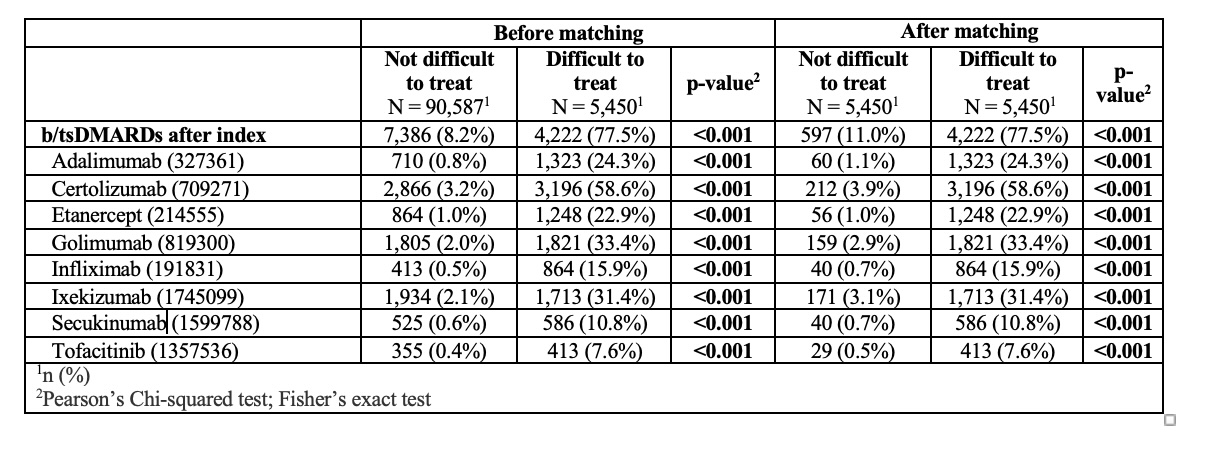
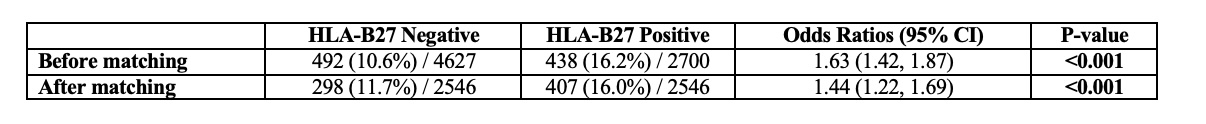
Results: A total of 96,037 patients with AS were included in the study, with 90,587 classified as ND2T and 5,450 as D2T. After propensity score matching for age, sex, race, ethnicity, and HLA-B27 status, the groups were balanced, each containing 5,450 patients (Table 1). BMI (29.6 vs. 28.7, p< 0.001). Hypertension (15.4% vs. 13.8%, p=0.018), chronic kidney disease (3.2% vs. 2.2%, p< 0.001), and depression ((14.4% vs. 11.1%, p< 0.001) were higher in the D2T group. There was a significant association between D2T status and the presence of crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis, and iridocyclitis. The use of b/tsDMARDs was significantly higher in the D2T group. 77.5% of D2T patients versus 11.0% of ND2T patients using (p< 0.001 for all comparisons). Among D2T patients, 7% were on one TNF inhibitor, 64.8% on two, 18.7% on three, 4.4% on four, and 1.2% on five. Additionally, 22.7% were on one anti-IL17, 12.3% on two anti-IL17s, 12.3% on one Janus Kinase Inhibitor (JAKi), and 3% on two JAKis (Table 2). The HLA-B27 positive patients showed higher odds of being D2T with an odds ratio of 1.44 (95% CI: 1.22, 1.69) (Table 3).
Conclusion: Our study, utilizing a longitudinal clinical and claims database, showed that in a matched cohort, D2T AS patients showed distinct clinical characteristics, including higher BMI, increased prevalence of certain comorbidities, and stronger association with EAM. Positive HLA-B27 status was associated with higher odds of being in the D2T group, suggesting genetic factors might influence treatment response in axSpA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Daoud A, Murphy J, Pamuk O, Magrey M. Characteristics of Difficult-to-Treat Ankylosing Spondylitis- Results from Real-World Data [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characteristics-of-difficult-to-treat-ankylosing-spondylitis-results-from-real-world-data/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characteristics-of-difficult-to-treat-ankylosing-spondylitis-results-from-real-world-data/